Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Other names: TSH 3rd Gen, TSH, 3rd generation, THYROID STIMULATING HORMONE, TSH, High Sensitivity, TSH W/REFLEX TO FT4, TSH, THIRD GENERATION, Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), Thyroid Stim.Hormone, TSH-ICMA
Understanding TSH Levels: How to Interpret Your Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Test
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) is a key marker of thyroid health and overall metabolic function. Measuring TSH is often the first step in evaluating conditions such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and more subtle thyroid imbalances.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to interpret TSH levels, what can influence your test results, and what steps to consider if your values fall outside the reference range.
What Is TSH and Why Does It Matter?
TSH (thyrotropin) is produced by the pituitary gland and regulates how much thyroid hormone your thyroid produces. It signals the thyroid to release:
-
T4 (thyroxine)
-
T3 (triiodothyronine)
These hormones influence metabolism, energy production, heart rate, body temperature, digestion, and mood.
TSH is part of a tightly regulated feedback loop involving the hypothalamus, pituitary, and thyroid. When thyroid hormone levels fall, TSH rises to stimulate the thyroid. When thyroid hormone levels are high, TSH is suppressed. Because of this relationship, TSH is a highly sensitive indicator of thyroid dysfunction.
TSH Reference Ranges by Thyroid Condition
| Thyroid State | TSH Range (mIU/L) |
|---|---|
| Hyperthyroidism | 0.0 – 0.4 |
| Normal (Euthyroid) | 0.4 – 4.0 |
| Subclinical Hypothyroidism | 4.0 – 10.0 |
| Overt Hypothyroidism | >10.0 |
Subclinical hypothyroidism refers to an elevated TSH with normal free T4 levels.
Always interpret results using your laboratory’s reference ranges and clinical context. Different labs may use slightly different cutoffs based on assay methods and population norms.
TSH Reference Ranges by Age and Pregnancy
| Population | TSH Range (mIU/L) |
|---|---|
| 1–2 days old | 3.20–34.60 |
| 3–4 days old | 0.70–15.40 |
| 5 days–4 weeks | 1.70–9.10 |
| 1–11 months | 0.80–8.20 |
| 1–19 years | 0.50–4.30 |
| Adults (non-pregnant) | 0.40–4.50 |
| Pregnancy – 1st trimester | 0.26–2.66 |
| Pregnancy – 2nd trimester | 0.55–2.73 |
| Pregnancy – 3rd trimester | 0.43–2.91 |
Pregnancy significantly alters thyroid physiology. Always use trimester-specific reference ranges when interpreting TSH in pregnant individuals.
What Can Affect Your TSH Test Results (and What to Do About It)
1. Laboratory Variability and Assay Differences
Different laboratories may use different testing platforms, which can affect results.
Action:
If results don’t match symptoms, repeat testing at the same lab under similar conditions.
2. Antibody Interference
Certain antibodies can interfere with immunoassays used to measure TSH.
-
Heterophile antibodies (from animal-derived medications or transfusions)
-
Thyroid autoantibodies (such as TPO or thyroglobulin antibodies)
Action:
If TSH and free T4 results are inconsistent, consider thyroid antibody testing.
3. Medications and Supplements
Several substances can alter TSH levels, including:
-
Corticosteroids
-
Amiodarone
-
Lithium
-
High-dose biotin
-
Iodine-rich supplements
Action:
Inform your healthcare provider of all medications and supplements. Biotin should typically be stopped at least 48 hours before testing.
4. Time of Day and Fasting
TSH follows a circadian rhythm and peaks overnight.
Action:
Test in the early morning (typically 7–9 a.m.) and under consistent fasting conditions when possible.
5. Acute Illness, Stress, or Sleep Deprivation
Acute illness or severe stress can temporarily suppress TSH, a phenomenon sometimes called non-thyroidal illness syndrome.
Action:
Delay testing until recovery from acute illness or major stressors.
6. Pregnancy-Related Hormonal Changes
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) suppresses TSH, especially early in pregnancy.
Action:
Always interpret TSH using pregnancy-specific reference ranges.
Recognizing High and Low TSH Symptoms
Symptoms alone are not diagnostic and can overlap with many other conditions. Blood testing is required to confirm thyroid dysfunction.
Low TSH (Possible Hyperthyroidism)
Commonly associated symptoms include:
-
Rapid or irregular heartbeat
-
Weight loss with increased appetite
-
Anxiety or irritability
-
Heat intolerance
High TSH (Possible Hypothyroidism)
Commonly associated symptoms include:
-
Fatigue or sluggishness
-
Weight gain
-
Cold intolerance
-
Dry skin and constipation
-
Low mood or depression
Key Takeaways and What to Do Next
-
TSH is an important screening marker—but not the whole story.
