Serotonin plays important roles in the resolution of mood, sleep, and appetite.
Serotonin is an inhibitory neurotransmitter synthesized by enzymes that act on tryptophan and/or 5-HTP.
Neurotransmitters are divided into two basic categories:
– Excitatory neurotransmitters stimulate the brain and body.
– Inhibitory neurotransmitters calm the brain and body.
Just as levels of individual neurotransmitters are important in maintaining optimum health, so is the proper balance between your excitatory and inhibitory systems.
Serotonin, generally regarded as the “happiness molecule,” contributes to the feelings of calm and well-being that eases depression and anxiety, supports sleep, and decreases appetite.
Serotonin is stored in presynaptic vesicles and released to transmit electrochemical signals across the synapse. Extensive research has been conducted surrounding serotonin and acts as a target for symptoms like low mood, compulsions, anxiousness, and headaches.
Serotonin acts, in most cases, as an inhibitory neurotransmitter and, like GABA, modulates neuron voltage potentials to inhibit glutamate activity and neurotransmitter firing. Serotonin neurons have large numbers of axons and are important in integrating neural circuits. This also provides an explanation for serotonin’s role in so many health concerns.
References:
– How to increase serotonin in the human brain without drugs [L]
– Carcinoid Syndrome [L]
Kamoun P, Douay O. Sérotonine et autisme [Serotonin and autism]. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 1980;38(4):201-5. French. PMID: 6160783.
Leibowitz SF. The role of serotonin in eating disorders. Drugs. 1990;39 Suppl 3:33-48. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199000393-00005. PMID: 2197074.
Stasi C, Sadalla S, Milani S. The Relationship Between the Serotonin Metabolism, Gut-Microbiota and the Gut-Brain Axis. Curr Drug Metab. 2019;20(8):646-655. doi: 10.2174/1389200220666190725115503. PMID: 31345143.
Moroianu LA, Cecilia C, Ardeleanu V, Pantea Stoian A, Cristescu V, Barbu RE, Moroianu M. Clinical Study of Serum Serotonin as a Screening Marker for Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 May 11;58(5):652. doi: 10.3390/medicina58050652. PMID: 35630069; PMCID: PMC9146121.
What does it mean if your Serotonin result is too high?
Elevated serotonin may be associated with symptoms of:
- increased anxiety,
- agitation
- and diarrhea (IBS- like symptoms).
Serotonin levels may be increased by low protein or high-carbohydrate meals, insulin, and tryptophan or 5-HTP supplementation. Many mood altering medications, including SSRIs and SNRIs, may influence serotonin levels. L-theanine may affect serotonin function.
Note: Significantly elevated serotonin levels may be associated with additional pathology (i.e. carcinoid tumor). Suggest further work up depending on the clinical picture.
Serotonin signaling in the central nervous system (CNS) may influence mood, appetite, sleep, memory and learning, homeostasis, and sexual behaviors. Altered levels of urinary or plasma serotonin are thought to play a role in many disorders including anxiety, depression, obsessive compulsive disorder and phobias.
Elevated plasma serotonin and platelet serotonin levels are a common finding in autistic patients, and may contribute to psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia.
There are a great many serotonin receptors with different affinities, expression and function.
The main diseases that may be associated with elevated levels of serotonin are neuroectodermal tumors, in particular carcinoid tumors arising from gastrointestinal (GI) enterochromaffin cells.
Only about 10% of midgut carcinoids produce enough serotonin to cause symptoms.
Symptoms of serotonin excess (Serotonin Syndrome), are wide-ranging. A triad of symptoms including altered mental status (usually anxiety), neuromuscular hyperactivity or hyperreflexia, and autonomic instability, is suspicious for serotonin excess.
Exogenous estrogens have been shown to raise both serotonin and 5-HIAA levels in postmenopausal women.
Serotonin levels may be increased by exercise, increased daylight (or daylight equivalent) exposure, low-protein or high-carbohydrate meals, insulin, or by Tryptophan or 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) supplements.
