Ghrelin (Total)
Other names: Ghrelin Total, Plasma
Ghrelin (Total), Plasma: A Key Biomarker in Energy Regulation and Metabolism
Ghrelin, often referred to as the "hunger hormone," is a peptide produced primarily in the stomach and plays a crucial role in regulating appetite, energy balance, and metabolism. The biomarker "Ghrelin (Total), Plasma" measures the total concentration of ghrelin in the bloodstream, including both its active and inactive forms. Total ghrelin levels are of interest in various clinical and research settings, as fluctuations in these levels have been linked to a range of physiological processes, including food intake, growth hormone release, and glucose metabolism.
The active form of ghrelin binds to receptors in the hypothalamus, stimulating appetite and promoting food consumption. It also signals the pituitary gland to release growth hormone, which influences fat storage and muscle development. However, total ghrelin includes both this active form and the unacylated or inactive form, which lacks the ability to bind to ghrelin receptors but may have other metabolic effects. Measuring total ghrelin provides a more comprehensive understanding of the hormone’s overall role in the body.
In clinical practice, ghrelin levels are often examined in the context of metabolic disorders such as obesity, diabetes, and cachexia. For instance, patients with obesity tend to have lower baseline levels of ghrelin, which may contribute to impaired appetite regulation, while those suffering from cachexia or anorexia nervosa may have elevated ghrelin levels as the body attempts to stimulate food intake. Thus, understanding ghrelin dynamics through plasma measurements can offer insights into disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets.
Additionally, ghrelin is involved in the regulation of energy homeostasis beyond just hunger control. It influences glucose metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and fat distribution. Researchers are exploring its role in conditions such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. With advancements in biomarker analysis, measuring total ghrelin in plasma is becoming increasingly valuable for developing personalized treatments that address metabolic imbalances and improve overall health outcomes.
Normal reference ranges:
The normal reference range for total ghrelin levels in plasma can vary depending on factors such as age, gender, body mass index (BMI), and specific laboratory methods. However, general reference ranges for total ghrelin are typically reported as follows:
Healthy adults: 100–1,200 pg/mL
Fasting state: Ghrelin levels tend to be higher in fasting individuals, often ranging from 500 to 2,500 pg/mL, as ghrelin stimulates hunger and prepares the body for food intake.
Postprandial state: After eating, ghrelin levels typically drop and can range from 100 to 900 pg/mL.
It's important to note that these ranges can vary slightly based on the assay method and population being studied. Additionally, specific ranges should be interpreted by healthcare professionals in the context of individual health conditions.
References:
Kojima, M., Hosoda, H., Date, Y., Nakazato, M., Matsuo, H., & Kangawa, K. (1999). Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature, 402(6762), 656-660. https://doi.org/10.1038/45230
Müller, T. D., Nogueiras, R., Andermann, M. L., Andrews, Z. B., Anker, S. D., Argente, J., ... & Tschöp, M. H. (2015). Ghrelin. Molecular Metabolism, 4(6), 437-460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2015.03.005
Sangiao-Alvarellos, S., & Cordido, F. (2010). Effect of ghrelin on glucose-insulin homeostasis: Therapeutic implications. International Journal of Peptides, 2010, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/234709
Khatib, M. N., Gaidhane, A. M., Gaidhane, S., Simkhada, P., & Zahiruddin, Q. S. (2014). Ghrelin: Ghrelin as a regulatory Peptide in growth hormone secretion. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research, 8(8), MC13-MC16. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2014/10711.4765
What does it mean if your Ghrelin (Total) result is too high?
Elevated levels of total ghrelin in plasma can signify several physiological and pathological conditions. Ghrelin, being the "hunger hormone," plays a critical role in stimulating appetite, so abnormal increases in its levels are often linked to energy imbalance or metabolic disorders. Here are some key conditions associated with elevated ghrelin levels:
-
Anorexia Nervosa and Cachexia: In individuals with anorexia nervosa or cachexia (a condition characterized by severe weight loss and muscle wasting, often due to chronic illness), elevated ghrelin levels are common. The body increases ghrelin production in response to low energy stores in an attempt to stimulate appetite and encourage food intake.
