Iron
Other names: Iron (serum), IRON, TOTAL, IRON, SERUM
Iron - the basics:
- Iron is supplied by the diet.
- As much as 70% of the iron in the body is found in the hemoglobin of the red blood cells (RBCs).
- The other 30% is stored in the form of ferritin and hemosiderin (=iron-storage complex within cells, not widely available).
- About 10% of the ingested iron is absorbed in the small intestine and transported to the plasma.
- Abnormal levels of iron are characteristic of many diseases, including iron-deficiency anemia and hemochromatosis (=Iron overload).
Where is iron found in the body?
Most iron in the body is bound to red blood cells or stored in the spleen and cannot be directly tested.
Iron is found in different parts of the body:
- In the blood. About 65% of all iron is in the blood. Iron in the blood is mostly bound to the transportation protein transferrin.
- In muscles
- In the liver (called ferritin)
- In enzymes in the body.
Iron and transferrin:
- After iron is absorbed in the small intestine and transported to the plasma, there the iron is bound to a globulin protein called transferrin and carried to the bone marrow for incorporation into hemoglobin.
- Transferrin exists in relation to the need for iron. When iron stores are low, transferrin levels increase, whereas transferrin is low when there is too much iron.
- Usually about one-third of the transferrin is being used to transport iron. Because of this, the blood serum has considerable extra iron-binding capacity, which is the Unsaturated Iron Binding Capacity (UIBC). The TIBC equals UIBC plus the serum iron measurement. Some laboratories measure UIBC, some measure TIBC, and some measure transferrin.
- The serum iron determination is a measurement of the quantity of iron bound to transferrin.
Why is iron so important?
- Iron is an essential element required for hemoglobin production.
- The human body requires iron to perform many vital physiological functions.
What is hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin oxygenates the blood. Without iron, red blood cells cannot reproduce in the body.
How is iron absorbed in the body?
- The body takes in iron from the food you eat so it is important to have good sources of iron in your diet. Only about 10% of the iron you consume is absorbed.
- The process of iron absorption is tightly regulated because your body does not have any biochemical ways of removing iron. Instead, iron is lost through processes such as bleeding, menstruation, and breast-feeding. Additionally, iron within the body is constantly being recycled and reused.
What does a serum test do?
A serum iron test measures iron levels in the serum component of the blood. A serum iron test is ordered after abnormal results are found in a hemoglobin test or a complete blood count, or when you are showing symptoms of anemia.
How is iron measured?
- Iron is often measured in micrograms per deciliter (mcg/dl), normal ranges for serum iron differ depending on an individual’s age and sex.
- Child-bearing women have the highest requirements for iron because of the monthly loss of blood in their menstrual cycles.
- If your results are abnormal, additional tests will determine whether iron is being stored in your liver, not being transported to the right places in your body, or what type of anemia you have.
What does it mean if your Iron result is too high?
High Serum Iron Levels – What It Means and What You Can Do
Seeing a high iron (serum) level on your lab report?
Here’s what it could mean, why it happens, and what steps you can take.
What Is Chronic Iron Overload?
Chronic iron overload — also called hemochromatosis or hemosiderosis — happens when too much iron builds up in the body.
Excess iron is often deposited in vital organs like the brain, liver, and heart, which can lead to serious health issues if left untreated.
Important:
Recent or massive blood transfusions can temporarily raise iron levels. If you've recently had a transfusion, it’s best to repeat iron testing later for an accurate result.
Common Causes of High Iron Levels
High serum iron can happen for several reasons, including:
-
Hemolytic anemia (when red blood cells break apart)
-
Iron overdose (taking too much iron through supplements or diet)
-
Iron overload (body’s inability to properly eliminate iron)
-
Liver conditions (hemochromatosis, hemosiderosis, hepatitis, liver failure)
-
Frequent blood transfusions
-
Lead poisoning
-
Use of birth control pills
-
High intake of vitamin B6 or B12
How Iron Overload Can Affect Your Health
Even mild cases of iron overload can increase the risk of:
-
Liver disease (cirrhosis, liver cancer)
-
Heart disease (heart attack, heart failure)
-
Diabetes mellitus
-
Joint problems (osteoarthritis, osteoporosis)
-
Metabolic syndrome
-
Hormone imbalances (hypothyroidism, hypogonadism)
Iron overload can also worsen or speed up certain brain-related conditions like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s disease, epilepsy, and multiple sclerosis.
