DHT, Percent Free Dialysis
Other names: DHT, Free, LCMS/Dialysis (Cont.), Free 5-a-dihydrotestoterone
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), Percent Free Dialysis is a laboratory measurement used to assess the bioavailable portion of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in the bloodstream. DHT is a potent androgen hormone derived from testosterone through the action of the enzyme 5a-reductase. This conversion primarily takes place in target tissues, such as the skin, prostate, and hair follicles, and DHT plays a crucial role in male sexual development and secondary sexual characteristics.
What is DHT?
Dihydrotestosterone is one of the most powerful androgens, even more potent than testosterone itself. Its effects include:
- Development of male genitalia during fetal development
- Growth of body hair and facial hair
- Sebaceous gland activity
- Contribution to male-pattern baldness
- Influence on prostate growth
DHT acts by binding to androgen receptors in target tissues, influencing cellular activity and gene expression.
Why Measure DHT, Percent Free Dialysis?
The DHT, Percent Free Dialysis test specifically measures the fraction of circulating DHT that is not bound to proteins like sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG). Most DHT in the blood is tightly bound to SHBG, rendering it biologically inactive. However, the free fraction (DHT not bound to SHBG) represents the bioavailable DHT - the portion of the hormone that can actively interact with cells and tissues.
This measurement is critical because only the free fraction of DHT is available to exert its physiological effects. Assessing the free fraction of DHT provides a more accurate reflection of how much of the hormone is available to the body, which can be useful in diagnosing certain hormonal disorders and assessing androgen utilization.
Clinical Applications:
The DHT, Percent Free Dialysis test is particularly important for diagnosing and evaluating conditions related to androgen metabolism, including:
5a-Reductase Deficiency:
This genetic condition involves a deficiency of the enzyme that converts testosterone to DHT. Individuals with this condition may present with ambiguous genitalia or underdeveloped male genitalia despite normal or elevated testosterone levels. Measuring DHT levels, especially the free fraction, helps to confirm the diagnosis.
Androgen Utilization Disorders:
Conditions where the body either underutilizes or overutilizes androgens can be better understood through this test. For instance, in cases of androgen insensitivity syndrome, where the body does not respond to DHT effectively, free DHT levels may still be normal or elevated.
Monitoring Androgen Replacement Therapy:
In patients undergoing testosterone replacement therapy, evaluating DHT levels helps ensure that excessive DHT, which can contribute to side effects like prostate enlargement or hair loss, is not being produced.
How is the Test Performed?
The DHT, Percent Free Dialysis test is typically conducted using a method known as equilibrium dialysis. This process involves separating the free hormone from the protein-bound hormone in a sample of blood. The percentage of free DHT is then calculated, providing insight into the bioavailable fraction of the hormone.
Conclusion
The DHT, Percent Free Dialysis test is a valuable tool for understanding androgen physiology and diagnosing conditions such as 5α-reductase deficiency. By assessing the bioavailable fraction of DHT, this test offers crucial insights into the body's hormonal balance and can guide the management of various disorders related to androgen metabolism.
References:
Azzouni, F., Godoy, A., Li, Y., & Mohler, J. (2012). The 5 alpha-reductase isozyme family: A review of basic biology and their role in human diseases. Advances in Urology, 2012, Article ID 530121. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/530121
Hoffman, R. M. (2020). Clinical practice. Screening for prostate cancer. New England Journal of Medicine, 382(11), 1076-1078. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMcp1905812
Rossi, A., Cantisani, C., Melis, L., Iorio, A., & Scali, E. (2021). Finasteride and dutasteride in androgenetic alopecia: A review. Dermatologic Therapy, 34(1), e14591. https://doi.org/10.1111/dth.14591
Libianto, R., Norman, R. J., & Cassar, S. (2021). Androgens and polycystic ovary syndrome: Pathophysiology and implications for clinical management. Human Reproduction Update, 27(5), 707-732. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmab008
Stout, S. M., & Stumpf, J. L. (2010). Finasteride treatment of hair loss in women. The Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 44(6), 1090-1097. https://doi.org/10.1345/aph.1M684
Gupta, A. K., & Charrette, A. (2014). The efficacy and safety of 5α-reductase inhibitors in androgenetic alopecia. Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery, 18(6), 356-363. https://doi.org/10.2310/7750.2014.14118
What does it mean if your DHT, Percent Free Dialysis result is too high?