Always interpret TSH alongside free T4, free T3, thyroid antibodies, and symptoms. -
Treat people, not just numbers.
Symptoms, medical history, and trends over time matter more than a single lab value. -
Consistency improves accuracy.
Test at the same time of day, under similar conditions, and ideally at the same laboratory. -
Follow-up is essential.
Borderline or abnormal TSH levels often require repeat testing after lifestyle changes or treatment adjustments.
Tracking TSH together with related thyroid markers over time provides far more insight than isolated results. Platforms like HealthMatters.io allow you to visualize trends, compare markers, and place your thyroid labs in proper clinical context.
What does it mean if your Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) result is too high?
Elevated TSH Levels: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
High levels of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) typically indicate an underactive thyroid, commonly referred to as primary hypothyroidism or subclinical hypothyroidism. When thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) are low, the hypothalamus and pituitary gland increase TSH production to stimulate the thyroid. Elevated TSH levels can signify a range of thyroid-related conditions, each with unique causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
TSH Reference Ranges
TSH reference ranges can vary between laboratories and age groups. For adults, the general normal range is 0.4–4.0 mIU/L, although some experts suggest an upper limit of 2.5 mIU/L for optimal thyroid health. During pregnancy, TSH levels are typically lower:
- First trimester: 0.1–2.5 mIU/L
- Second trimester: 0.2–3.0 mIU/L
- Third trimester: 0.2–3.0 mIU/L
Common Symptoms of Elevated TSH Levels
Symptoms of hypothyroidism, associated with elevated TSH, vary depending on severity. Common signs include:
- Fatigue and Weakness: Persistent tiredness and lack of energy.
- Cold Intolerance: Increased sensitivity to cold temperatures.
- Weight Gain: Unexplained weight gain despite normal diet and activity.
- Constipation: Difficulty passing stools, even with a fiber-rich diet.
- Cognitive Issues: Memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and brain fog.
- Dry Skin and Hair: Flaky skin and brittle hair prone to falling out.
- Hoarseness: A raspy or deepened voice.
- Swelling (Edema): Puffiness in the face, around the eyes, or in extremities.
- Muscle Pain or Weakness: Unexplained cramps or general weakness.
- Mood Changes: Depression, irritability, or heightened anxiety.
Possible Causes of Elevated TSH Levels
1. Primary Hypothyroidism
Insufficient production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland.
2. Subclinical Hypothyroidism
Mild hypothyroidism with elevated TSH but normal T3 and T4 levels, often asymptomatic.
3. Transient Hypothyroidism
Temporary thyroid dysfunction, often following thyroiditis or viral illness.
4. Autoimmune Thyroiditis (Hashimoto's)
Chronic inflammation caused by the immune system attacking the thyroid gland.
5. Thyroiditis Variants
- Painless Thyroiditis: Temporary inflammation leading to hypothyroidism.
- Subacute Granulomatous Thyroiditis: Post-viral thyroid swelling and pain.
- Postpartum Thyroiditis: Thyroid inflammation after childbirth.
6. Iodine Imbalance
Both iodine deficiency and excess can impair thyroid function.
7. Drug-Induced Hypothyroidism
Medications like lithium or amiodarone can interfere with thyroid hormone production.
8. Thyroidectomy or Radioiodine Therapy
Surgical removal or radioactive iodine treatment can lead to hypothyroidism due to reduced thyroid tissue.
9. Congenital Thyroid Disorders
Conditions present from birth, such as thyroid agenesis or hormone synthesis defects.
10. Generalized Thyroid Hormone Resistance
A rare genetic disorder where body cells are resistant to thyroid hormone.
Diagnosis of Elevated TSH Levels
To confirm thyroid dysfunction, your doctor may order the following tests:
- TSH, T3, and T4 Blood Tests: High TSH with low T3 and T4 confirms hypothyroidism.
- Thyroid Antibodies: Detect autoimmune thyroid diseases like Hashimoto's.
- Thyroid Ultrasound: Examine the thyroid for nodules or inflammation.
- Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test: Assess thyroid hormone production efficiency.
Treatment Options for Elevated TSH
Treatment varies based on the cause and severity of symptoms:
1. Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy
- Levothyroxine: A synthetic T4 hormone that restores normal thyroid hormone levels and lowers TSH.
- Dosages are adjusted based on regular monitoring to maintain optimal thyroid function.
- Taken consistently on an empty stomach, either 30–60 minutes before breakfast or at bedtime, 4 hours after the last meal.
