Ferritin
Other names: Ferritin, Serum
Understanding Ferritin and Iron in Your Body
Iron is a crucial element for our health, playing a vital role in oxygen transport throughout our body. Ferritin, a key protein in this process, acts as the body's iron storage system. Let's explore its importance and how it's measured.
The Role of Iron and Ferritin
Our bodies rely on iron in red blood cells to carry oxygen everywhere. Without enough iron, our red blood cells are unable to efficiently supply oxygen, potentially leading to a condition called anemia. Anemia can cause fatigue, weakness, and other health issues.Ferritin is a blood cell protein that holds iron and releases it in controlled intervals. It is produced by every cell in the body but is found most commonly in the liver, spleen, skeletal muscles, and bone marrow.
Ferritin Blood Tests
A ferritin blood test checks the amount of ferritin in the blood, which indicates how much iron is stored in your body. A healthcare professional might order a ferritin blood test to:
- Find the cause of anemia, especially iron deficiency anemia
- Detect inflammation in the body
- Diagnose iron overload conditions like hemochromatosis
- Monitor the effectiveness of iron treatments (whether to raise or lower iron levels)
Normal Ferritin Ranges
Ferritin levels are measured in nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL). Normal ranges vary by age and gender:
| Age/Gender | Normal Range (ng/mL) |
|---|---|
| 0-1 month | 25-200 |
| 1-2 months | 200-600 |
| 2-5 months | 50-200 |
| 6 months - 14 years | 10-140 |
| Adult male | 24-336 |
| Adult female | 11-307 |
Health Implications
Low ferritin levels may indicate iron deficiency, which can lead to anemia. Symptoms might include fatigue, weakness, and pale skin. High ferritin levels could suggest iron overload, inflammation, or liver disease. Symptoms of iron overload may include joint pain, fatigue, and skin discoloration.By understanding ferritin and its role in iron storage, you can better monitor your health and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
What does it mean if your Ferritin result is too high?
Hemochromatosis, a large buildup of iron in the body, can cause a very high ferritin blood level. In individuals with hereditary hemochromatosis, the daily absorption of iron from the intestines is greater than the amount needed to replace losses. Since the normal body cannot increase iron excretion, the absorbed iron accumulates in the body.
The excess iron deposits in the joints, liver, testicles, and heart, which causes damage to these organs and results in signs and symptoms of hemochromatosis. Some other diseases like alcoholism, thalassemia, and some types of anemia that cause red blood cells to be destroyed can also lead to hemochromatosis.
High ferritin levels may also be caused by Hodgkin’s disease, leukemia, infection, inflammatory conditions (such as arthritis or lupus), or a diet that is too high in iron. Symptoms of iron overload may include:
- Joint pain
- Fatigue / weakness
- Weight loss
- Lack of energy
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of sex drive
- Loss of body hair
- Heart problems such as congestive heart failure
-----------------------
Elevated ferritin levels, when all other iron markers (such as serum iron, total iron-binding capacity (TIBC), and transferrin saturation) are normal, can indicate several possible conditions. Ferritin is a protein that stores iron, and its levels can be influenced by factors other than iron status. Some possible reasons for elevated ferritin levels include:
-
Inflammation or Infection: Ferritin is an acute-phase reactant, meaning its levels can increase in response to inflammation or infection. Conditions such as chronic inflammatory diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis) or acute infections can raise ferritin levels.
-
Liver Disease: Liver diseases, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, or fatty liver disease, can lead to elevated ferritin levels because the liver plays a key role in storing and regulating iron.
-
Malignancy: Certain cancers, particularly hematologic malignancies (like leukemia and lymphoma) and solid tumors, can cause elevated ferritin levels.
-
Chronic Kidney Disease: Ferritin levels can be elevated in chronic kidney disease due to decreased clearance and increased inflammation.
-
Metabolic Syndrome: Conditions associated with metabolic syndrome, such as obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes, can be linked to elevated ferritin levels.