-
Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS): This genetic disorder is characterized by chronic overeating (hyperphagia), and individuals with PWS often have significantly elevated ghrelin levels. The elevated ghrelin levels contribute to their uncontrollable hunger and can lead to obesity if not carefully managed.
-
Fasting and Starvation: During periods of prolonged fasting or starvation, ghrelin levels naturally rise as part of the body’s effort to increase food-seeking behavior and restore energy balance. This is a normal physiological response to hunger.
-
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Elevated ghrelin levels have been observed in certain gastrointestinal conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and some forms of functional dyspepsia. The exact mechanism is not fully understood, but it may relate to disruptions in gut-brain signaling.
-
Hypoglycemia: Low blood sugar levels can also trigger an increase in ghrelin, as the body attempts to stimulate food intake and restore glucose levels. In this context, elevated ghrelin may reflect the body's adaptive response to hypoglycemia.
Elevated ghrelin levels are typically a signal that the body is seeking to correct an energy deficit or respond to altered metabolic conditions. However, persistent high levels may indicate underlying disorders that require further investigation.
Lowering ghrelin levels, particularly if elevated ghrelin is contributing to increased hunger or metabolic issues, can be approached through lifestyle and dietary modifications. Here are several effective ways to naturally lower ghrelin levels:
1. Eat More Protein
High-protein foods help suppress ghrelin production, keeping you feeling fuller for longer. Protein slows down the release of ghrelin compared to carbohydrates or fats. Adding more lean proteins like chicken, fish, eggs, and plant-based proteins like beans and legumes to your diet can help reduce hunger signals and decrease ghrelin levels.
2. Get Adequate Sleep
Sleep deprivation is associated with increased ghrelin levels, which can make you feel hungrier throughout the day. Studies have shown that getting 7-8 hours of quality sleep per night can help balance ghrelin and leptin (another hunger-regulating hormone), reducing the likelihood of overeating and curbing hunger.
3. Eat Fiber-Rich Foods
Dietary fiber helps promote satiety by slowing digestion and lowering ghrelin levels. Consuming fiber-rich foods like whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes can help suppress the hormone and keep you feeling full longer after meals.
4. Consume Healthy Fats
Incorporating healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, into your diet can reduce ghrelin levels and promote feelings of fullness. These fats take longer to digest and can slow down the release of ghrelin, helping control hunger throughout the day.
5. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can elevate ghrelin levels and trigger emotional eating. Practices like mindfulness, meditation, regular physical activity, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress, which may, in turn, help regulate ghrelin levels and reduce cravings.
6. Eat Small, Frequent Meals
Eating smaller, balanced meals more frequently can help stabilize ghrelin levels and prevent the hormone from spiking. This approach keeps hunger in check and avoids the extremes of fasting, which can significantly elevate ghrelin levels.
7. Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water throughout the day can help reduce hunger and control ghrelin production. Sometimes, dehydration can be mistaken for hunger, leading to unnecessary eating. Staying hydrated helps maintain normal hormone levels, including ghrelin.
Important note: By incorporating these lifestyle changes, you can effectively lower ghrelin levels, reduce hunger, and support healthy weight management. However, if elevated ghrelin levels are due to an underlying health condition, it's important to consult a healthcare professional for tailored advice.