Elevated levels of free dihydrotestosterone (DHT) can indicate several physiological and pathological conditions related to excessive androgen activity. Since DHT is a potent androgen, elevated levels of bioavailable DHT can lead to an overactivation of androgen receptors in various tissues, resulting in several clinical symptoms and conditions.
Potential Causes of Elevated DHT Levels:
-
Androgenic Alopecia (Male-Pattern Baldness):
- Elevated DHT is one of the primary contributors to male-pattern baldness. In susceptible individuals, excess DHT binds to androgen receptors in hair follicles, leading to hair miniaturization and thinning over time.
-
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH):
- DHT is a key hormone driving the growth of prostate tissue. Elevated DHT levels can cause the prostate to enlarge, leading to BPH, which may present with urinary difficulties, such as frequent urination, weak urine stream, or incomplete bladder emptying.
-
Prostate Cancer:
- While DHT is not the direct cause of prostate cancer, elevated levels can promote the growth of androgen-sensitive prostate cancer cells. Therefore, high DHT levels are often linked to a higher risk of prostate cancer progression in individuals with the condition.
-
Hirsutism in Women:
- Elevated DHT levels in women can lead to excessive hair growth on the face, chest, and back (a condition known as hirsutism). This is often associated with conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and androgen-secreting tumors.
-
Acne and Seborrhea:
- High DHT levels can overstimulate the sebaceous glands, leading to increased sebum production and contributing to acne formation, particularly in men and women prone to hormonal acne.
Symptoms of Elevated DHT Levels:
-
In Men:
- Male-pattern baldness (receding hairline, thinning hair)
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (enlarged prostate and urinary symptoms)
- Oily skin and acne
- Increased body and facial hair growth (in some cases)
-
In Women:
- Hirsutism (excessive hair growth on face, chest, and back)
- Acne, particularly in areas with more sebaceous glands (face, chest, back)
- Thinning scalp hair (female-pattern hair loss)
Treatment Options for Elevated DHT Levels
The treatment for elevated DHT levels depends on the underlying condition and the symptoms experienced. Several treatment strategies are available to reduce DHT production or block its effects:
-
5α-Reductase Inhibitors:
- Finasteride and Dutasteride are medications that inhibit the enzyme 5α-reductase, which is responsible for converting testosterone to DHT. These drugs are commonly used to treat:
- Male-pattern baldness: Reducing DHT levels in the scalp can slow hair loss and, in some cases, promote hair regrowth.
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): By lowering DHT levels, these medications can shrink the prostate, relieve urinary symptoms, and reduce the risk of needing surgery.
- Finasteride and Dutasteride are medications that inhibit the enzyme 5α-reductase, which is responsible for converting testosterone to DHT. These drugs are commonly used to treat:
-
Anti-Androgens:
- Spironolactone: This medication blocks androgen receptors and reduces the effects of DHT on tissues. It is often used to treat conditions like hirsutism and acne in women, as well as some forms of androgen-driven hair loss.
-
Topical Treatments for Hair Loss:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): While not directly reducing DHT levels, minoxidil can improve blood flow to the scalp and promote hair growth. It is often used alongside DHT-reducing treatments like finasteride.
-
Hormonal Therapies:
- In women with elevated DHT levels due to conditions like PCOS, oral contraceptives or medications like metformin may help regulate androgen production and reduce symptoms like hirsutism and acne.
-
Lifestyle Changes:
- Dietary Adjustments: A balanced diet rich in vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can help support hormonal balance.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity may help manage androgen levels by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing the effects of conditions like PCOS.
- Weight Management: In individuals with obesity, excess body fat can contribute to hormone imbalances, so maintaining a healthy weight can help regulate androgen production.
Conclusion
Elevated levels of DHT can result in several androgen-related conditions, including male-pattern baldness, benign prostatic hyperplasia, hirsutism, and acne. Understanding DHT levels, particularly the free, bioavailable fraction, is important for diagnosing these conditions and implementing effective treatments. Options include 5α-reductase inhibitors, anti-androgens, and lifestyle modifications, all of which can help manage the symptoms and underlying causes of elevated DHT.