-
Hemochromatosis: While typically associated with elevated iron markers, early stages or milder forms of hereditary hemochromatosis might present with high ferritin and normal other iron markers.
-
Alcohol Consumption: Chronic heavy alcohol use can cause liver damage, leading to increased ferritin levels.
-
Genetic Factors: Some people may have genetic predispositions to elevated ferritin levels without other iron overload indicators.
If elevated ferritin is detected, it is important for healthcare providers to consider these possibilities and potentially conduct further testing to determine the underlying cause.
What are potential options to decrease elevated Ferritin levels?
There are several potential options to decrease elevated ferritin levels:
1. Dietary changes:
- Follow a low-iron diet, especially for those with hemochromatosis
- Consume foods rich in phytic acid and polyphenols, which can reduce iron absorption (e.g. whole grains, vegetables)
- Increase intake of green tea and coffee, which can inhibit iron absorption
- Increase fiber intake
- Limit alcohol consumption, as it can damage the liver and increase ferritin
2. Adopt a plant-based diet:
- The Low Inflammatory Foods Everyday (LIFE) diet, rich in dark green leafy vegetables, was shown to reduce ferritin levels
3. Phlebotomy (blood removal):
- For those with hemochromatosis, regular phlebotomy is recommended until ferritin falls to around 50 ng/mL
4. Address underlying conditions:
- Treat any inflammatory conditions, liver disease, or metabolic disorders that may be causing elevated ferritin
5. Lifestyle changes:
- Quit smoking, as it's associated with higher ferritin levels
- Manage obesity, as it's a common cause of elevated ferritin
6. Avoid iron supplements and iron-fortified foods unless prescribed by a doctor
7. For mild elevations, observation over time may be appropriate under medical supervision
It's crucial to work with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause of elevated ferritin and develop an appropriate treatment plan. The approach may vary depending on the severity of elevation and any associated conditions.
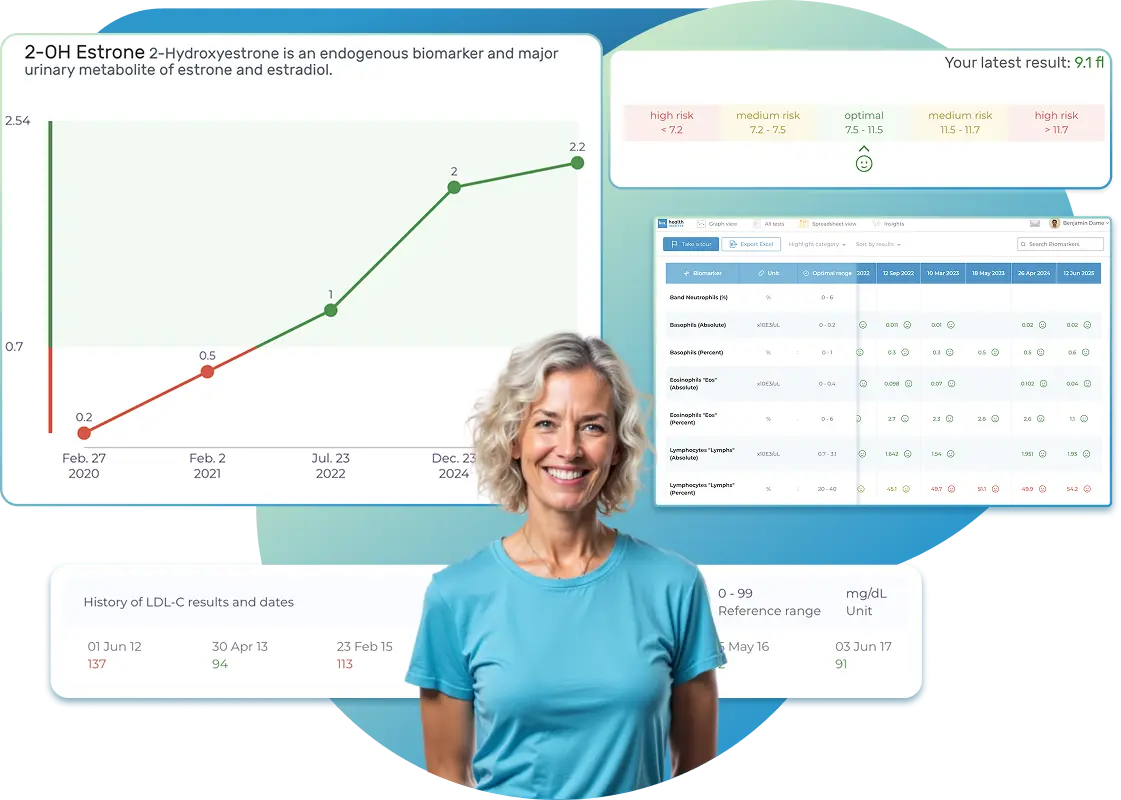
All Your Lab Results.
