Other names for this Glucose test marker:
Random blood sugar; Blood sugar level; Fasting blood sugar; Glucose test; Diabetic screening - blood sugar test; Diabetes - blood sugar test
What is Glucose?
A blood sugar test measures the amount of a sugar called glucose in a sample of your blood. Glucose (also known as blood sugar) is a major source of energy for most cells of the body, including brain cells. Glucose is a building block for carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are found in fruit, cereal, bread, pasta, and rice. Carbohydrates are quickly turned into glucose in your body. This can raise your blood glucose level. A hormone called insulin helps move glucose from your bloodstream into your cells. Elevated fasting blood glucose is often a sign of Type 2 diabetes. Very high glucose levels, whether fasting or not, usually indicate Type 1 diabetes.
Glucose is often part of a regular blood test called the comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP).
Do I need to fast for a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP)?
In order to prepare, you’ll likely need to avoid eating or drinking (fast) for 10 to 12 hours before your comprehensive metabolic panel blood test so that the glucose reflects a fasting sample, instead of sugars from food you’ve eaten. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions when they order the test for you.
What is the Glucose test checking for?
The glucose test checks your blood sugar levels -- abnormally high or low glucose levels could indicate a range of issues.
Sugar is an important energy source for the body but high or uncontrolled blood sugar can cause damage.
Normally, your blood glucose levels increase slightly after you eat. This increase causes your pancreas to release insulin so that your blood glucose levels do not get too high. Blood glucose levels that remain high over time can damage your eyes, kidneys, nerves, and blood vessels.
Blood glucose tests are done to:
- Check for prediabetes and diabetes.
- Monitor treatment of diabetes.
- Check for diabetes that occurs during pregnancy (gestational diabetes).
- Determine if an abnormally low blood sugar level (hypoglycemia) is present. A test to measure blood levels of insulin and a protein called C-peptide may be done along with a blood glucose test to determine the cause of hypoglycemia.
More info on your Glucose results:
Glucose levels in a blood sample taken from your vein (called a blood plasma value) may differ a little from glucose levels checked with a finger stick. Each lab has a different range for what is normal. Your lab report should show the range that your lab uses for each test. The normal range is just a guide. Your doctor will also look at your results based on your age, health, and other factors. A value that isn't in the normal range may still be normal for you. Too much or too little glucose in the blood can be a sign of a serious medical condition. High blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia) may be a sign of diabetes, a disorder that can cause serious, long-term health conditions.
High blood sugar may also be caused by other conditions that can affect insulin or glucose levels in your blood, such as problems with your pancreas or adrenal glands.
Low blood glucose levels (hypoglycemia) are common among people with type 1 diabetes and people with type 2 diabetes who take certain diabetes medicines. Certain conditions, such as liver disease, may cause low levels of blood glucose in people without diabetes, but this is uncommon. Without treatment, severe low blood sugar can lead to major health problems, including seizures and brain damage.
Diabetes and Blood Sugar:
Diabetes is a serious disease in which your body has trouble controlling the level of sugar in your blood (also called "glucose"). Good control of blood sugar and other self-management actions can help slow or stop this damage from happening.
You're more likely to develop diabetes if you:
- Are overweight or have obesity
- Are age 45 or older
- Have a family history of diabetes
- Have high blood pressure
- Don't exercise enough
- Have a history of heart disease or stroke
- Have had gestational diabetes (diabetes that happens only during pregnancy)
- If you are pregnant, you will likely get a blood glucose test between the 24th and 28th week of your pregnancy to check for gestational diabetes.
What is a normal Glucose level?
If you had a fasting blood glucose test, a level between 70 and 100 mg/dL (3.9 and 5.6 mmol/L) is considered normal.
If you had a random blood glucose test, a normal result depends on when you last ate. Most of the time, the blood glucose level will be 125 mg/dL (6.9 mmol/L) or lower.
There are various types of Glucose tests:
There are several different types of blood glucose tests.
