Eosinophils "Eos" (Percent)
Other names: % Eosinophils, Eosinophils %
What Are Eosinophils?
Eosinophils are a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) that plays a crucial role in your immune system. They protect your body by defending against parasites, allergens, and harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Although eosinophils make up less than 5% of all white blood cells, they are vital in identifying and responding to infections and inflammatory reactions.
An increase in eosinophil levels may indicate your body is fighting an infection or an allergic reaction, while significantly high levels could suggest a more serious medical condition.
Functions of Eosinophils
Eosinophils contribute to the immune system by:
- Defending against parasitic infections (e.g., worms like hookworms or strongyloides).
- Combating fungal, bacterial, and viral infections.
- Participating in the inflammatory response, particularly in allergies.
- Contributing to conditions such as asthma, eczema, and allergic reactions through their role in inflammation.
When activated, eosinophils release toxic proteins stored in their granules to destroy invading pathogens. However, excessive eosinophil activity can lead to chronic inflammation and tissue damage.
Eosinophils in the Context of White Blood Cells
White blood cells (leukocytes) are essential for immune defense, and eosinophils are one of three types of granulocytes, along with neutrophils and basophils. Eosinophils specialize in preventing the growth of foreign organisms, particularly parasites, within host cells.
Your bone marrow continuously produces all white blood cells, including eosinophils, which circulate in the bloodstream for several hours to days before migrating to tissues.
Eosinophil Count (Absolute)
An eosinophil count is typically included in a complete blood count (CBC) with differential, which provides a breakdown of white blood cell types. Elevated eosinophil levels may indicate:
- Allergic reactions (e.g., asthma, eczema).
- Parasitic infections.
- Certain cancers, such as leukemia or Hodgkin's lymphoma.
- Drug sensitivities.
This test helps doctors assess your immune health and identify underlying conditions.
Why Do You Need an Eosinophil Count?
Your healthcare provider may order an eosinophil count if you are experiencing symptoms such as:
- Diarrhea.
- Itching.
- Fever.
- Rash.
- Runny nose, particularly if linked to allergies.
- Weight loss.
Conditions associated with elevated eosinophils include asthma, drug allergies, autoimmune diseases, and parasitic infections.
Where Are Eosinophils Found?
Eosinophils primarily reside in body tissues rather than circulating in the blood. Common locations include:
- Bone marrow.
- Lungs.
- Skin.
- Stomach and intestines.
- Fat (adipose tissue).
Appearance of Eosinophils
Eosinophils are larger than most white blood cells and are characterized by:
- A two-lobed nucleus, resembling two raindrops connected by a thin strand.
- Granules in the cytoplasm that give a sandy texture under the microscope.
Under staining, eosinophils appear purple or pink, which makes them distinct during lab analysis.
Normal Eosinophil Levels
- Normal range: 0 to 400 cells per microliter (<0.4 × 10x9/L).
- Reference ranges: Often reported as an absolute count or a percentage of white blood cells.
If your levels fall outside this range, further investigation may be needed to determine the underlying cause.
Conclusion
Eosinophils are a critical part of your immune system, playing key roles in fighting infections and regulating inflammation. While their activity helps protect against harmful invaders, excessive eosinophil activity can lead to chronic inflammation or tissue damage. Monitoring eosinophil levels through blood tests provides valuable insights into your immune health and helps diagnose conditions such as allergies, infections, and autoimmune diseases.
References
- Weller PF, et al. Eosinophil biology and causes of eosinophilia. UpToDate.
- McPherson RA, et al. Leukocytic disorders. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome.
- Taylor MR, et al. The expanded spectrum of toxocaral disease. The Lancet.
- National Institutes of Health. Macrophage and Eosinophil Function in Immunity.
What does it mean if your Eosinophils "Eos" (Percent) result is too high?
What Is a High Eosinophil Count?
A high eosinophil count, known as eosinophilia, occurs when the number of eosinophils in your blood exceeds normal levels. Eosinophilia is classified into three severity categories:
- Mild: 500–1,500 eosinophils per microliter (mL) of blood.
- Moderate: 1,500–5,000 eosinophils per mL of blood.
- Severe: More than 5,000 eosinophils per mL of blood.
Severe eosinophilia can become a medical emergency, as untreated cases may lead to organ damage.
What Causes Eosinophilia?
Eosinophilia can result from various medical conditions, including:
- Parasitic infections: Worm infections, such as hookworms or strongyloides.
- Allergic reactions: Seasonal allergies, eczema, or asthma.
- Autoimmune diseases: Lupus, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis.
- Cancers: Hodgkin’s lymphoma, leukemia, and rare cancers like breast, ovarian, or prostate cancer.