One Simple Dashboard.
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results Easily
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
What does it mean if your Ferritin result is too low?
Decreased levels of ferritin in the blood signify a reduced amount of iron stored in the body, which can lead to iron deficiency, the most common cause of anemia.
Ferritin acts as a cellular storage protein for iron, so its levels are a good indicator of the body's iron reserves. When these reserves are low, the body struggles to produce enough hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that enables them to carry oxygen. This condition can lead to iron deficiency anemia, characterized by symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, dizziness, and strange cravings for non-nutritive substances like ice or dirt, a condition known as pica.
The diagnosis of iron deficiency involves blood tests that measure ferritin, hemoglobin, and hematocrit levels, along with a complete blood count (CBC).
Causes of decreased ferritin levels include chronic blood loss (from heavy menstrual periods or internal bleeding), a diet insufficient in iron, an inability to absorb iron properly, and certain diseases that affect iron metabolism.
Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying cause of the iron deficiency and may include dietary changes to include more iron-rich foods, iron supplements, and, in some cases, intravenous iron therapy or treatment for conditions causing blood loss. For severe or persistent cases, a healthcare professional might investigate more deeply to rule out or treat underlying conditions contributing to the deficiency.
Laboratories
Bring All Your Lab Results Together — In One Place
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.
Pricing Table
Gather Your Lab History — and Finally Make Sense of It
Finally, Your Lab Results Organized and Clear
Personal plans
$79/ year
Advanced Plan
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 5 reports entered for you
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
$250/ once
Unlimited Account
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 10 reports entered for you