Fasting blood sugar (FBS) measures blood glucose after you have not eaten for at least 8 hours. It is often the first test done to check for prediabetes and diabetes.
Random blood sugar (RBS) measures blood glucose regardless of when you last ate. Several random measurements may be taken throughout the day. Random testing is useful because glucose levels in healthy people do not vary widely throughout the day. Blood glucose levels that vary widely may mean a problem. This test is also called a casual blood glucose test.
A 2-hour postprandial blood sugar test measures blood sugar exactly 2 hours after you start eating a meal. This test is most often done at home when you have diabetes. It can see if you are taking the right amount of insulin with meals.
The hemoglobin A1c test and the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) are other tests used to look at blood sugar levels. The A1c test can be used to estimate your average blood sugar level over the past 2 to 3 months. The OGTT is commonly used to diagnose diabetes that occurs during pregnancy (gestational diabetes).
What are symptoms of high blood glucose levels?
Symptoms of high blood glucose levels include:
- Increased thirst and urination (peeing)
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue
- Sores that do not heal
- Weight loss when you're not trying to lose weight
- Numbness or tingling in your feet or hands
- Symptoms of low blood glucose levels include:
- Feeling shaky or jittery
- Hunger
- Fatigue
- Feeling dizzy, confused, or irritable
- Headache
- A fast heartbeat or arrhythmia (a problem with the rate or rhythm of your heartbeat)
- Having trouble seeing or speaking clearly
- Fainting or seizures
If you or your child have these symptoms in addition to vomiting, deep labored breathing and/or confusion, go to the nearest emergency room as soon as possible. You may have diabetes-related ketoacidosis, which is a life-threatening condition.
What are symptoms of low blood glucose levels?
Symptoms of low blood sugar include:
- Shaking or trembling.
- Sweating and chills.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Faster heart rate.
- Intense hunger.
- Anxiousness or irritability.
You need to consume carbohydrates (sugar) to treat hypoglycemia, such as a banana or apple juice. Severe hypoglycemia can be life-threatening.
References:
American Diabetes Association: American Diabetes Association; c1995–2022. The Big Picture: Checking Your Blood Sugar https://www.diabetes.org/healthy-living/medication-treatments/blood-glucose-testing-and-control/checking-your-blood-sugar
American Diabetes Association: American Diabetes Association; c1995–2022. Gestational Diabetes; https://www.diabetes.org/diabetes/gestational-diabetes
American Pregnancy Association: American Pregnancy Association; c2021. Glucose Tolerance Test; http://americanpregnancy.org/prenatal-testing/glucose-tolerence-test/
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Basics About Diabetes; https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/diabetes.html
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Monitoring Your Blood Sugar; https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/managing/managing-blood-sugar/bloodglucosemonitoring.html
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) regarding Assisted Blood Glucose Monitoring and Insulin Administration; https://www.cdc.gov/injectionsafety/providers/blood-glucose-monitoring_faqs.html
FDA: US Food and Drug Administration US Department of Health and Human Services; FDA expands indication for continuous glucose monitoring system, first to replace fingerstick testing for diabetes treatment decisions; 2016 Dec 20 https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-expands-indication-continuous-glucose-monitoring-system-first-replace-fingerstick-testing
Godinjak A, Iglica A, Burekovic A, Jusufovic S, Ajanovic A, Tancica I, Kukuljac A. Hyperglycemia in Critically Ill Patients: Management and Prognosis. Med Arch. 2015 Jun https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26261382/
Hinkle J, Cheever K. Brunner & Suddarth's Handbook of Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests. 2nd Ed, Kindle. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; c2014. Glucose Monitoring; 317 p.
Mathew P, Thoppil D. Hypoglycemia. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534841/
Mathew TK, Tadi P. Blood Glucose Monitoring. StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555976/
National Library of Medicine. Blood Glucose Test. (https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/blood-glucose-test/)
What does it mean if your GLUCOSE (FASTING) result is too high?