What You Can Do: Treatment Options
The main treatment for iron overload is iron reduction therapy.
If your hemoglobin levels are healthy enough, your doctor may recommend:
-
Therapeutic phlebotomy (regular blood removal)
-
Blood donation to lower iron stores
Always follow your doctor’s guidance before starting any iron-lowering treatment.
Should You Check Other Markers Too?
Yes!
When iron is high, it's important to also look at related markers like TIBC, UIBC, transferrin saturation, and ferritin for a full picture.
In some cases, iron poisoning is suspected when serum iron is higher than Total Iron Binding Capacity (TIBC).
| Condition | Serum Iron | TIBC/Transferrin | UIBC | Transferrin Saturation (%) | Ferritin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemochromatosis/Hemosiderosis | High | Low | Low | High | High |
| Hemolytic Anemia | High | Low/Normal | Low/Normal | High | High |
| Sideroblastic Anemia | High/Normal | Low/Normal | Low/Normal | High | High |
| Iron Poisoning | High | Normal | Low | High | Normal |
Final Thoughts
High iron levels are important to investigate but manageable with the right care.
Talk to your doctor about the next steps based on your full lab results and overall health picture.
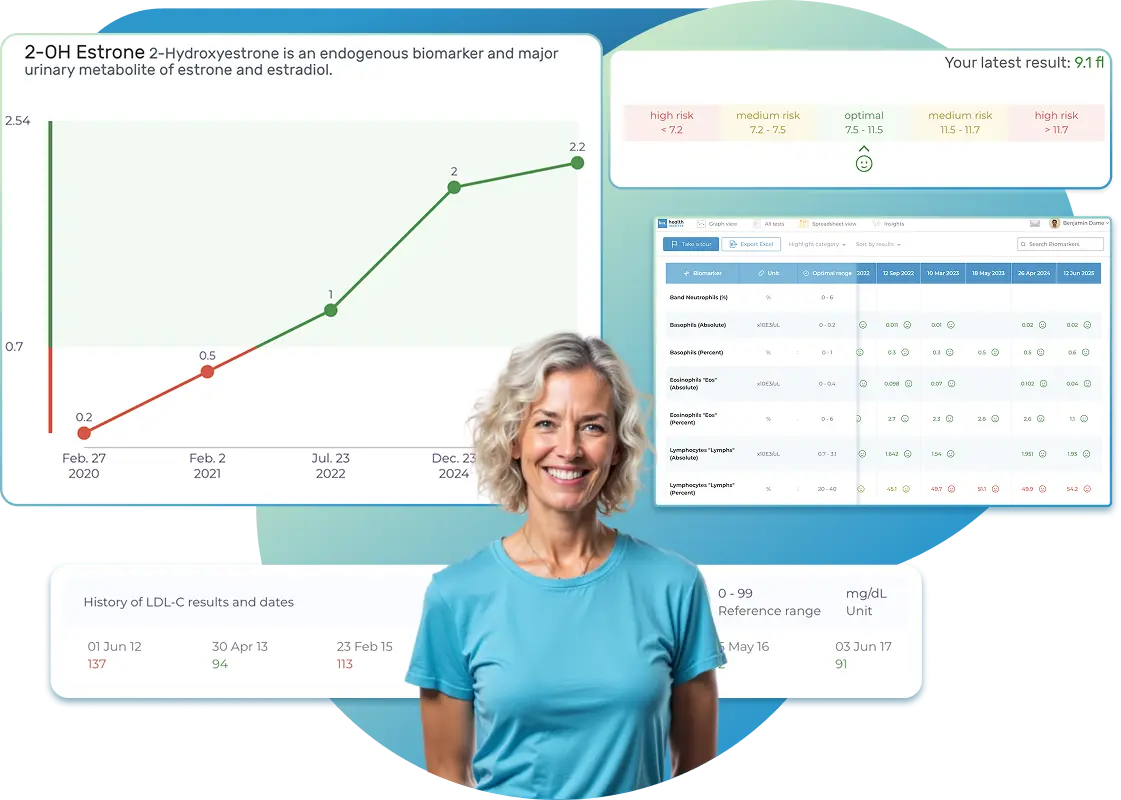
All Your Lab Results.
One Simple Dashboard.