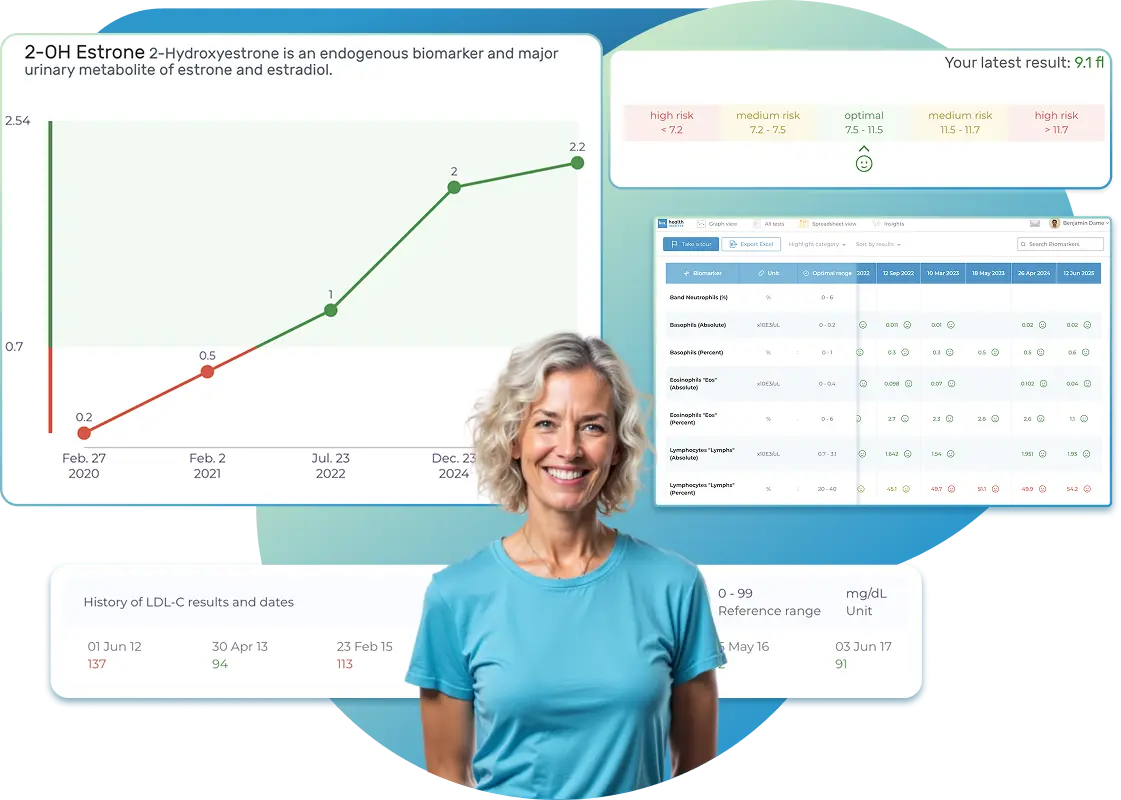
All Your Lab Results.
One Simple Dashboard.
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results Easily
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
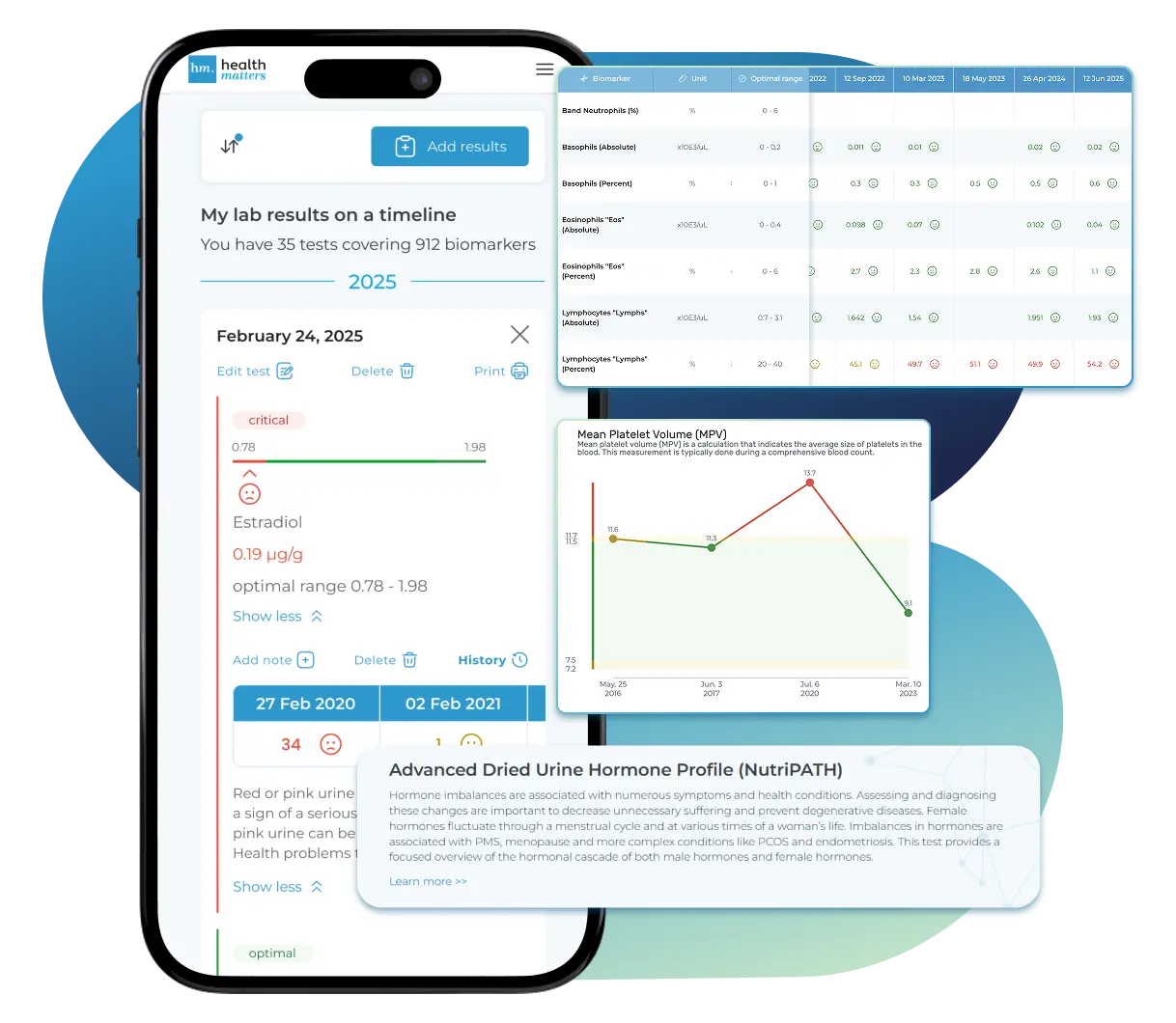
Laboratories
Bring All Your Lab Results Together — In One Place
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.
Pricing Table
Gather Your Lab History — and Finally Make Sense of It
Finally, Your Lab Results Organized and Clear
Personal plans
$79/ year
Advanced Plan
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 5 reports entered for you
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
$250/ once
Unlimited Account
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 10 reports entered for you
- No subscriptions. No extra fees.
$45/ month
Pro Monthly
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track lab results for multiple clients
- Customize reference ranges per client
- Export lab histories and reports
- Begin with first report entered by us
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
About membership
What's included in a Healthmatters membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
 Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Let Your Lab Results Tell the Full Story
Once your results are in one place, see the bigger picture — track trends over time, compare data side by side, export your full history, and share securely with anyone you trust.





Bring all your results together to compare, track progress, export your history, and share securely.
What Healthmatters Members Are Saying
Frequently asked questions
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
- Individuals who want to track and understand their health over time.
- Health professionals, such as doctors, nutritionists, and wellness coaches, need to manage and interpret lab data for their clients.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
- Upload lab reports from any lab
- View your data in interactive graphs, tables, and timelines
- Track trends and monitor changes over time
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export and share your full lab history
- Access your results anytime, from any device
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 10000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
- The GI Effects® Comprehensive Stool Profile,
- GI-MAP,
- The NutrEval FMV®,
- The ION Profile,
- Amino Acids Profile,
- Dried Urine Test for Comprehensive Hormones (DUTCH),
- Organic Acids Test,
- Organix Comprehensive Profile,
- Toxic Metals,
- Complete Blood Count (CBC),
- Metabolic panel,
- Thyroid panel,
- Lipid Panel,
- Urinalysis,
- And many, many more.
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
We implement proven measures to keep your data safe.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
