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, can present with symptoms such as:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing wounds / infections
An elevated blood glucose test score indicates that you have a type of diabetes or are at risk for developing one. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and teenagers whose bodies aren’t able to produce enough insulin. It’s a chronic condition that requires continuous treatment. Type 2 diabetes is usually diagnosed in overweight and obese adults. The impact of type 2 diabetes may be reduced through weight loss and healthy eating. Pre-diabetes happens when you’re at increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes.
Gestational diabetes occurs if you develop diabetes while you’re pregnant; it typically goes away after the pregnancy ends. Typically, a pregnant woman will be screened for gestational diabetes between their 24th and 28th week of pregnancy, unless they have already begun displaying symptoms. A woman may be tested earlier if she is at risk for type 2 diabetes. When a woman has type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes, her healthcare practitioner will usually order glucose levels throughout her pregnancy and after delivery to monitor her condition.
Hyperthyroidism, kidney problems, pancreatitis, and pancreatic cancer are also known to cause high blood glucose levels.
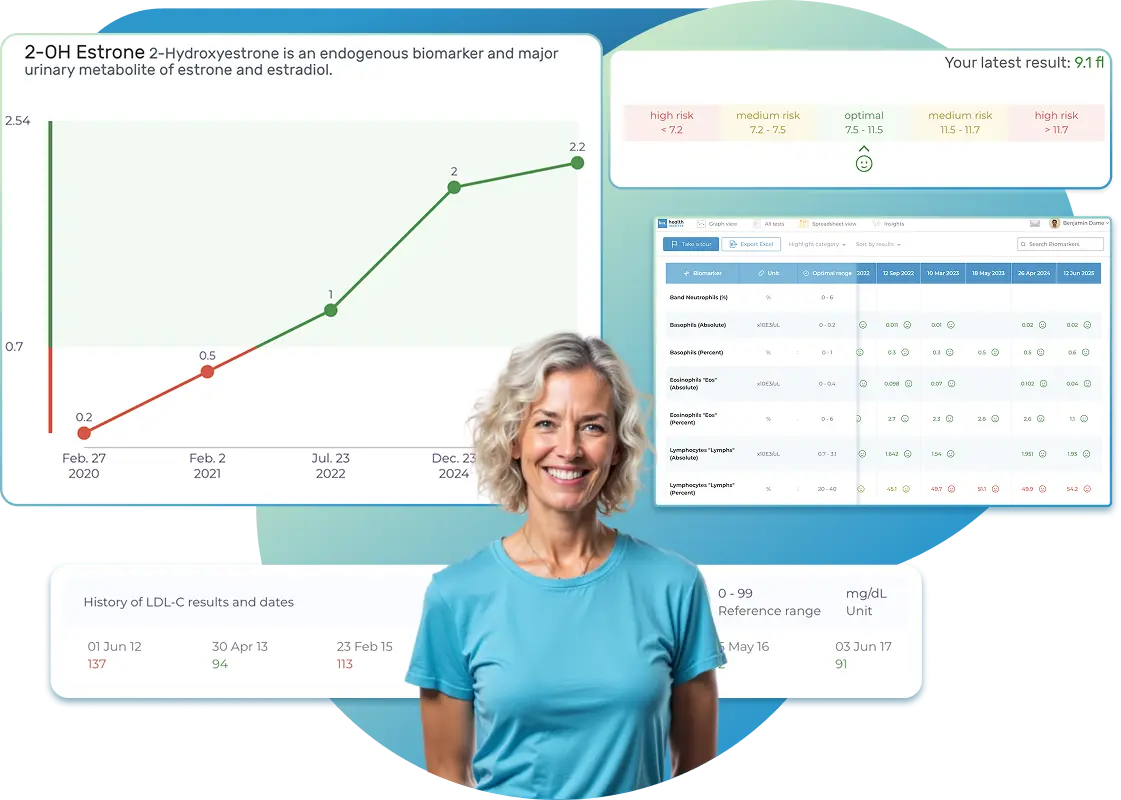
All Your Lab Results.
