Coprococcus, a genus of bacteria within the gut microbiome, is often analyzed in gut health tests to assess its levels and overall contribution to intestinal health. Belonging to the Firmicutes phylum, Coprococcus plays a significant role in the complex ecosystem of the gut. It is known for its involvement in the fermentation of dietary fibers and the production of important metabolic byproducts, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). SCFAs, including butyrate, are vital for maintaining the health of the intestinal lining, providing energy to colon cells, and regulating inflammation and immune function.
The presence and abundance of Coprococcus in the gut can be influenced by various factors. Diet, particularly the intake of fiber-rich foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes, significantly impacts the levels of Coprococcus, as these bacteria thrive on the fibers found in these foods. A diet lacking in such fibers can lead to a decrease in Coprococcus, affecting the overall balance and health of the gut microbiome. Additionally, lifestyle factors like stress, sleep patterns, and physical activity, as well as the use of medications like antibiotics, can also influence the levels of these bacteria.
In gut health tests, the analysis of Coprococcus levels can provide insights into the state of the gut microbiome and its potential impact on overall health. A balanced level of Coprococcus is often associated with a healthy gut microbiome, which is crucial for effective digestion, nutrient absorption, and a robust immune system. Alterations in the levels of Coprococcus, either too high or too low, can be indicative of dysbiosis or an imbalance in the gut microbiota. This dysbiosis has been linked to various gastrointestinal conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and may also have implications for systemic health issues, including metabolic and mood disorders.
Addressing imbalances in Coprococcus typically involves dietary and lifestyle modifications aimed at fostering a healthy gut microbiome. This includes incorporating a diverse range of fiber-rich foods to support the growth of beneficial bacteria like Coprococcus. Probiotics and prebiotics can also be beneficial, with probiotics introducing beneficial strains and prebiotics serving as fuel for the existing gut bacteria. Lifestyle changes such as managing stress, ensuring adequate and quality sleep, and engaging in regular physical activity can also positively influence the diversity and health of the gut microbiome. In cases where gut dysbiosis is linked to specific health conditions or symptoms, a healthcare provider may suggest further diagnostic testing or targeted treatments to address the underlying issues.
What does it mean if your Coprococcus result is too high?
High levels of Coprococcus in the gut, as identified through gut microbiome testing, can provide valuable insights into the state of an individual's intestinal health and overall well-being. Coprococcus is a genus of bacteria known for its role in fermenting dietary fibers and producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, which are essential for colon health, immune regulation, and inflammation control. While these bacteria are typically beneficial, an unusually high concentration in the gut may indicate an imbalance or dysbiosis in the microbiome.
The causes of elevated Coprococcus levels can be multifactorial. Diet plays a crucial role; a diet particularly high in specific types of fibers may lead to an overgrowth of these bacteria. While generally beneficial, an excessive concentration of any single bacterial genus can disrupt the delicate balance of the gut ecosystem. Additionally, factors such as a lack of dietary diversity, prolonged use of certain medications like antibiotics, and lifestyle factors including stress and sedentary habits can contribute to this imbalance.
The implications of high Coprococcus levels are not entirely clear and can vary depending on the overall composition of the gut microbiome and the individual's health. In some cases, an overrepresentation of Coprococcus might be linked to gastrointestinal conditions such as bloating, gas, or irregular bowel movements. It could also have broader implications for systemic health, given the gut's role in immune function and inflammation regulation.
When addressing high levels of Coprococcus, the treatment approach generally aims to restore a balanced and diverse gut microbiome. Dietary modifications are often the first step, focusing on a balanced intake of various types of fibers and nutrients to support a diverse microbial community. This includes incorporating a wide range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes into the diet. Probiotic supplements might be recommended to introduce a variety of beneficial bacterial strains, and prebiotics can help nourish the existing beneficial bacteria.
Lifestyle modifications can also play a significant role in rebalancing the gut microbiome. Managing stress through mindfulness practices, getting adequate sleep, and engaging in regular physical activity are known to positively impact gut health. Additionally, it's important to use antibiotics judiciously and only when necessary, as they can disrupt the gut flora.
