Hemoglobin
Other names: Haemoglobin
What is hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin is the main component of red blood cells. Hemoglobin (abbreviation: Hb) is a red substance made of iron and protein.
What's the function of hemoglobin?
- In the blood, it carries oxygen to the cells in the body from the lungs.
- Hemoglobin also carries carbon dioxide away from the cells to the lungs, later exhaled from the body. Carbon dioxide is a colorless and odorless gas present in small amounts in the air. It is a result of metabolism in the body. Metabolism is the chemical action in cells that release energy from nutrients or use energy to create other substances.
What are normal reference ranges for hemoglobin?
Normal hemoglobin levels differ depending on several factors, including age, sex at birth, hormonal supplementation, altitude of residence as well as presence of different hemoglobin types that impact hemoglobin turnover and affinity for oxygen binding.
Like other blood values, slightly high or low levels of hemoglobin may be normal for some people. Still, suppose you are falling too far out of the normal range. In that case, your doctor will most likely order more comprehensive testing to determine the cause.
Normal Ranges for Hemoglobin in g/dL:
Men: 14 to 18
Women: 12 to 16
Children to up 18 years of age: 11 to 13
Critical Range: <5 or >20
Additional notes:
- Elevated hemoglobin by itself is not considered a disorder, but rather a symptom of a medical condition. Therefore, treatment must target the underlying cause.
- Hemoglobin counts of endurance athletes can be as much as 30% higher than that of the average adult, which is considered normal.
Here are a few reasons why a hemoglobin test is being performed:
To check your overall health: Your doctor may test your hemoglobin as part of a complete blood count during a routine medical examination to monitor your general health and to screen for a variety of disorders, such as anemia.
To diagnose a medical condition: Your doctor may suggest a hemoglobin test if you're experiencing weakness, fatigue, shortness of breath or dizziness. These signs and symptoms may point to anemia or polycythemia vera. A hemoglobin test may help diagnose these or other medical conditions.
To monitor a medical condition: If you've been diagnosed with anemia or polycythemia vera, your doctor may use a hemoglobin test to monitor your condition and guide treatment.
What does it mean if your Hemoglobin result is too high?
Elevated hemoglobin by itself is not considered a disorder, but rather a symptom of a medical condition. Therefore, treatment must target the underlying cause.
It's important to note that hemoglobin counts of endurance athletes can be as much as 30% higher than that of the average adult, which is considered normal. Like other blood values, slightly high or low levels of hemoglobin may be normal for some people. Still, suppose you are falling too far out of the normal range. In that case, your doctor will most likely order more comprehensive testing to determine the cause.
High levels of hemoglobin are associated with increased blood thickness. This can slow down the blood flow and oxygen transport and, in some cases, form blood clots, which increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
High levels of hemoglobin are associated with increased blood thickness. Blood thickness can slow down the blood flow and oxygen transport. In some cases, blood clots can form. Blood clots increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Some specific causes of high hemoglobin might be:
- Dehydration
- Living at high altitude
- Medications such as anabolic steroids (incl. testosterone) and others.
- Smoking
- Poor lung function
- Heart problems
- Kidney Cancer
- Liver Cancer
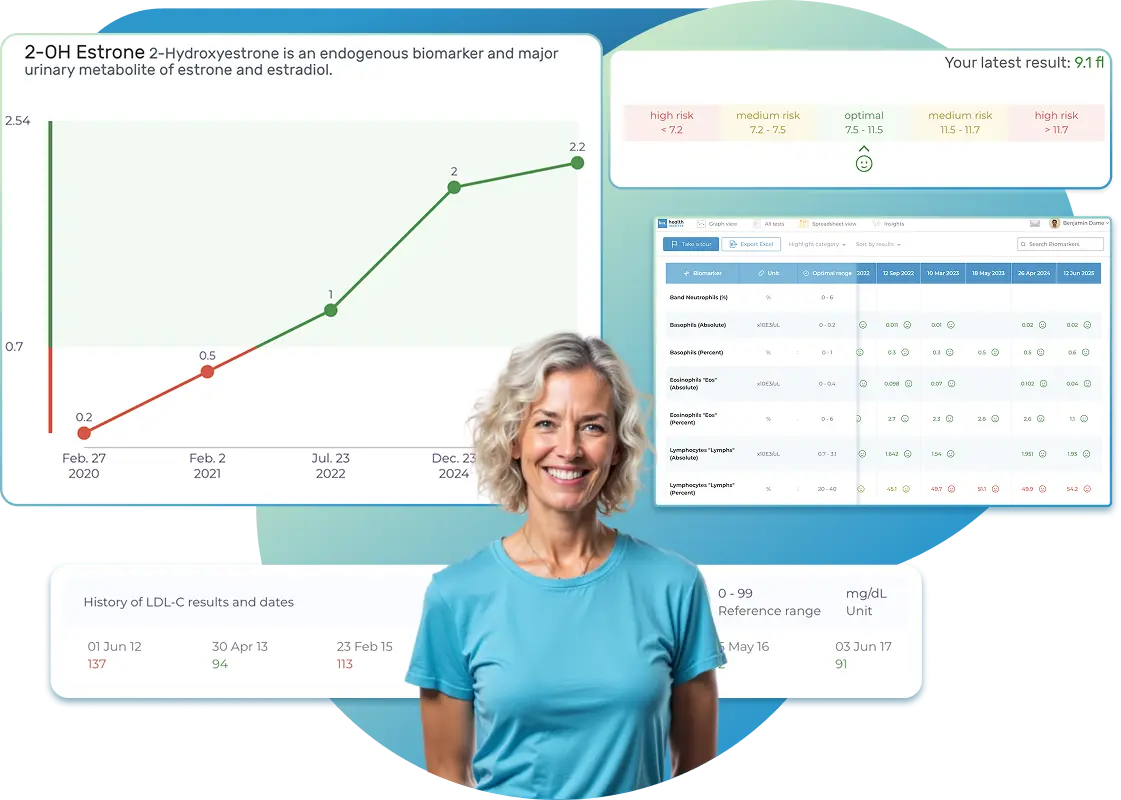
All Your Lab Results.
