An essential component of the thyroid hormones T4 and T3. Iodine is an essential nutrient, commonly found in dairy products, seafood, iodized salt, and grains. Severe iodine deficiency compromises thyroid hormone production and leads to serious diseases including irreversible cretinism, pregnancy complications, goiter, and decreased cognitive function. Mild to moderate iodine insufficiency can lead to thyroid deficiency. Excessive iodine intake, paradoxically, can also lead to thyroid deficiency. Iodine deficiency has also been associated with breast cancer. Since over 90% of dietary iodine is eliminated in urine, adequacy of recent iodine intake can be accurately assessed with dried urine testing.
Iodine Deficiency: A Global Health Concern
Iodine deficiency affects nearly 2 billion people worldwide. In the United States, urinary iodine levels have decreased by half since the 1970s, with around 10% of the population exhibiting some degree of deficiency. This resurgence in developed nations, including the U.S. and Western Europe, is largely attributed to the reduced consumption of iodine-rich foods such as eggs, dairy, and iodine-fortified salt, as part of dietary efforts to lower blood pressure and cholesterol.
The Importance of Adequate Iodine Across Life Stages
Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production, which plays a critical role in neurological development, particularly during pregnancy. In regions with severe iodine deficiency, pregnant women are at increased risk of miscarriage, stillbirths, or giving birth to children with cretinism and severe developmental disabilities. Even in areas with mild to moderate iodine deficiency, including parts of the U.S., children born to iodine-deficient mothers may experience impaired intellectual development and are at increased risk for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
For both children and adults, insufficient iodine intake leads to reduced thyroid hormone synthesis, resulting in hypothyroidism. Low iodine levels prompt the brain to produce more thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which can lead to an overgrowth of the thyroid (goiter). This condition is more prevalent in regions with consistently low iodine levels.
Potential Issues with Excess Iodine
While iodine deficiency is a common concern, excessive iodine intake can also disrupt thyroid function. High iodine levels from foods like seaweed or iodine supplements can lead to goiter, hyperthyroidism, or hypothyroidism. The elderly, especially those who have lived in low-iodine environments, are particularly susceptible to developing hyperthyroidism when exposed to a sudden increase in iodine. In some cases, acute iodine exposure can paradoxically suppress thyroid hormone synthesis, a phenomenon known as the Wolff-Chaikoff effect. While most individuals recover within a couple of days, those with underlying thyroid issues, such as subclinical hypothyroidism or autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto’s, may require long-term treatment for hypothyroidism.
Recommended Iodine Intake for Optimal Thyroid Function
To maintain optimal thyroid function, it is crucial to consume adequate iodine. The World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend a daily iodine intake of 150 µg for non-pregnant adults, with an upper limit of 1,100 µg. In countries like Japan, where iodine consumption is much higher due to seaweed intake, the recommended upper limit is set at 3,000 µg.
Iodine’s Role Beyond the Thyroid
Although iodine’s role in thyroid function is well-known, it also plays a crucial role in other bodily tissues. It acts as an antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-carcinogen. Many tissues, including the salivary glands, pancreas, skin, mammary glands, uterus, and ovaries, utilize iodine. One of iodine’s unique properties is its ability to protect tissues from oxidative stress by interacting with unsaturated fatty acids and forming protective compounds. These iodinated lipids help prevent benign growths, such as fibrocystic breast disease and uterine fibroids, and may reduce the risk of cancer in iodine-concentrating tissues.
Iodine’s Antimicrobial and Protective Properties
Iodine has long been recognized for its antimicrobial properties. It concentrates in tissues exposed to infectious agents, such as the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and salivary glands, helping to protect against infections. Additionally, iodine’s ability to inhibit the proliferation of abnormal cells through its interaction with PPAR receptors highlights its potential as an anticancer agent, particularly in breast tissue and other hormone-sensitive areas.
Iodine Sufficiency: Varying Requirements Across Tissues
While the recommended daily iodine intake for thyroid health is between 150-300 µg, studies suggest that higher iodine levels may be necessary for optimal health in other tissues. For example, research indicates that iodine levels in the range of 3,000-6,000 µg daily may be required to protect against fibrocystic breast disease and other conditions. This intake level is consistent with that of countries like Japan, where breast cancer rates are significantly lower than in the U.S.