Some studies indicate that therapeutic massage may also elevate serotonin levels.
The herbs St. John’s wort and ginseng may elevate serotonin levels.
Medications that may increase serotonin include:
- serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
- antidepressants: bupropion, trazodone
- migraine medications
- pain medications
- lithium
- dextromethorphan (cough suppressant)
- antiemetics
The gastrointestinal tract produces about 80% of the body’s serotonin. During the “first pass” through hepatic circulation, monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) metabolizes 30-80% of GI serotonin to 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA).
Serotonin metabolism requires selenium, magnesium and vitamin B3 as cofactors.
Mutations, or single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), in MAO-A may affect serotonin degradation. SNPS or mutations in serotonin receptors may affect responses to serotonin.
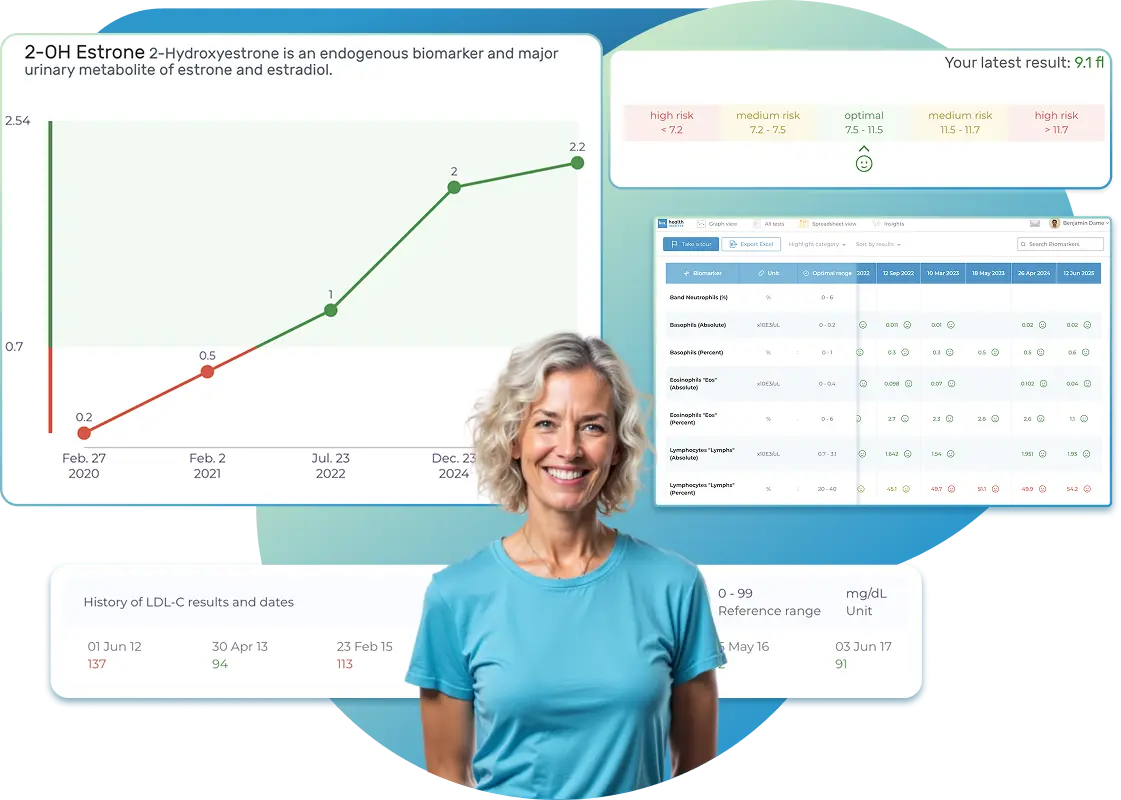
All Your Lab Results.
One Simple Dashboard.
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results Easily
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
What does it mean if your Serotonin result is too low?