One Simple Dashboard.
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results Easily
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
What does it mean if your GLUCOSE (FASTING) result is too low?
Blood sugar levels change often during the day. When they drop below 70 mg/dL, this is called having low blood sugar. At this level, you need to take action to bring it back up. Low blood sugar is especially common in people with type 1 diabetes.
Identifying low blood sugar:
Knowing how to identify low blood sugar is important because it can be dangerous if left untreated.
What are the causes of low blood sugar?
There are many reasons why you may have low blood sugar, including:
- Taking too much insulin.
- Not eating enough carbs for how much insulin you take.
- Timing of when you take your insulin.
- The amount and timing of physical activity.
- Drinking alcohol.
- How much fat, protein, and fiber are in your meal.
- Hot and humid weather.
- Unexpected changes in your schedule.
- Spending time at a high altitude.
- Going through puberty.
- Menstruation.
What are symptoms of low blood sugar?
How you react to low blood sugar may not be the same as how someone else with low blood sugar reacts. It’s important to know your signs.
Common symptoms may include:
- Fast heartbeat
- Shaking
- Sweating
- Nervousness or anxiety
- Irritability or confusion
- Dizziness
- Hunger
- Hypoglycemia Unawareness
What is hypoglycemia unawareness?
You may not have any symptoms when your blood sugar is low (hypoglycemia unawareness). If you don’t have symptoms, it will be harder to treat your low blood sugar early. This increases your risk of having severe lows and can be dangerous. This is more likely to happen if you:
- Have had diabetes for more than 5-10 years.
- Frequently have low blood sugar.
- Take certain medicines, such as beta blockers for high blood pressure.
If you meet one or more of the above and you have hypoglycemia unawareness, you may need to check your blood sugar more often to see if it’s low. This is very important to do before driving or being physically active.
What are the different types of low blood sugar?
Hypoglycemia is a condition caused by low blood glucose (blood sugar) levels. Glucose is the main way your body gets energy. The condition is most common in people with diabetes who have issues with medicine, food, or exercise. But sometimes people who don't have diabetes can also get low blood glucose.
There are two kinds of nondiabetic hypoglycemia:
Reactive hypoglycemia, which happens a few hours after you eat a meal
Fasting hypoglycemia, which might be linked to medicine or a disease
What Causes Reactive Hypoglycemia?
Reactive hypoglycemia comes from having too much insulin in your blood. It usually happens within a few hours after you eat. Other possible causes include:
- Having prediabetes or being more likely to have diabetes
- Stomach surgery
- Rare enzyme defects
- What Causes Fasting Hypoglycemia?
Fasting hypoglycemia can have several causes:
- Medicines, such as aspirin and sulfa drugs
- Too much alcohol use
- Diseases of the liver, kidney, heart, and pancreas
- Low levels of some hormones
- Certain tumors
Here are a few other types of low blood sugar:
Nighttime low blood sugar:
While low blood sugar can happen at any time during the day, some people may experience low blood sugar while they sleep. Reasons this may happen include:
- Having an active day.
- Being physically active close to bedtime.
- Taking too much insulin.
- Drinking alcohol at night.
Eating regular meals and not skipping them can help you avoid nighttime low blood sugar. Eating when you drink alcohol can also help. If you think you’re at risk for low blood sugar overnight, have a snack before bed.
You may wake up when you have low blood sugar, but you shouldn’t rely on that. A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) can alert you with an alarm if your blood sugar gets low while you’re sleeping.
Severe low blood sugar:
As your low blood sugar gets worse, you may experience more serious symptoms, including:
- Feeling weak.
- Having difficulty walking or seeing clearly.
- Acting strange or feeling confused.
- Having seizures.
Severe low blood sugar is below 54 mg/dL. Blood sugar this low may make you faint (pass out). Often, you’ll need someone to help you treat severe low blood sugar.
