Testosterone
Other names: Testosterone (total), Testosterone, Total, Testosterone, Total, TESTOSTERONE TOTAL, Total Testosterone, TESTOSTERONE, TOT.,S., Testosterone, Total (Males), TESTOSTERONE, SERUM, TESTOSTERONE, TOTAL, MS, Testosterone, Total, LC/MS
This test assesses the level of the hormone testosterone in your bloodstream. Testosterone, an androgen, is primarily responsible for the development of male characteristics. It is synthesized in the testes for males, ovaries for females, and the adrenal glands.
During puberty in males, testosterone induces several changes, including the growth of hair, muscles, penis, and testes, along with a deepening of the voice. It continues to be produced in adult males, promoting sex drive and aiding in sperm maturation.
Females also produce small amounts of testosterone in their ovaries, contributing to various bodily functions.
The pituitary gland in the brain regulates testosterone production by releasing signaling hormones such as luteinizing hormone.
Most of the testosterone in the blood binds to two proteins: albumin and sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG). Some remains unbound, known as free testosterone, which is easily utilized by the body. This unbound form, along with albumin-bound testosterone, is termed bioavailable testosterone.
In the assessment of testosterone levels by healthcare providers, total testosterone levels are initially tested, encompassing all three types. Free testosterone measurements can provide additional information when total testosterone levels are low.
Both males and females can experience health issues due to low or high testosterone levels. High testosterone in females may lead to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), resulting in infertility, irregular menstruation, acne, obesity, blood sugar problems, and excessive facial hair growth.
As males age, testosterone levels typically decline, but this natural decrease is not considered hypogonadism. The FDA currently advises against treating age-related low testosterone in males.
References:
https://www.urologyhealth.org/urology-a-z/l/low-testosterone
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/24215-testosterone-test
What does it mean if your Testosterone result is too high?
Abnormally high testosterone levels are also known as hypergonadism.
Possible signs and symptoms of high testosterone include:
- Acne
- Aggression
- Early puberty, in young men
- Excessive “hairiness”
- High blood pressure
- High libido
- High red blood cell count
- Increased risk-taking behaviors
- Infertility and decreased sperm count
Abnormally high testosterone levels can be caused by:
Tumors: Adrenal and testicular tumors may cause abnormally high testosterone.
Anabolic steroid abuse: Sometimes used by athletes and bodybuilders to build more muscle mass or increase athletic performance. Some athletes take Clomid illegally to boost performance.
Testosterone supplementation: Sometimes prescribed by a physician, and sometimes purchased illegally without a prescription.
Testosterone gel: Coming into contact with someone who is using testosterone gel can be an issues. The gel can accidentally be rubbed off onto someone else, raising their testosterone levels unintentionally.
Lowering high testosterone levels in men can be achieved through dietary and lifestyle changes. Here are some effective strategies:
→ Dietary Adjustments:
- Reduce consumption of foods high in saturated fats and processed sugars, as they can increase testosterone levels.
- Avoid or limit soy products, dairy, and alcohol, as they may lower testosterone levels.
- Incorporate foods like flaxseed and soy products into your diet, as they can help reduce testosterone production.
→ Lifestyle Changes:
- Maintain a healthy weight through regular exercise, as obesity is linked to higher testosterone levels.
- Manage stress levels through relaxation techniques, as chronic stress can raise testosterone levels.
→ Medications and Hormone Therapy:
- Consult with a healthcare professional about hormone-based birth control or androgen blockers if necessary.
It's important to note that these methods should be discussed with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate approach based on individual health needs.