2. Management of Underlying Conditions
- Thyroiditis: Temporary anti-inflammatory treatments, like corticosteroids, for subacute cases.
- Drug-Induced Hypothyroidism: Adjusting or discontinuing the offending medication (e.g., lithium).
3. Iodine Management
- Balancing iodine intake through diet or supplements can help resolve iodine-related hypothyroidism.
4. Surgery or Radioactive Iodine Therapy
- For severe cases like thyroid cancer or large goiters, thyroidectomy or radioactive iodine may be necessary, followed by lifelong thyroid hormone replacement.
5. Monitoring in Subclinical Hypothyroidism
- Regular monitoring without immediate treatment is often recommended if symptoms are mild or absent.
- Treatment is typically initiated if TSH exceeds 10 mIU/L or if there is a high risk of progression to overt hypothyroidism.
Special Considerations
Pregnancy
- Proper thyroid function is critical for maternal and fetal health.
- Women with hypothyroidism may require higher doses of levothyroxine during pregnancy, with TSH levels monitored each trimester.
Medication Interactions
Certain substances can interfere with levothyroxine absorption, including:
- Calcium and iron supplements
- Proton pump inhibitors (e.g., omeprazole)
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs (e.g., cholestyramine)
- Estrogen-containing medications
Always inform your doctor about all medications and supplements.
Follow-Up and Long-Term Care
Regular monitoring is essential:
- Initial phase: TSH levels should be rechecked every 6–8 weeks after starting or adjusting treatment.
- Maintenance phase: Once stable, annual check-ups are generally sufficient.
Adjustments to medication dosage may be needed due to changes in weight, age, or overall health.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Support
Managing elevated TSH involves more than just medication:
- Diet: A nutrient-rich diet with adequate iodine, selenium, and zinc supports thyroid health. Avoid excessive goitrogenic foods (e.g., raw cruciferous vegetables) if iodine is low.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps combat fatigue, weight gain, and mood changes.
- Mental Health Support: Addressing hypothyroidism-related depression or cognitive difficulties may benefit from counseling or support groups.
By following these guidelines and working closely with your healthcare provider, most individuals with elevated TSH levels can effectively manage their condition and maintain a high quality of life.
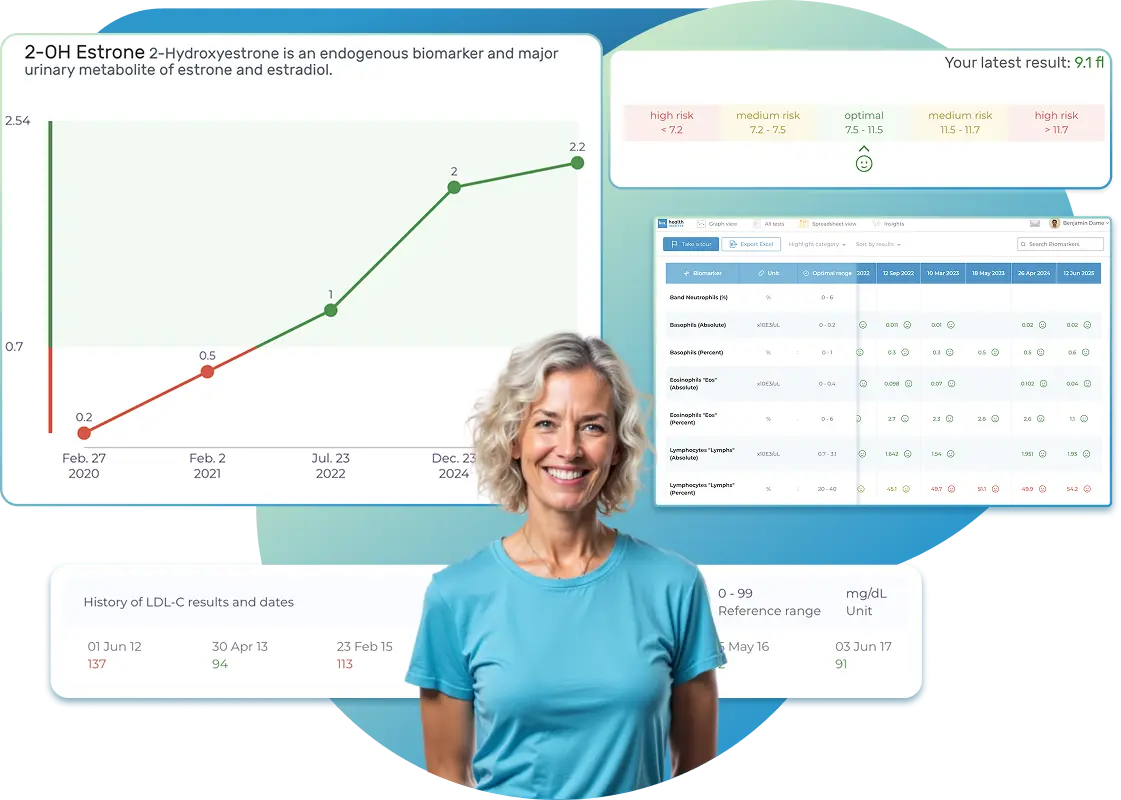
All Your Lab Results.