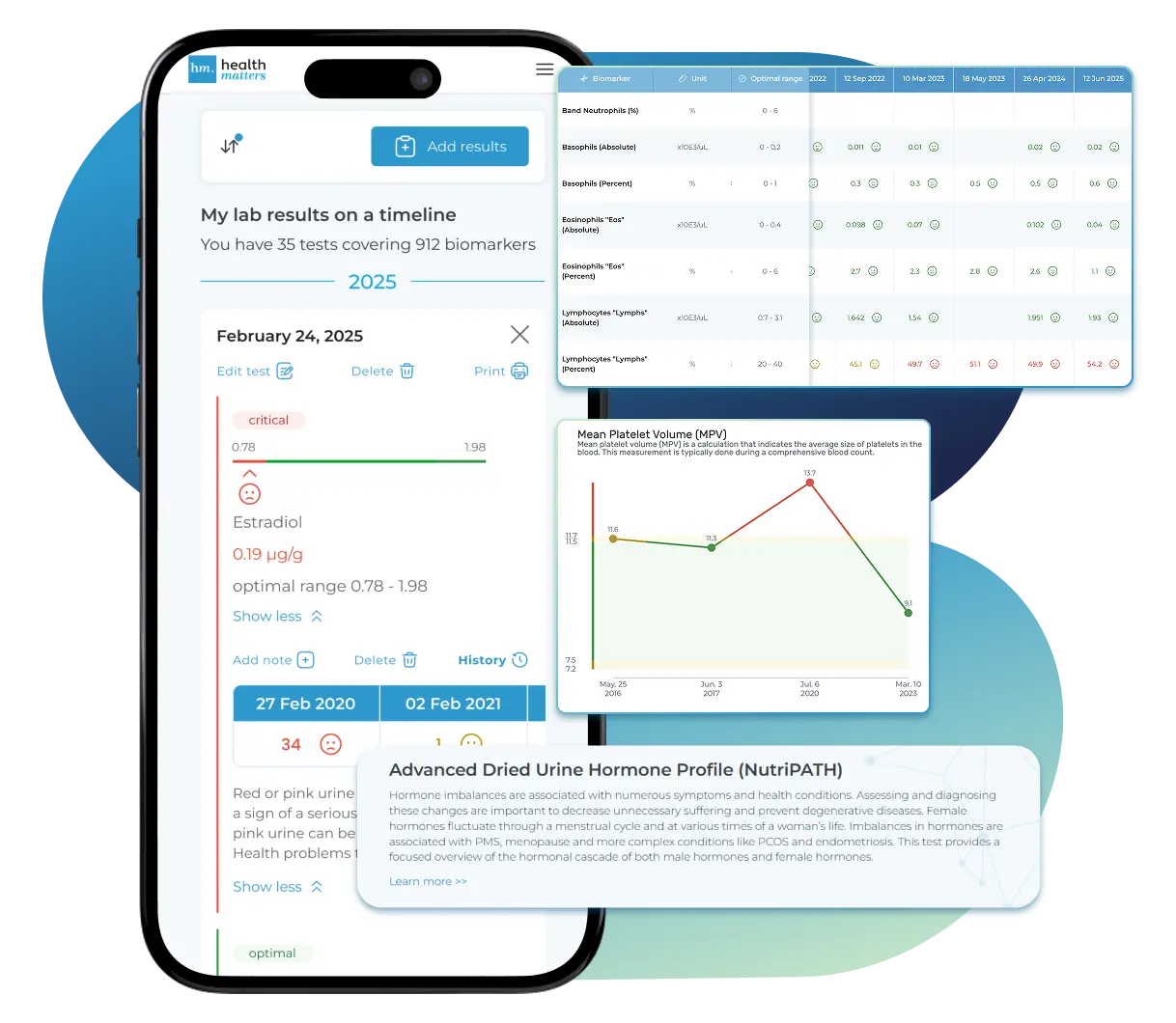
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results Easily
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
What does it mean if your Iron result is too low?
Iron deficiency is a condition resulting from too little iron in the body. Iron deficiency can be the result of numerous and multiple causes.
Possible Causes:
- Your diet may not contain enough iron-rich foods. Even a vitamin C deficiency affects the absorption of iron in the diet, and it’s possible that if you’re low in vitamin C, you won’t absorb enough iron from other foods.
- If you are a woman in the child-bearing years, then heavy menstrual periods could contribute to low iron levels. That’s because blood is exiting the body at high levels – and taking iron with it.