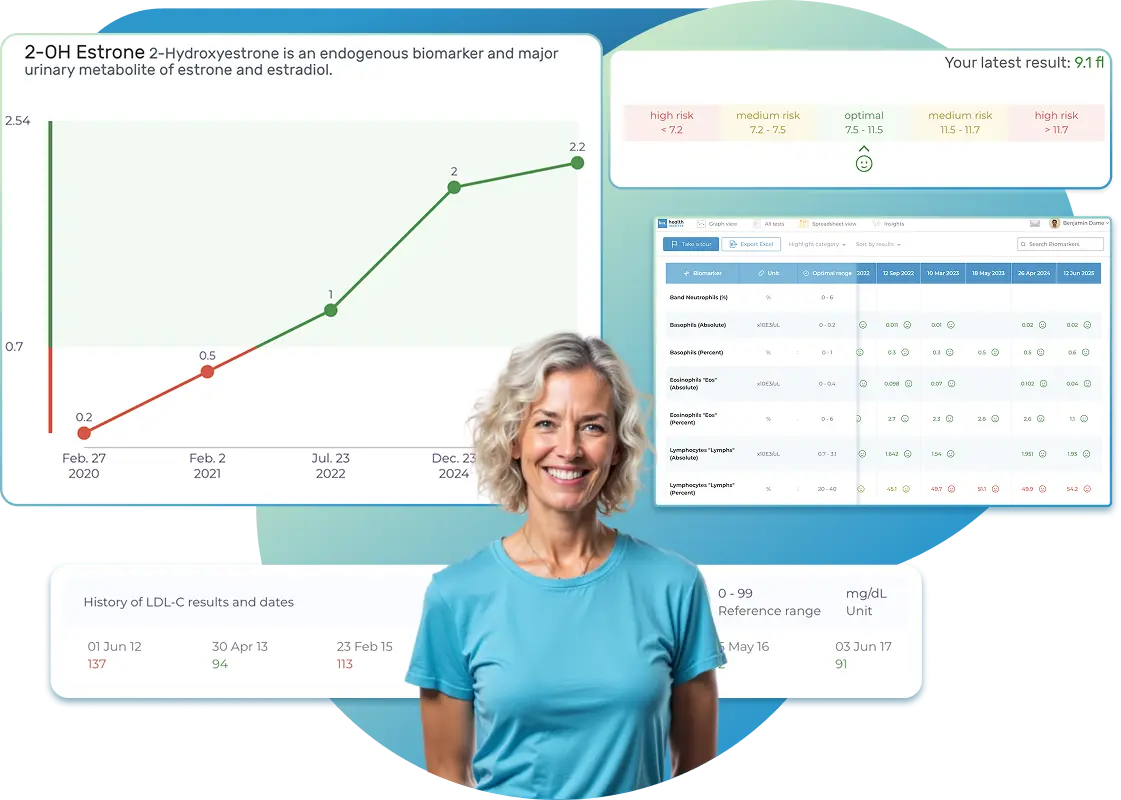
All Your Lab Results.
One Simple Dashboard.
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results Easily
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
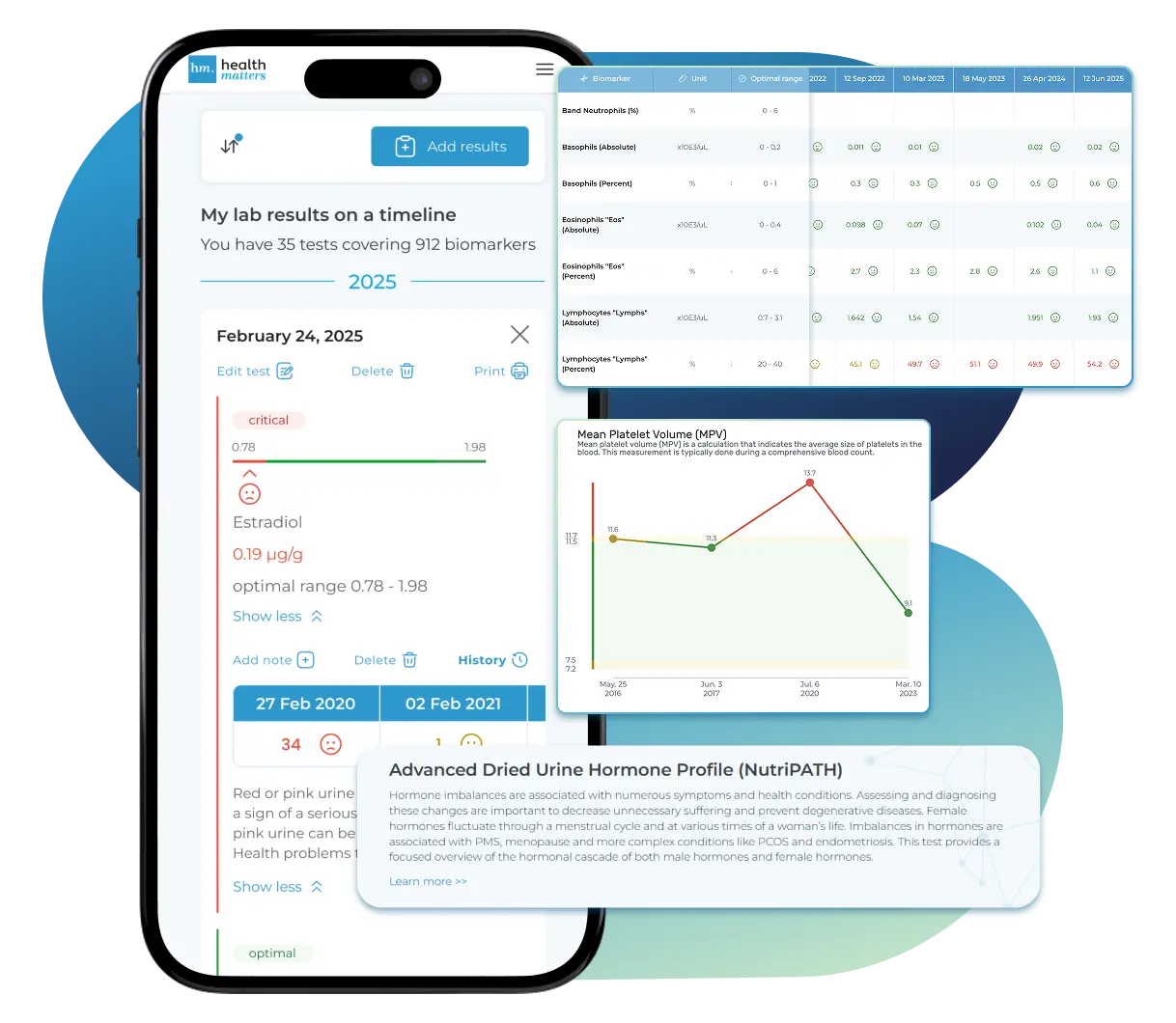
What does it mean if your Iodine result is too low?
A low iodine level on a Urinary Toxic & Essential Elements test by ZRT Laboratories typically indicates iodine deficiency, which can have significant implications for thyroid function and overall health. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the possible diagnosis, symptoms, and potential treatment options:
Diagnosis
- Iodine Deficiency: Low iodine levels are usually associated with insufficient iodine intake through diet or supplements. Iodine is a crucial nutrient for the synthesis of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), and its deficiency can lead to thyroid dysfunction.
- Hypothyroidism: If iodine deficiency is significant and prolonged, it may lead to hypothyroidism—a condition where the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormones. This can cause various systemic issues since thyroid hormones regulate metabolism, energy levels, and other critical bodily functions.
- Subclinical Hypothyroidism: In milder cases, iodine deficiency might not cause overt symptoms of hypothyroidism but can result in elevated TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone) levels, signaling the thyroid gland to work harder.
Symptoms of Iodine Deficiency
-
Thyroid-related symptoms:
- Goiter: Enlargement of the thyroid gland as it attempts to compensate for the lack of iodine.
- Fatigue and weakness: Due to reduced thyroid hormone production.
- Weight gain: Slower metabolism often leads to unintentional weight gain.
- Cold intolerance: A slower metabolism reduces heat production in the body.
- Dry skin: Poor thyroid function can lead to dry, flaky skin.
- Hair thinning: Thyroid hormones also play a role in hair growth and maintenance.
- Cognitive issues: Difficulty concentrating, memory problems, and mental fog may arise due to the lower thyroid function.
-
Pregnancy-related issues:
- Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can lead to developmental problems in the fetus, including impaired cognitive development and an increased risk of congenital hypothyroidism.