- No subscriptions. No extra fees.
$45/ month
Pro Monthly
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track lab results for multiple clients
- Customize reference ranges per client
- Export lab histories and reports
- Begin with first report entered by us
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
About membership
What's included in a Healthmatters membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
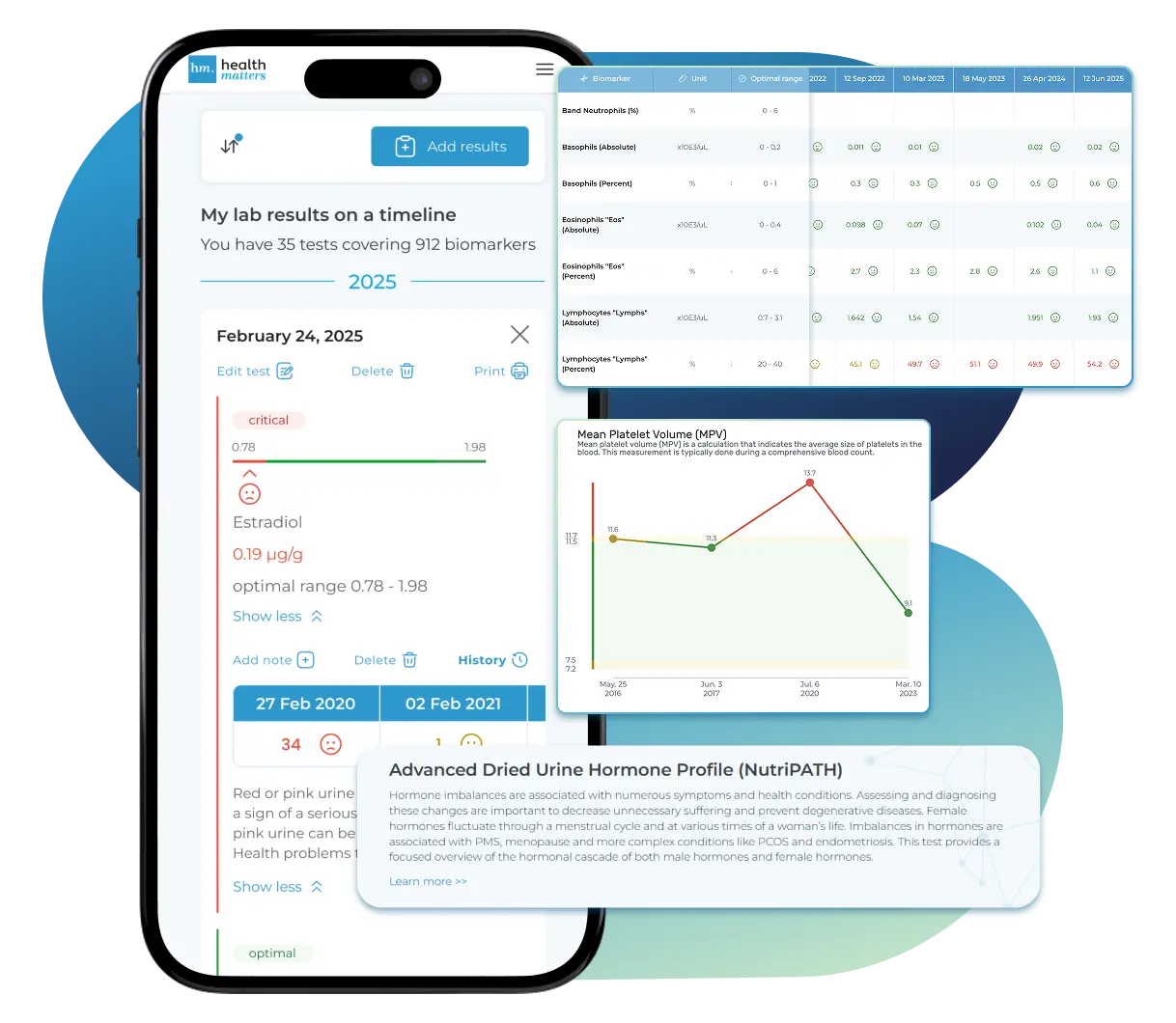
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
 Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Let Your Lab Results Tell the Full Story
Once your results are in one place, see the bigger picture — track trends over time, compare data side by side, export your full history, and share securely with anyone you trust.





Bring all your results together to compare, track progress, export your history, and share securely.
What Healthmatters Members Are Saying
Frequently asked questions
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
- Individuals who want to track and understand their health over time.
- Health professionals, such as doctors, nutritionists, and wellness coaches, need to manage and interpret lab data for their clients.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
- Upload lab reports from any lab
- View your data in interactive graphs, tables, and timelines
- Track trends and monitor changes over time
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export and share your full lab history
- Access your results anytime, from any device
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 10000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
- The GI Effects® Comprehensive Stool Profile,
- GI-MAP,
- The NutrEval FMV®,
- The ION Profile,
- Amino Acids Profile,
- Dried Urine Test for Comprehensive Hormones (DUTCH),
- Organic Acids Test,
- Organix Comprehensive Profile,
- Toxic Metals,
- Complete Blood Count (CBC),
- Metabolic panel,
- Thyroid panel,
- Lipid Panel,
- Urinalysis,
- And many, many more.
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
We implement proven measures to keep your data safe.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
