One Simple Dashboard.
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results Easily
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
What does it mean if your Hemoglobin result is too low?
Hemoglobin: What It Is and Why It Matters
What Is Hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin is a protein in your red blood cells that carries oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body. It also helps transport carbon dioxide back to the lungs to be exhaled. When your body doesn’t produce enough red blood cells, your hemoglobin levels can drop.
Why Do Hemoglobin Levels Drop?
Low hemoglobin—also known as anemia—can signal a variety of health issues. Common causes include vitamin and mineral deficiencies, chronic diseases, blood loss, and bone marrow disorders. A routine blood test can help detect low hemoglobin and prompt further investigation.
Signs and Symptoms of Low Hemoglobin (Anemia)
If your hemoglobin levels are too low, you may experience:
-
Fatigue or weakness
-
Difficulty concentrating
-
Pale skin
-
Shortness of breath
-
Chest pain or heart palpitations during exertion
-
Lightheadedness or fainting (in severe cases)
How Is Low Hemoglobin Treated?
Treatment depends on the cause. For example:
-
Iron-deficiency anemia: Iron supplements and iron-rich foods (like red meat, spinach, or lentils)
-
Vitamin B12 or folate deficiency: Dietary changes or supplementation
-
Chronic disease or kidney issues: Treatment of the underlying condition or use of medications like erythropoietin
-
Severe cases: Blood transfusions may be needed
Addressing the root cause usually restores normal hemoglobin levels.
Common Causes of Low Hemoglobin
-
Reduced red blood cell production: Bone marrow disorders or chronic illnesses
-
Increased red blood cell loss: Autoimmune diseases or hemolytic anemias
-
Blood loss: From injury, surgery, menstruation, or internal bleeding
-
Nutrient deficiencies: Low iron, vitamin B12, or folate intake
-
Poor nutrient absorption: Conditions like celiac disease or bariatric surgery
Health Conditions That Can Affect Red Blood Cell Production
-
Lymphoma: Crowds out healthy cells in the bone marrow
-
Leukemia: Impairs bone marrow’s ability to make red blood cells
-
Aplastic anemia: Bone marrow stops producing enough blood cells
-
Pernicious anemia: Poor absorption of vitamin B12
-
Multiple myeloma: Disrupts normal bone marrow function
-
Myelodysplastic syndromes: Stem cells don't mature into healthy blood cells
-
Chronic kidney disease: Reduces production of erythropoietin, a hormone critical for red blood cell formation
-
Certain medications: Chemotherapy, antiretrovirals, and immunosuppressants
Who’s at Risk for Low Hemoglobin?
-
Older adults
-
People with iron-deficient diets or poor nutrition
-
Endurance athletes (due to red blood cell breakdown)
-
Menstruating or pregnant individuals
-
People with chronic illnesses (e.g., kidney disease, autoimmune conditions, IBD)
Laboratories
Bring All Your Lab Results Together — In One Place
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.
Pricing Table
Gather Your Lab History — and Finally Make Sense of It
Finally, Your Lab Results Organized and Clear
Personal plans
$79/ year
Advanced Plan
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 5 reports entered for you
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
$250/ once
Unlimited Account
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 10 reports entered for you
- No subscriptions. No extra fees.