One Simple Dashboard.
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results Easily
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
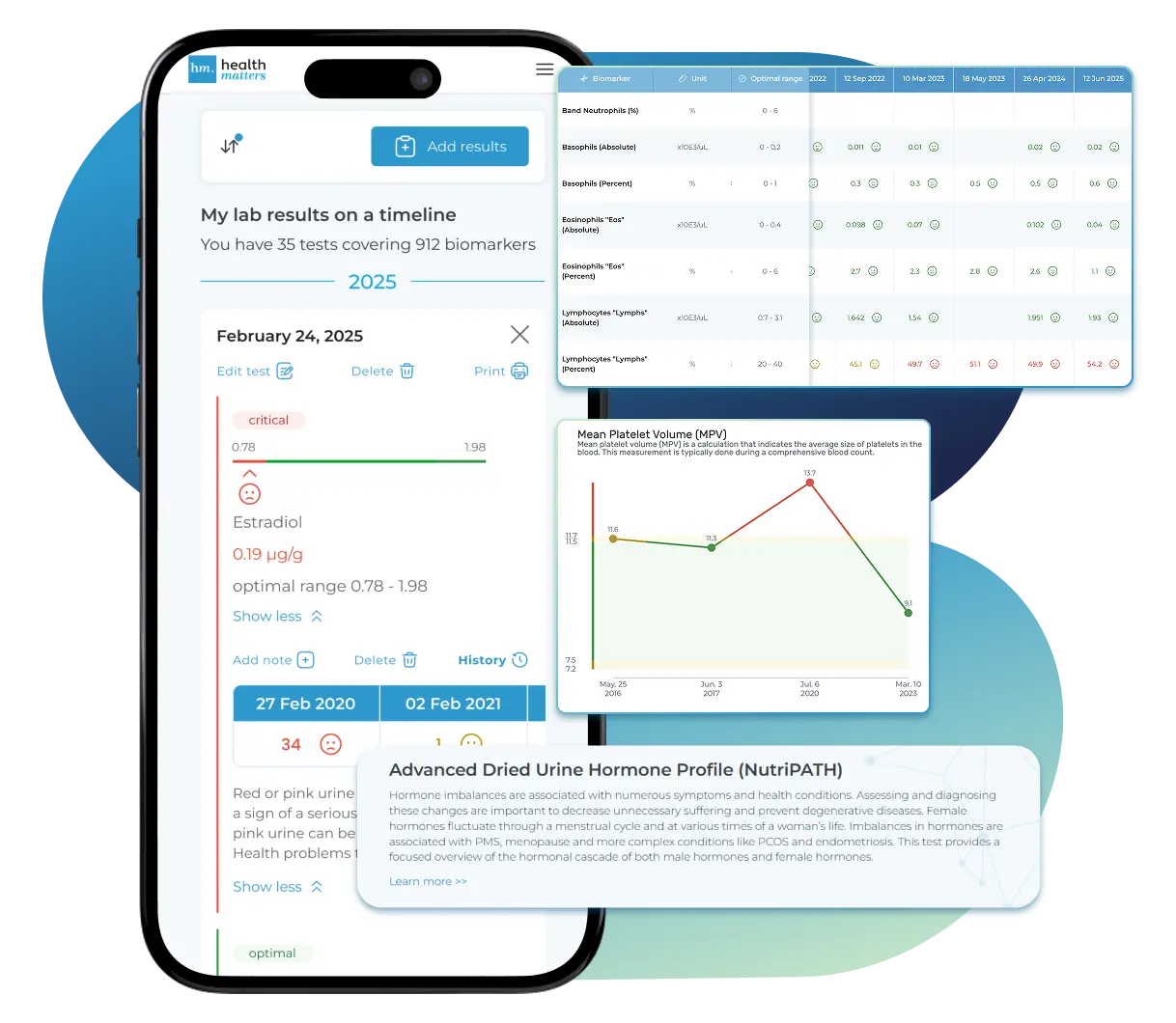
What does it mean if your Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) result is too low?