- Significant drug reactions: Severe responses to certain medications.
- Organ transplant rejection.
- Adrenal gland deficiency.
- Hypereosinophilic syndromes: A group of disorders characterized by organ damage caused by eosinophilia.
- Other conditions: Scarlet fever, vasculitis, and severe allergic inflammation.
Does a High Eosinophil Count Indicate Cancer?
Although rare, persistently high eosinophil levels can indicate certain types of cancer. Examples include:
- Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
- Breast cancer.
- Cervical cancer.
- Colorectal cancer.
- Ovarian cancer.
- Prostate cancer.
If your healthcare provider suspects cancer, they may recommend further diagnostic tests, such as biopsies, blood panels, or imaging studies, to confirm the cause.
Common Treatments for High Eosinophil Counts
Treatment for eosinophilia depends on its cause and severity. Your healthcare provider may order additional tests to determine an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment. Possible approaches include:
- Treating underlying conditions: Managing the root cause of eosinophilia, such as treating parasitic infections, autoimmune diseases, or cancers.
- Adjusting medications: Stopping or changing medications if they are causing an allergic reaction.
- Avoiding certain foods: For esophagitis, avoiding fatty, spicy, or acidic foods.
- Taking anti-inflammatory medications: To reduce inflammation caused by eosinophilia.
Most conditions associated with high eosinophil counts are chronic and require long-term management.
How Can I Keep My Eosinophils Healthy?
To support healthy eosinophil levels and maintain immune health:
- Avoid allergens: Identify and limit exposure to known triggers.
- Eat a balanced diet: Include nutrient-rich foods to support overall immune health.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can suppress immune function.
- Practice good hygiene: Regular handwashing can reduce the risk of infections.
Conclusion
A high eosinophil count can signal your body’s response to infections, allergies, or more serious conditions like autoimmune diseases or cancer. Identifying and treating the underlying cause is essential to prevent complications. If you experience symptoms or are diagnosed with eosinophilia, consult your healthcare provider for further testing and appropriate management strategies.
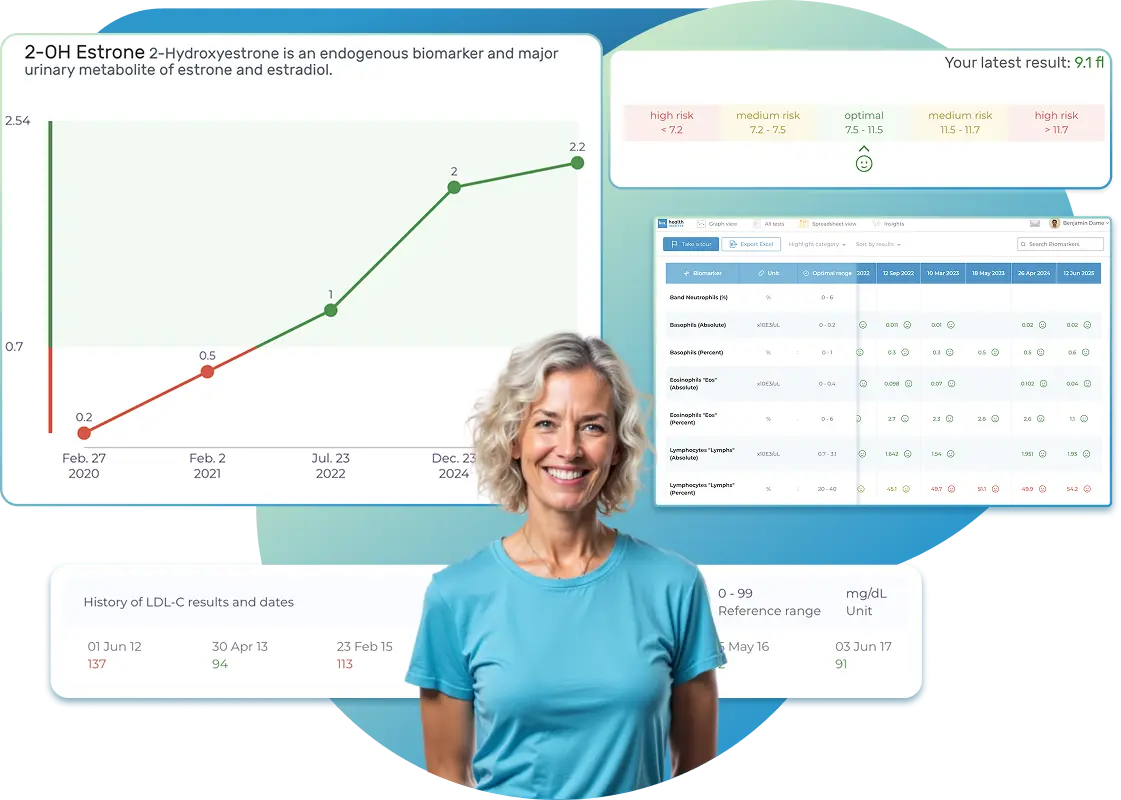
All Your Lab Results.