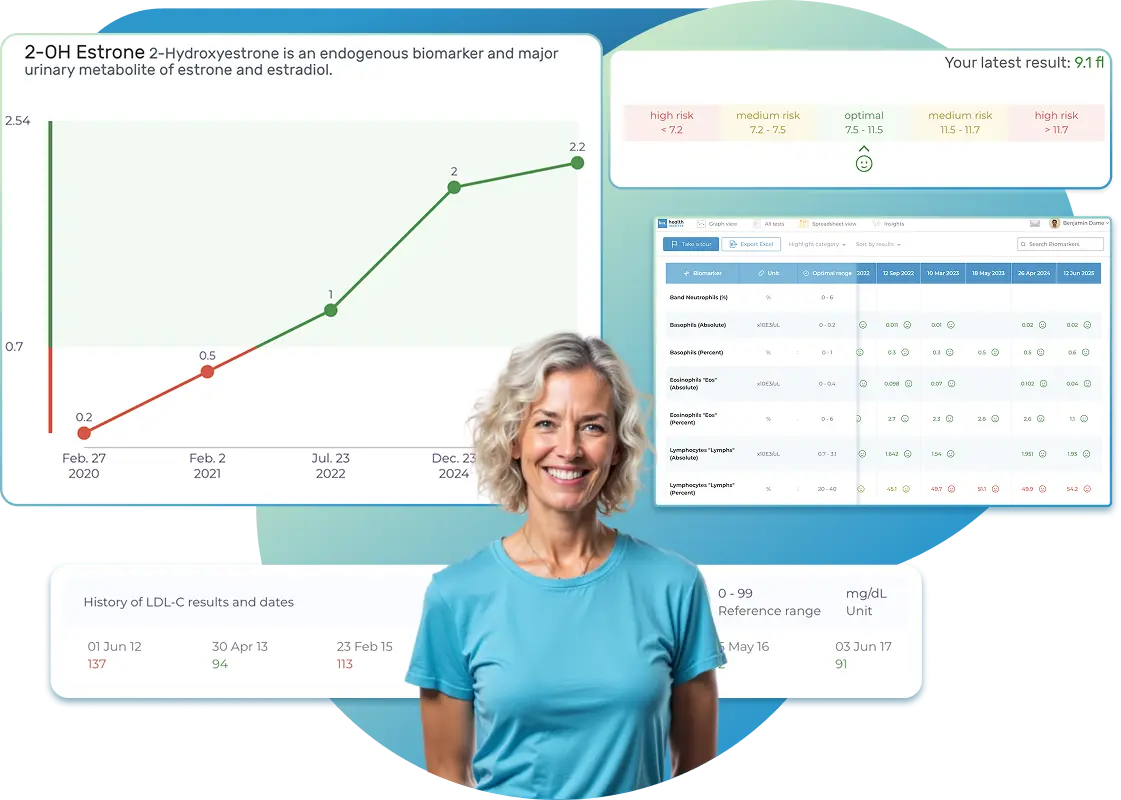
All Your Lab Results.
One Simple Dashboard.
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results Easily
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
Laboratories
Bring All Your Lab Results Together — In One Place
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.
Pricing Table
Gather Your Lab History — and Finally Make Sense of It
Finally, Your Lab Results Organized and Clear
Personal plans
$79/ year
Advanced Plan
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 5 reports entered for you
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
$250/ once
Unlimited Account
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 10 reports entered for you
- No subscriptions. No extra fees.
$45/ month
Pro Monthly
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track lab results for multiple clients
- Customize reference ranges per client
- Export lab histories and reports
- Begin with first report entered by us
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
About membership
What's included in a Healthmatters membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
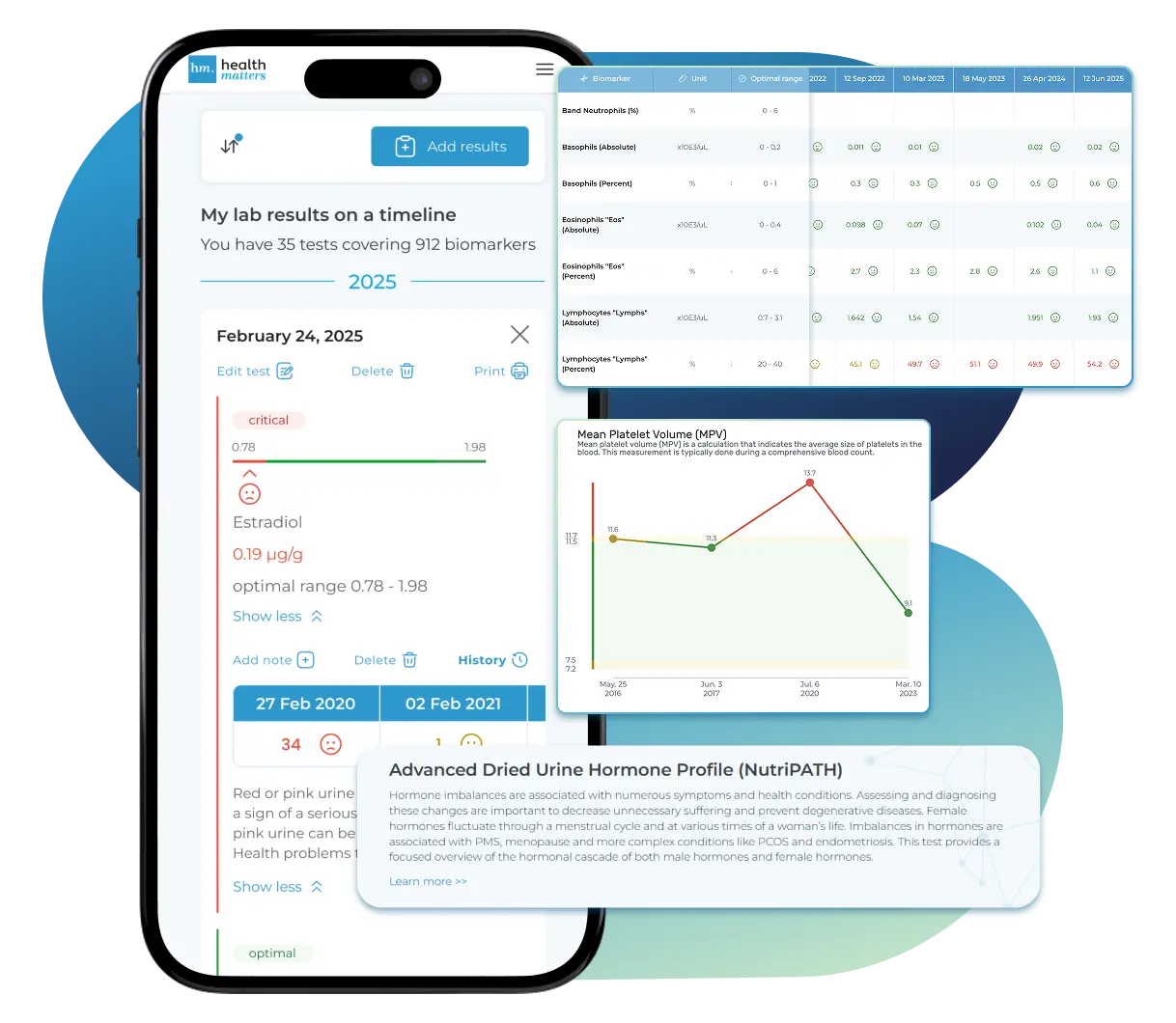
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
 Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Let Your Lab Results Tell the Full Story
Once your results are in one place, see the bigger picture — track trends over time, compare data side by side, export your full history, and share securely with anyone you trust.





Bring all your results together to compare, track progress, export your history, and share securely.
What Healthmatters Members Are Saying
Frequently asked questions
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
- Individuals who want to track and understand their health over time.
- Health professionals, such as doctors, nutritionists, and wellness coaches, need to manage and interpret lab data for their clients.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
- Upload lab reports from any lab
- View your data in interactive graphs, tables, and timelines
- Track trends and monitor changes over time
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export and share your full lab history
- Access your results anytime, from any device
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 10000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
- The GI Effects® Comprehensive Stool Profile,
- GI-MAP,
- The NutrEval FMV®,
- The ION Profile,
- Amino Acids Profile,
- Dried Urine Test for Comprehensive Hormones (DUTCH),
- Organic Acids Test,
- Organix Comprehensive Profile,
- Toxic Metals,
- Complete Blood Count (CBC),
- Metabolic panel,
- Thyroid panel,
- Lipid Panel,
- Urinalysis,
- And many, many more.
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
We implement proven measures to keep your data safe.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
