Low serotonin may contribute to mood concerns including anxiety, OCD, depression, anger and a sense of discontentment. Low serotonin may also be associated with poor sleep quality and appetite changes, as well as chronic fatigue, rheumatoid arthritis, and over-all lassitude. Failure to regenerate tetrahydrobiopterin [BH4], an essential cofactor for serotonin synthesis, may decrease serotonin levels, and could be reflected in urine. BH4 regeneration may be supported by folates, vitamin B3, C, molybdenum and zinc.
Additionally, production of serotonin requires vitamin D, iron and vitamin B6. Tryptophan is the essential precursor of serotonin. 5-HTP may increase serotonin, and L-theanine may affect serotonin function.
Serotonin signaling in the central nervous system (CNS) may influence mood, appetite, sleep, memory and learning, homeostasis, and sexual behaviors. There are a great many serotonin receptors with different affinities, expression and function. Decreased serotonin levels have been associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), anger, insomnia, and depression. Some eating disorders and migraine headaches may also be related to low serotonin levels.
Low urinary serotonin levels during pregnancy have been associated with increased risk of premature birth. In the peripheral nervous system, low levels of serotonin may affect gastrointestinal motility (constipation), and possibly bone mass.
Low serotonin levels have been associated with irritable bowel syndrome. Cyproheptadine is an antihistamine that decreases serotonin levels.
Studies indicate that serotonin depletion is more likely to affect mood in those with a family history of mood disorders. Mutations or single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in specific enzymes may affect serotonin synthesis or degradation. Several SNPs have been identified and linked to depression; research continues in this area.
Serotonin is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier and must be synthesized in the peripheral and central nervous system. Tetrahydrobiopterin, iron and Vitamin B6 are required cofactors for serotonin synthesis.
The gastrointestinal (GI) tract produces about 80% of the body’s serotonin. During the “first pass” through hepatic circulation monoamine oxidase (MAO) metabolizes 30-80% of GI-derived serotonin to 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA).
Serotonin may also be converted to 5-HIAA in the lungs. Urine and plasma levels of serotonin may vary with the intake of certain foods rich in serotonin, and medications that alter serotonin levels.
Laboratories
Bring All Your Lab Results Together — In One Place