One Simple Dashboard.
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results Easily
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
What does it mean if your Eosinophils "Eos" (Percent) result is too low?
What Causes Low Eosinophil Levels?
An abnormally low eosinophil count, known as eosinopenia, can occur due to various factors, often related to lifestyle, hormonal changes, or underlying health conditions. In many cases, low eosinophil levels are not a cause for concern unless accompanied by other abnormalities in white blood cell counts.
Common Causes of Low Eosinophil Levels
Alcohol Intoxication
Excessive alcohol consumption can suppress the immune system, reducing eosinophil production and function.
Excess Cortisol Production
High cortisol levels, such as those seen in Cushing's disease, can lower eosinophil counts.
- Cortisol is a natural hormone produced by the adrenal glands that helps the body respond to stress.
- Cushing's syndrome occurs when cortisol levels remain elevated over an extended period, suppressing the immune system and reducing eosinophil levels.
Time of Day
Under normal conditions, eosinophil levels fluctuate throughout the day:
- Lowest in the morning.
- Highest in the evening.
This natural variation is part of the body’s circadian rhythm.
When Are Low Eosinophil Levels Concerning?
In most cases, low eosinophil counts are not a major concern unless they are part of a broader issue, such as:
- Alcohol abuse or suspected Cushing’s disease.
- Abnormally low counts across all types of white blood cells, which may indicate a bone marrow problem.
Potential Treatments for Low Eosinophil Counts
Treatment for low eosinophil levels depends on the underlying cause. Often, eosinopenia resolves on its own as the body compensates through other immune system mechanisms. However, in certain cases:
- Underlying conditions like Cushing’s syndrome or alcohol-related immune suppression may require long-term management.
- Medications that suppress the immune system, such as corticosteroids, may need to be adjusted if they are affecting eosinophil production and function.
Are Low Eosinophils Normal?
Low eosinophil levels are common in healthy adults and are not typically problematic on their own. However, specific conditions or treatments may suppress eosinophil production, such as:
- Corticosteroids and other immune-suppressant medications, which can reduce the production and function of eosinophils.
Conclusion
While eosinophil counts can naturally fluctuate or be temporarily suppressed by factors like alcohol consumption, stress hormones, or certain medications, low levels are rarely a cause for concern unless accompanied by other abnormal white blood cell counts. In cases where low eosinophil levels persist, it’s important to evaluate potential underlying health conditions, such as bone marrow issues or immune suppression, and address them accordingly.
Laboratories
Bring All Your Lab Results Together — In One Place
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.
Pricing Table
Gather Your Lab History — and Finally Make Sense of It
Finally, Your Lab Results Organized and Clear
Personal plans
$79/ year
Advanced Plan
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 5 reports entered for you
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
$250/ once
Unlimited Account
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 10 reports entered for you
- No subscriptions. No extra fees.
$45/ month
Pro Monthly
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track lab results for multiple clients
- Customize reference ranges per client
- Export lab histories and reports
- Begin with first report entered by us
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
About membership
What's included in a Healthmatters membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
 Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Let Your Lab Results Tell the Full Story
Once your results are in one place, see the bigger picture — track trends over time, compare data side by side, export your full history, and share securely with anyone you trust.





Bring all your results together to compare, track progress, export your history, and share securely.
What Healthmatters Members Are Saying
Frequently asked questions
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
- Individuals who want to track and understand their health over time.
- Health professionals, such as doctors, nutritionists, and wellness coaches, need to manage and interpret lab data for their clients.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
- Upload lab reports from any lab
- View your data in interactive graphs, tables, and timelines
- Track trends and monitor changes over time
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export and share your full lab history
- Access your results anytime, from any device
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 10000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
- The GI Effects® Comprehensive Stool Profile,
- GI-MAP,
- The NutrEval FMV®,
- The ION Profile,
- Amino Acids Profile,
- Dried Urine Test for Comprehensive Hormones (DUTCH),
- Organic Acids Test,
- Organix Comprehensive Profile,
- Toxic Metals,
- Complete Blood Count (CBC),
- Metabolic panel,
- Thyroid panel,
- Lipid Panel,
- Urinalysis,
- And many, many more.
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
We implement proven measures to keep your data safe.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
