$45/ month
Pro Monthly
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track lab results for multiple clients
- Customize reference ranges per client
- Export lab histories and reports
- Begin with first report entered by us
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
About membership
What's included in a Healthmatters membership
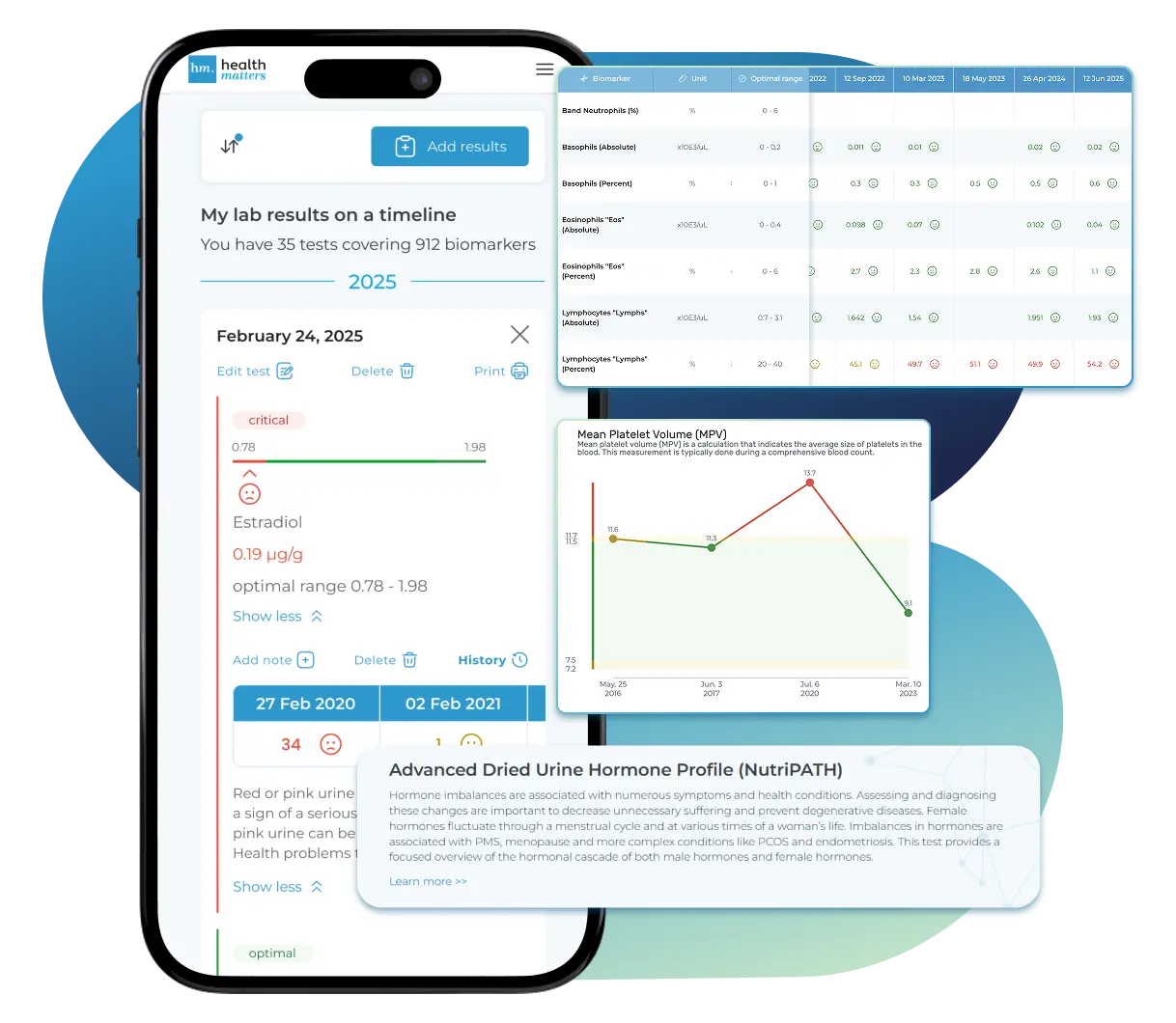
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
 Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Let Your Lab Results Tell the Full Story
Once your results are in one place, see the bigger picture — track trends over time, compare data side by side, export your full history, and share securely with anyone you trust.





Bring all your results together to compare, track progress, export your history, and share securely.
What Healthmatters Members Are Saying
Frequently asked questions
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
- Individuals who want to track and understand their health over time.
- Health professionals, such as doctors, nutritionists, and wellness coaches, need to manage and interpret lab data for their clients.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
- Upload lab reports from any lab
- View your data in interactive graphs, tables, and timelines
- Track trends and monitor changes over time
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export and share your full lab history
- Access your results anytime, from any device
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 10000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
- The GI Effects® Comprehensive Stool Profile,
- GI-MAP,
- The NutrEval FMV®,
- The ION Profile,
- Amino Acids Profile,
- Dried Urine Test for Comprehensive Hormones (DUTCH),
- Organic Acids Test,
- Organix Comprehensive Profile,
- Toxic Metals,
- Complete Blood Count (CBC),
- Metabolic panel,
- Thyroid panel,
- Lipid Panel,
- Urinalysis,
- And many, many more.
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
We implement proven measures to keep your data safe.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
