- Acute or chronic blood loss, including from ulcers or bleeding from the GI tract
- Anemia (iron-deficiency, sickle cell, vitamin B6 deficiency, vitamin B12 deficiency, vitamin C deficiency)
- Pregnancy
- Bone marrow conditions
- Infections
- Hypothyroidism
- Kwashiorkor (malnutrition)
- Associated with blood loss during surgery
Possible symptoms:
- premature births
- low birth weight babies
- delayed growth and development
- delayed normal infant activity and movement.
- Lower IQs have been linked to iron deficiency occurring during critical periods of growth.
- Iron deficiency can result in poor memory or poor cognitive skills (mental function) and can result in poor performance in school, work, etc.
Possible signs of iron deficiency:
A person who is iron deficient may also be anemic and as a result may have one or more symptoms of anemia.
These can include:
- chronic fatigue
- Weakness
- Dizziness
- Headaches
- Depression
- sore tongue
- sensitivity to cold (low body temp)
- shortness of breath doing simple tasks (climbing stairs, walking short distances, doing housework)
- restless legs syndrome
- pica (the desire to chew ice or non-food items,)
- and loss of interest in work, recreation, relationships, and intimacy.
Most at risk for iron deficiency:
Women, children and the elderly are most at risk. African American and Hispanic women and their young children are prone to iron deficiency, possibly because of diet or perhaps different hemoglobin needs. Men are rarely iron deficient; but when they are, it is generally due to blood loss from the digestive tract (sometimes indicating disease), diseases that affect iron absorption, and in some cases, alcohol abuse. Except for those who are strict vegetarians, men rarely have dietary iron deficiency.
Possible correlations to other markers:
You should also correlate your low iron levels to other biomarkers.
A decreased serum iron level, elevated total iron-binding capacity (TIBC), and low transferrin saturation value are characteristic of iron-deficiency anemia.
Here are possible scenarios of correlation:
|
Disease |
Iron |
TIBC/ Transferrin |
UIBC |
Transferrin Saturation (%) |
Ferritin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Iron Deficiency |
Low |
High |
High |
Low | Low |
|
Chronic Illness |
Low |
Low/Normal |
Low/Normal | Low/Normal |
High/Normal |
- You can also look at RDW (=Red Cell Distribution Width) and MCV (=Mean Corpuscular Volume), if you have those measurements, to distinguish between different kinds of anemias. Refer to your RDW and MCV markers for more information.
- Low zinc levels can also be associated with iron deficiency anemia. Zinc is the co-factor of several enzymes and plays a role in iron metabolism, so zinc deficiency is associated with IDA (=iron deficiency anemia). Refer to your zinc marker for more information.
Laboratories
Bring All Your Lab Results Together — In One Place
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.
Pricing Table
Gather Your Lab History — and Finally Make Sense of It
Finally, Your Lab Results Organized and Clear
Personal plans
$79/ year
Advanced Plan
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 5 reports entered for you
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
$250/ once
Unlimited Account
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 10 reports entered for you
- No subscriptions. No extra fees.
$45/ month
Pro Monthly
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track lab results for multiple clients
- Customize reference ranges per client
- Export lab histories and reports
- Begin with first report entered by us
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
About membership
What's included in a Healthmatters membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
 Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Let Your Lab Results Tell the Full Story
Once your results are in one place, see the bigger picture — track trends over time, compare data side by side, export your full history, and share securely with anyone you trust.





Bring all your results together to compare, track progress, export your history, and share securely.
What Healthmatters Members Are Saying
Frequently asked questions
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
- Individuals who want to track and understand their health over time.
- Health professionals, such as doctors, nutritionists, and wellness coaches, need to manage and interpret lab data for their clients.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
- Upload lab reports from any lab
- View your data in interactive graphs, tables, and timelines
- Track trends and monitor changes over time
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export and share your full lab history
- Access your results anytime, from any device
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 10000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
- The GI Effects® Comprehensive Stool Profile,
- GI-MAP,
- The NutrEval FMV®,
- The ION Profile,
- Amino Acids Profile,
- Dried Urine Test for Comprehensive Hormones (DUTCH),
- Organic Acids Test,
- Organix Comprehensive Profile,
- Toxic Metals,
- Complete Blood Count (CBC),
- Metabolic panel,
- Thyroid panel,
- Lipid Panel,
- Urinalysis,
- And many, many more.
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
We implement proven measures to keep your data safe.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
