People with diabetes may experience low blood sugar as often as once or twice a week, even when managing their blood sugar closely. Knowing how to identify and treat it is important for your health.
How to treat low blood sugar (Hypoglycemia):
Keeping your blood sugar levels on target as much as possible can help prevent or delay long-term, serious health problems. While this is important, closely managing your blood sugar levels also increases your chance for low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL is considered low. If you think you have low blood sugar, check it. If you aren’t able to check it, go ahead and treat it.
Untreated low blood sugar can be dangerous, so it’s important to know what to do about it and to treat it immediately.
The 15-15 Rule:
For low blood sugar between 55-69 mg/dL, raise it by following the 15-15 rule: have 15 grams of carbs and check your blood sugar after 15 minutes. If it’s still below your target range, have another serving. Repeat these steps until it’s in your target range. Once it’s in range, eat a nutritious meal or snack to ensure it doesn’t get too low again.
Tips to keep in mind:
It takes time for blood sugar to rise after eating. Give some time for treatment to work. Following the 15-15 rule helps.
Young children usually need less than 15 grams of carbs, especially infants and toddlers. Ask your doctor how much your child needs.
Check your blood sugar often when lows are more likely, such as when the weather is hot or when you travel.
Hypoglycemia Prevention:
If you have diabetes, you can make some more easy changes to help keep your blood sugar steady:
- Eat at least three evenly spaced meals each day with between-meal snacks as prescribed.
- Exercise 30 minutes to 1 hour after meals. Check your sugars before and after exercise, and discuss with your doctor what types of changes you can make.
- Double-check your insulin and dose of diabetes medicine before taking it.
- If you drink alcohol, be moderate and monitor your blood sugar levels.
- Know when your medicine is at its peak level.
- Test your blood sugar as directed by your doctor.
- Carry an identification bracelet that says you have diabetes.
If you don’t have diabetes, ask your doctor if you need to adjust what you eat or how much you exercise. Diet changes like these might help:
- Eat small meals and snacks every few hours.
- Include a broad variety of foods, including protein, fatty, and high-fiber foods.
- Don't eat a lot of high-sugar foods.
- Work with your doctor to figure out anything else that may be causing your symptoms.
Laboratories
Bring All Your Lab Results Together — In One Place