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.
Pricing Table
Gather Your Lab History — and Finally Make Sense of It
Finally, Your Lab Results Organized and Clear
Personal plans
$79/ year
Advanced Plan
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 5 reports entered for you
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
$250/ once
Unlimited Account
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 10 reports entered for you
- No subscriptions. No extra fees.
$45/ month
Pro Monthly
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track lab results for multiple clients
- Customize reference ranges per client
- Export lab histories and reports
- Begin with first report entered by us
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
About membership
What's included in a Healthmatters membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
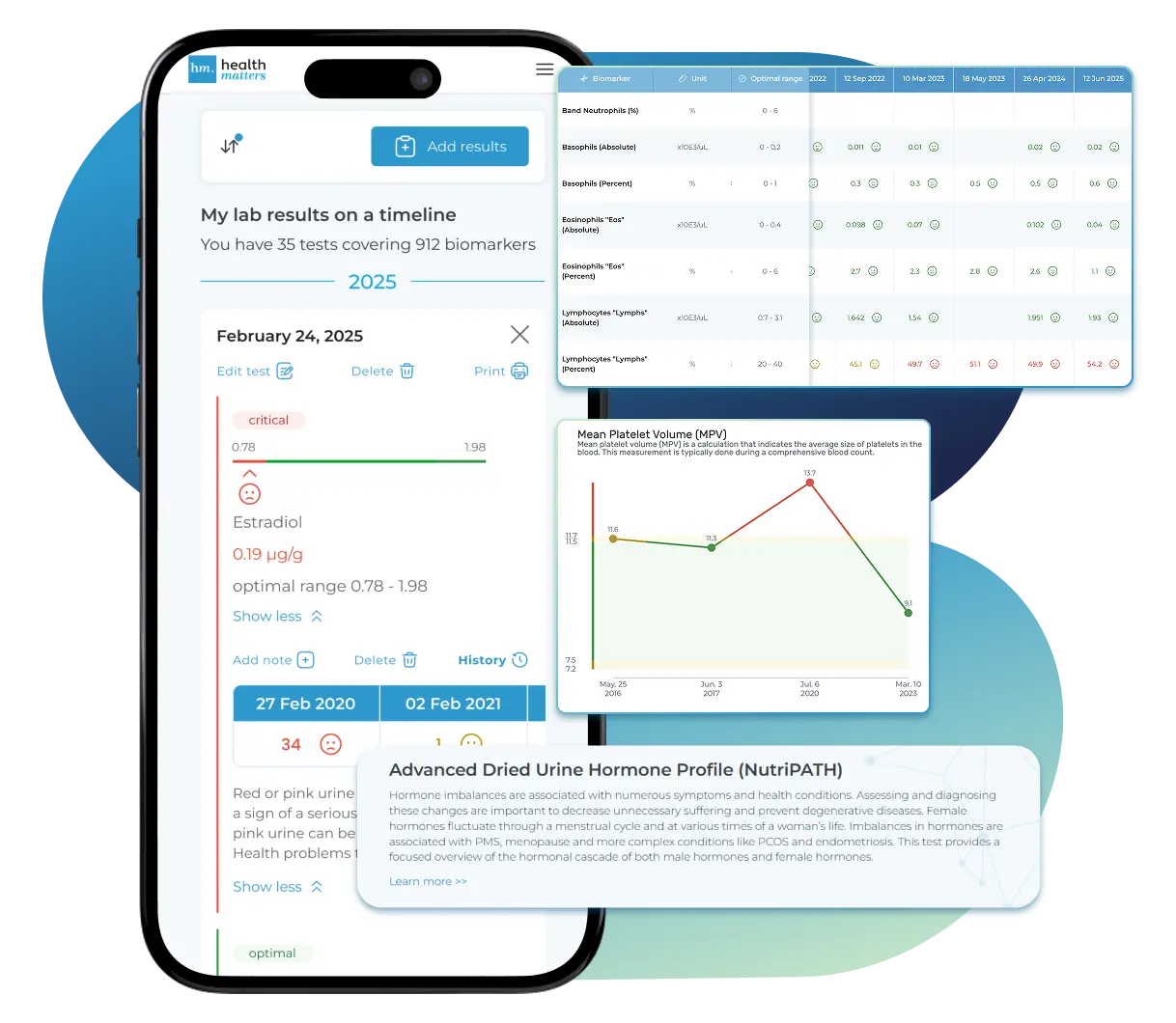
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
 Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Let Your Lab Results Tell the Full Story
Once your results are in one place, see the bigger picture — track trends over time, compare data side by side, export your full history, and share securely with anyone you trust.





Bring all your results together to compare, track progress, export your history, and share securely.
What Healthmatters Members Are Saying
Frequently asked questions
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
- Individuals who want to track and understand their health over time.
- Health professionals, such as doctors, nutritionists, and wellness coaches, need to manage and interpret lab data for their clients.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
- Upload lab reports from any lab
- View your data in interactive graphs, tables, and timelines
- Track trends and monitor changes over time
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export and share your full lab history
- Access your results anytime, from any device
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 10000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
- The GI Effects® Comprehensive Stool Profile,
- GI-MAP,
- The NutrEval FMV®,
- The ION Profile,
- Amino Acids Profile,
- Dried Urine Test for Comprehensive Hormones (DUTCH),
- Organic Acids Test,
- Organix Comprehensive Profile,
- Toxic Metals,
- Complete Blood Count (CBC),
- Metabolic panel,
- Thyroid panel,
- Lipid Panel,
- Urinalysis,
- And many, many more.
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
We implement proven measures to keep your data safe.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
