- Increased risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, or giving birth to children with neurological and developmental disorders.
-
In Children:
- Cognitive impairment, reduced intellectual ability, and increased risk of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
-
Other General Symptoms:
- Depression
- High cholesterol levels
- Muscle weakness or cramps
Potential Treatment Options
-
Dietary Adjustments:
- Increase iodine-rich foods: Foods such as seaweed, fish, dairy products, eggs, and iodized salt are rich sources of iodine. Incorporating these into the diet can help raise iodine levels.
- Seafood (such as cod, tuna, shrimp)
- Dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt)
- Eggs
- Iodized salt (Ensure salt intake is moderated if high blood pressure is a concern).
- Increase iodine-rich foods: Foods such as seaweed, fish, dairy products, eggs, and iodized salt are rich sources of iodine. Incorporating these into the diet can help raise iodine levels.
-
Iodine Supplementation:
- Iodine supplements: Potassium iodide is commonly used in supplements to correct iodine deficiency. However, supplementation should be done carefully and under the guidance of a healthcare professional to avoid iodine excess, which can also disrupt thyroid function.
- Recommended daily intake for non-pregnant adults: 150 µg/day.
- Pregnant women may need up to 250 µg/day to support both maternal and fetal thyroid function.
- Iodine supplements: Potassium iodide is commonly used in supplements to correct iodine deficiency. However, supplementation should be done carefully and under the guidance of a healthcare professional to avoid iodine excess, which can also disrupt thyroid function.
-
Thyroid Hormone Replacement:
- In cases where iodine deficiency has led to hypothyroidism, thyroid hormone replacement therapy with levothyroxine may be required. This is typically prescribed when iodine supplementation alone is insufficient or when hypothyroidism is already well-established.
-
Prenatal Supplements:
- For pregnant women: Prenatal vitamins containing iodine (around 150-250 µg) are often recommended to support both the mother and developing fetus.
-
Addressing Underlying Health Conditions:
- If iodine deficiency has contributed to or is exacerbated by Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or other thyroid-related autoimmune diseases, treatment should also focus on managing these conditions, often involving immune-modulating therapies or long-term thyroid hormone replacement.
Monitoring
- Regular Monitoring: After initiating iodine supplementation or dietary changes, regular follow-up tests are essential to ensure iodine levels have normalized and thyroid function is optimal.
- Urinary Iodine Tests: These may be repeated to monitor progress, especially in people who have developed hypothyroidism or who are pregnant and require precise iodine management.
Laboratories
Bring All Your Lab Results Together — In One Place
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.
Pricing Table
Gather Your Lab History — and Finally Make Sense of It
Finally, Your Lab Results Organized and Clear
Personal plans
$79/ year
Advanced Plan
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 5 reports entered for you
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
$250/ once
Unlimited Account
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 10 reports entered for you
- No subscriptions. No extra fees.
$45/ month
Pro Monthly
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track lab results for multiple clients
- Customize reference ranges per client
- Export lab histories and reports
- Begin with first report entered by us
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
About membership
What's included in a Healthmatters membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
 Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Let Your Lab Results Tell the Full Story
Once your results are in one place, see the bigger picture — track trends over time, compare data side by side, export your full history, and share securely with anyone you trust.





Bring all your results together to compare, track progress, export your history, and share securely.
What Healthmatters Members Are Saying
Frequently asked questions
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
- Individuals who want to track and understand their health over time.
- Health professionals, such as doctors, nutritionists, and wellness coaches, need to manage and interpret lab data for their clients.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
- Upload lab reports from any lab
- View your data in interactive graphs, tables, and timelines
- Track trends and monitor changes over time
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export and share your full lab history
- Access your results anytime, from any device
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 10000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
- The GI Effects® Comprehensive Stool Profile,
- GI-MAP,
- The NutrEval FMV®,
- The ION Profile,
- Amino Acids Profile,
- Dried Urine Test for Comprehensive Hormones (DUTCH),
- Organic Acids Test,
- Organix Comprehensive Profile,
- Toxic Metals,
- Complete Blood Count (CBC),
- Metabolic panel,
- Thyroid panel,
- Lipid Panel,
- Urinalysis,
- And many, many more.
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
We implement proven measures to keep your data safe.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
