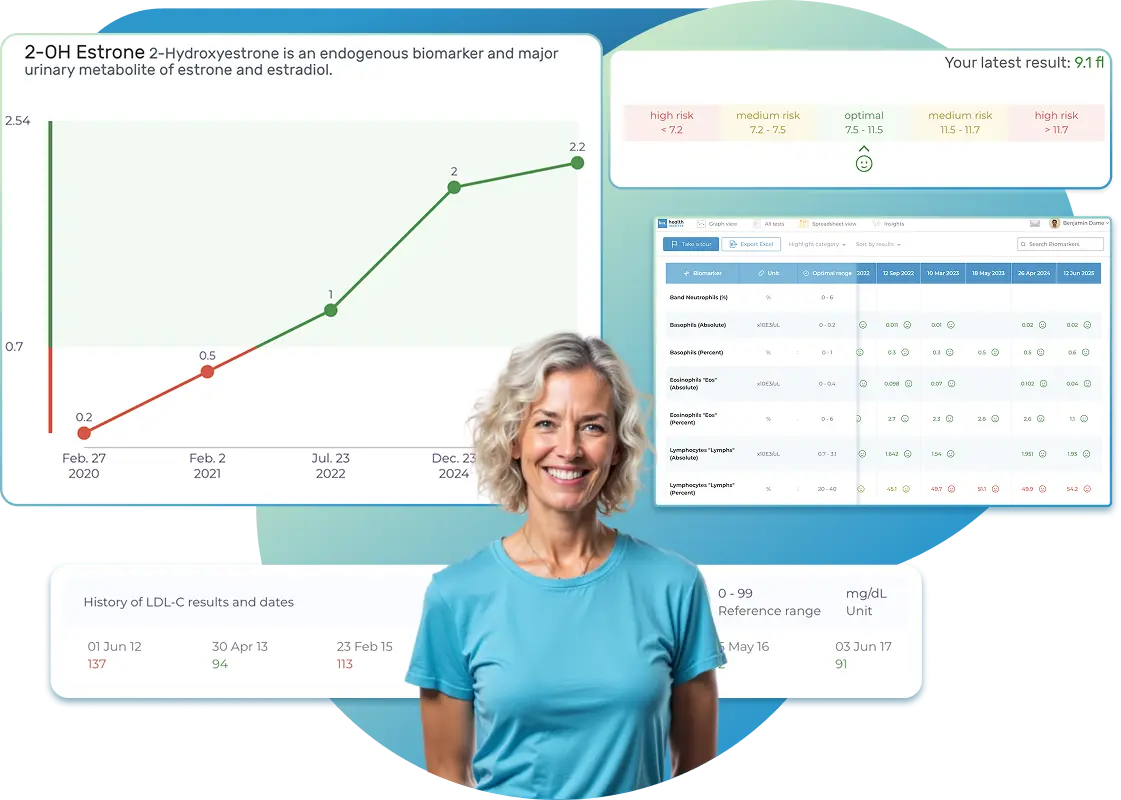
All Your Lab Results.
One Simple Dashboard.
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results Easily
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
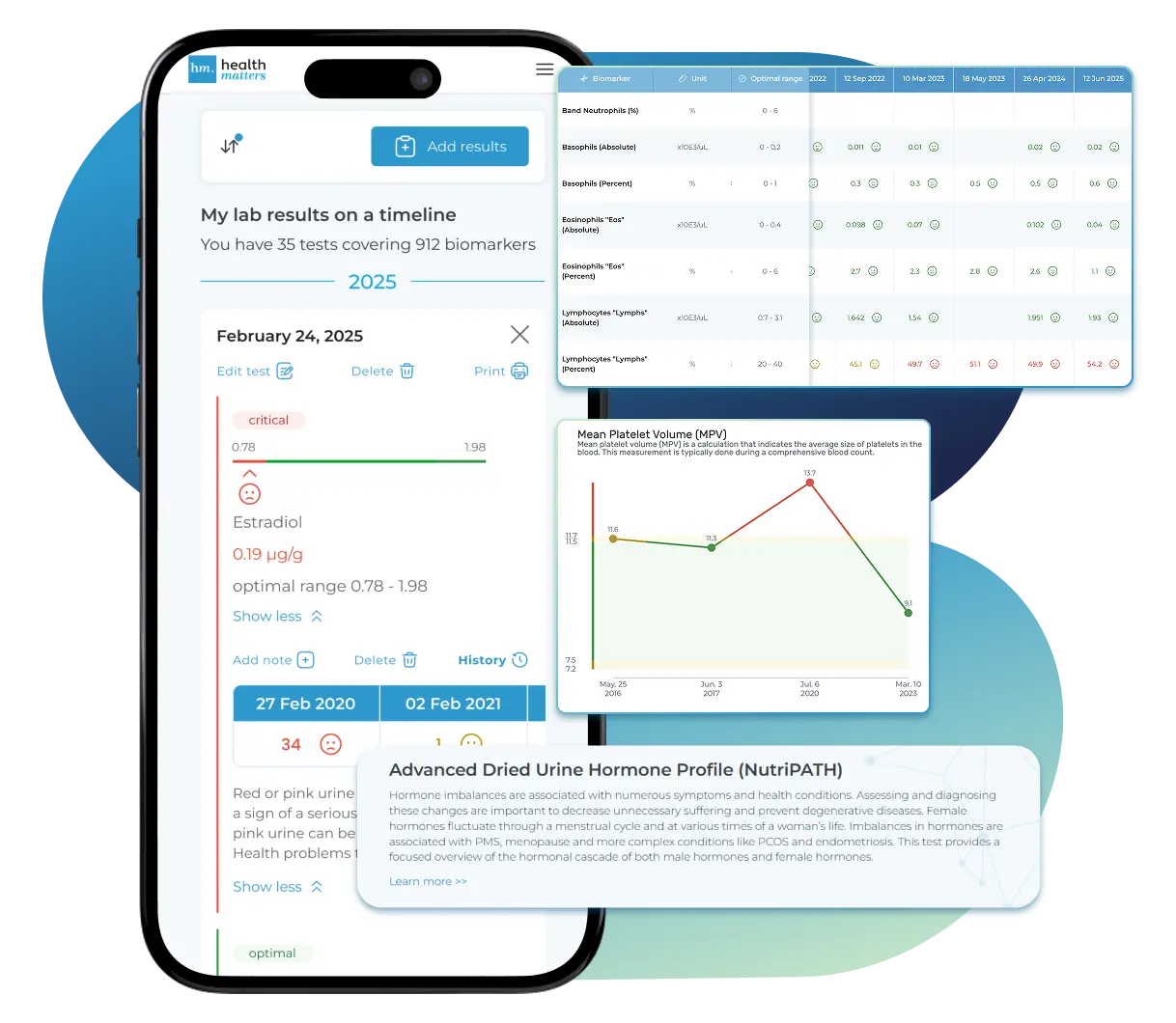
What does it mean if your Testosterone result is too low?
Potential symptoms of low testosterone in males include:
- Large breasts
- Low sex drive or lack of interest in sex
- Trouble getting an erection
- Low sperm count and other fertility problems
- Changes in the testicles
- Weak bones
- Irritability
- Trouble concentrating
- Loss of muscle mass
- Hair loss
- Depression
- Fatigue
- Anemia
Potential causes of low testosterone in men:
Age: Once men reach age 50, testosterone levels begin a natural decline. Male fertility does decline with age, though not as drastically as it does in women.
Obesity: Obesity may have an even bigger impact on testosterone levels than age. Research has found that increases in weight are directly related to lowering testosterone levels. Losing weight can bring your testosterone levels back up.
Smoking: Smoking also increases your risk of male infertility.
Being underweight: Abnormally low weight, malnutrition, and excessive exercise can lead to low testosterone levels and decreased fertility.
Klinefelter syndrome (KS): This is a genetic disorder where instead of having one X and one Y chromosome, the man has an additional X chromosome. It is a common cause of male infertility.
Kallmann syndrome: This is a genetic condition where puberty either fails to begin or doesn’t complete.
Pituitary disorders: This includes problems with how the pituitary functions. It may be the result of a pituitary tumor or brain tumor. Or, treatment of a brain tumor with radiation can cause long-term damage to the pituitary.
Undescended testicles: This usually resolves during early childhood. If not, though, it must be corrected. Otherwise, it can cause hormonal problems later in life.
Abnormally high levels of iron: This is also known as hemochromatosis.
Testicular injury: If just one testicular is injured, testosterone production may be normal.
Cancer treatment: Chemotherapy and radiation therapy can temporarily cause low testosterone and impair sperm production. However, sometimes the damage is permanent. One study found that 30 percent of men experienced low testosterone levels after treatment.
HIV/AIDS: the virus can interfere with how the testes, pituitary, and hypothalamus function. This, in turn, can lead to low testosterone levels.
Major illness or surgery: This will usually reverse itself after recovery time. Some infections, like mumps, can cause long-term hormonal problems.
Medical or recreational drug use: For example, marijuana can cause lower testosterone levels.
Extremely high levels of stress: High levels of the stress hormone cortisol have been associated with lower levels of testosterone.