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.
Pricing Table
Gather Your Lab History — and Finally Make Sense of It
Finally, Your Lab Results Organized and Clear
Personal plans
$79/ year
Advanced Plan
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 5 reports entered for you
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
$250/ once
Unlimited Account
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 10 reports entered for you
- No subscriptions. No extra fees.
$45/ month
Pro Monthly
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track lab results for multiple clients
- Customize reference ranges per client
- Export lab histories and reports
- Begin with first report entered by us
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
About membership
What's included in a Healthmatters membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
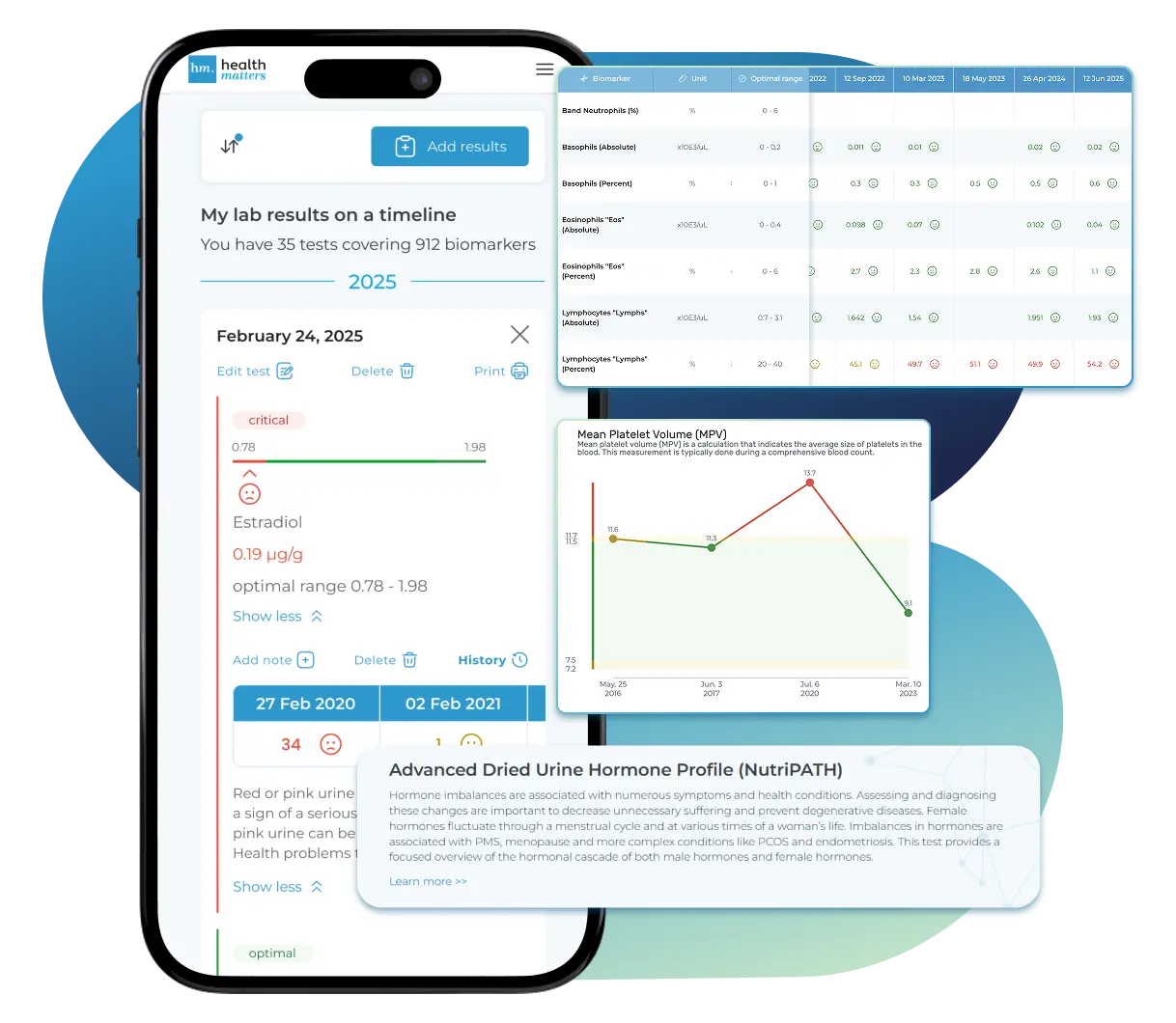
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
 Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Let Your Lab Results Tell the Full Story
Once your results are in one place, see the bigger picture — track trends over time, compare data side by side, export your full history, and share securely with anyone you trust.





Bring all your results together to compare, track progress, export your history, and share securely.
What Healthmatters Members Are Saying
Frequently asked questions
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
- Individuals who want to track and understand their health over time.
- Health professionals, such as doctors, nutritionists, and wellness coaches, need to manage and interpret lab data for their clients.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
- Upload lab reports from any lab
- View your data in interactive graphs, tables, and timelines
- Track trends and monitor changes over time
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export and share your full lab history
- Access your results anytime, from any device
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 10000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
- The GI Effects® Comprehensive Stool Profile,
- GI-MAP,
- The NutrEval FMV®,
- The ION Profile,
- Amino Acids Profile,
- Dried Urine Test for Comprehensive Hormones (DUTCH),
- Organic Acids Test,
- Organix Comprehensive Profile,
- Toxic Metals,
- Complete Blood Count (CBC),
- Metabolic panel,
- Thyroid panel,
- Lipid Panel,
- Urinalysis,
- And many, many more.
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
We implement proven measures to keep your data safe.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
