What Does a Low TSH Level Mean?
A low TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone) level often indicates that the body has an elevated amount of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). However, this is not always the case. While hyperthyroidism is the most common cause, a low TSH can also point to less obvious conditions.
Key Points:
-
Low TSH typically reflects high thyroid hormone levels, but exceptions exist.
-
It’s frequently associated with hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid).
-
In some cases, low TSH may indicate central (secondary) hypothyroidism, where the issue originates from the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, not the thyroid itself.
Subclinical Hyperthyroidism
If you have low TSH but normal T3 and T4 levels, you may be dealing with subclinical hyperthyroidism. This is a mild, often symptomless form of hyperthyroidism that still requires monitoring, as it can affect heart health and bone density over time.
→ Read our in-depth article on Subclinical Hyperthyroidism
Common Causes of Low TSH Levels
Several specific conditions and factors can suppress TSH production:
1. Graves’ Disease
An autoimmune condition where antibodies overstimulate the thyroid, causing it to produce excess hormones.
2. Thyroiditis
Inflammation of the thyroid gland, which can temporarily release stored thyroid hormones into the bloodstream. Types include:
-
Postpartum Thyroiditis
-
De Quervain's (subacute) Thyroiditis
3. Euthyroid Sick Syndrome
A non-thyroidal illness that disrupts normal thyroid function tests during acute or chronic systemic illness, often showing low TSH.
4. Excessive Thyroid Hormone Replacement
Overmedication with levothyroxine (T4) or liothyronine (T3) can suppress TSH levels.
5. Iodine-Induced Hyperthyroidism
Excessive iodine intake, from diet or medical imaging contrast agents, can overstimulate the thyroid.
6. Toxic Nodular Goiter (TNG)
Autonomously functioning thyroid nodules that produce thyroid hormones independently of TSH regulation.
7. Amiodarone-Induced Thyroid Dysfunction
The heart medication amiodarone, which contains high iodine levels, can disrupt normal thyroid function, leading to either hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
What to Do If Your TSH is Low
-
Confirm with Additional Testing: Request Free T3, Free T4, and thyroid antibody tests for a clearer diagnosis.
-
Evaluate Symptoms: Discuss symptoms like palpitations, weight changes, anxiety, or fatigue with your healthcare provider.
-
Review Medications and Supplements: Ensure your doctor knows if you’re taking thyroid medications, iodine supplements, or drugs like amiodarone.
-
Assess Pituitary Function: If T3 and T4 are low or normal despite low TSH, pituitary dysfunction (central hypothyroidism) should be considered.
-
Schedule Follow-Up Monitoring: For subclinical cases, regular testing every 3–6 months may be recommended.
Laboratories
Bring All Your Lab Results Together — In One Place
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.
Pricing Table
Gather Your Lab History — and Finally Make Sense of It
Finally, Your Lab Results Organized and Clear
Personal plans
$79/ year
Advanced Plan
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 5 reports entered for you
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
$250/ once
Unlimited Account
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 10 reports entered for you
- No subscriptions. No extra fees.
$45/ month
Pro Monthly
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track lab results for multiple clients
- Customize reference ranges per client
- Export lab histories and reports
- Begin with first report entered by us
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
About membership
What's included in a Healthmatters membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
 Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Let Your Lab Results Tell the Full Story
Once your results are in one place, see the bigger picture — track trends over time, compare data side by side, export your full history, and share securely with anyone you trust.





Bring all your results together to compare, track progress, export your history, and share securely.
What Healthmatters Members Are Saying
Frequently asked questions
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
- Individuals who want to track and understand their health over time.
- Health professionals, such as doctors, nutritionists, and wellness coaches, need to manage and interpret lab data for their clients.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
- Upload lab reports from any lab
- View your data in interactive graphs, tables, and timelines
- Track trends and monitor changes over time
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export and share your full lab history
- Access your results anytime, from any device
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 10000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
- The GI Effects® Comprehensive Stool Profile,
- GI-MAP,
- The NutrEval FMV®,
- The ION Profile,
- Amino Acids Profile,
- Dried Urine Test for Comprehensive Hormones (DUTCH),
- Organic Acids Test,
- Organix Comprehensive Profile,
- Toxic Metals,
- Complete Blood Count (CBC),
- Metabolic panel,
- Thyroid panel,
- Lipid Panel,
- Urinalysis,
- And many, many more.
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
We implement proven measures to keep your data safe.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
