Boosting low testosterone in men can be achieved through various natural methods:
→ Dietary Improvements: Maintain a healthy diet rich in nutrients. This includes consuming adequate protein, healthy fats, and carbohydrates.
→ Regular Exercise: Engage in both cardiovascular and resistance training exercises. Weightlifting, in particular, can help boost testosterone levels.
→ Stress Management: High stress levels can contribute to low testosterone. Employ stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
→ Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get enough quality sleep each night, as sleep is crucial for hormone regulation.
→ Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing excess body fat can help improve testosterone levels, as obesity is linked to lower testosterone.
→ Nutritional Supplements: Consider supplements like zinc and vitamin D, which are known to support testosterone production.
→ Include Testosterone-Boosting Foods: Incorporate foods such as ginger, oysters, pomegranates, leafy green vegetables, and fatty fish into your diet to naturally support testosterone levels.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before making significant lifestyle changes or taking supplements, especially if you suspect you have low testosterone levels. They can provide personalized guidance and determine the most suitable approach for your specific situation.
------------------------------------------------
What if your FSH and LH are also low?
Low levels of testosterone, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH) in a male typically indicate a condition related to the dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis. This axis is a complex set of hormone interactions that regulates the production of testosterone and other sex hormones.
When both FSH and LH are low, it suggests a problem with the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, rather than the testes themselves. This condition is often referred to as secondary hypogonadism or hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. It can be caused by various factors, including:
- Pituitary Disorders: Tumors, such as prolactinomas, or other pituitary gland abnormalities can impair hormone production.
- Hypothalamic Disorders: Issues with the hypothalamus, such as tumors, trauma, or congenital conditions like Kallmann syndrome, can affect the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which in turn influences FSH and LH production.
- Chronic Illness or Stress: Prolonged illness or significant physical or psychological stress can suppress the HPG axis.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as opioids or glucocorticoids, can interfere with hormone production.
- Obesity: Excess body fat can affect hormone levels and disrupt the normal functioning of the HPG axis.
Low testosterone levels can lead to a variety of symptoms, including decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, depression, reduced muscle mass and strength, and increased body fat.
Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to measure hormone levels, along with imaging studies like MRI to examine the pituitary gland. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include hormone replacement therapy, medications to stimulate hormone production, or addressing the primary condition affecting the hypothalamus or pituitary gland. Lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, stress management, and proper nutrition, can also help improve hormone levels and overall health. Consulting an endocrinologist or a healthcare provider specializing in hormone disorders is essential for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Laboratories
Bring All Your Lab Results Together — In One Place
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.
Pricing Table
Gather Your Lab History — and Finally Make Sense of It
Finally, Your Lab Results Organized and Clear
Personal plans
$79/ year
Advanced Plan
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 5 reports entered for you
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
$250/ once
Unlimited Account
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 10 reports entered for you
- No subscriptions. No extra fees.
$45/ month
Pro Monthly
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track lab results for multiple clients
- Customize reference ranges per client
- Export lab histories and reports
- Begin with first report entered by us
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
About membership
What's included in a Healthmatters membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
 Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Let Your Lab Results Tell the Full Story
Once your results are in one place, see the bigger picture — track trends over time, compare data side by side, export your full history, and share securely with anyone you trust.





Bring all your results together to compare, track progress, export your history, and share securely.
What Healthmatters Members Are Saying
Frequently asked questions
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
- Individuals who want to track and understand their health over time.
- Health professionals, such as doctors, nutritionists, and wellness coaches, need to manage and interpret lab data for their clients.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
- Upload lab reports from any lab
- View your data in interactive graphs, tables, and timelines
- Track trends and monitor changes over time
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export and share your full lab history
- Access your results anytime, from any device
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 10000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
- The GI Effects® Comprehensive Stool Profile,
- GI-MAP,
- The NutrEval FMV®,
- The ION Profile,
- Amino Acids Profile,
- Dried Urine Test for Comprehensive Hormones (DUTCH),
- Organic Acids Test,
- Organix Comprehensive Profile,
- Toxic Metals,
- Complete Blood Count (CBC),
- Metabolic panel,
- Thyroid panel,
- Lipid Panel,
- Urinalysis,
- And many, many more.
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
We implement proven measures to keep your data safe.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
