In cases where high Coprococcus levels are associated with specific health concerns or symptoms, a healthcare provider may recommend further diagnostic testing or targeted treatments. This could include personalized dietary plans, supplements, or other interventions tailored to the individual's health status and needs.
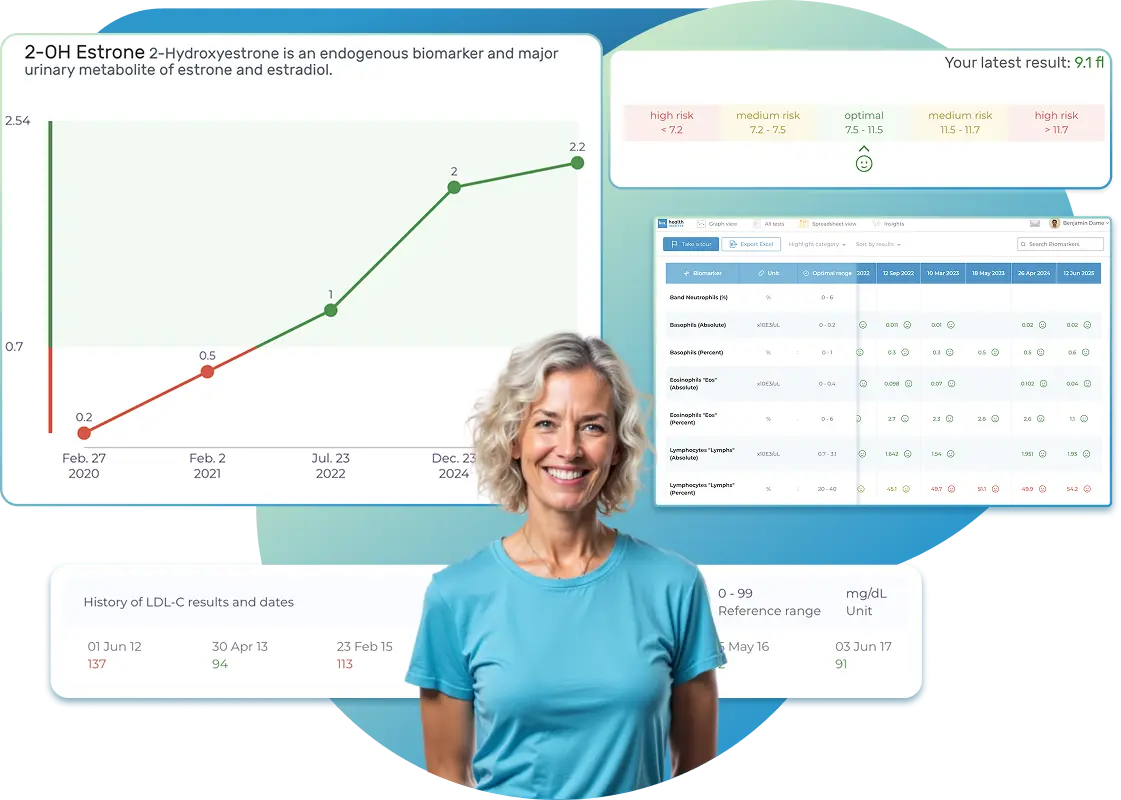
All Your Lab Results.
One Simple Dashboard.
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results Easily
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
What does it mean if your Coprococcus result is too low?
Low levels of Coprococcus in your gut, specifically the species Coprococcus eutactus and Coprococcus comes, can point to an imbalance in your gut microbiome with potential consequences for your health.
Causes of Low Coprococcus:
- Dietary deficiencies: A diet low in dietary fiber, which serves as fuel for Coprococcus bacteria, can lead to their decline.
- Antibiotic use: Broad-spectrum antibiotics can indiscriminately wipe out Coprococcus along with other bacteria, disrupting the gut balance.
- Digestive diseases: Conditions like Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis can damage the gut lining, making it harder for Coprococcus to thrive.
- Stress and mental health: Chronic stress and mental health conditions like anxiety and depression can alter the gut microbiome, potentially impacting Coprococcus levels.
- Prebiotic and probiotic imbalances: An absence of specific prebiotics that nurture Coprococcus or the dominance of other bacterial strains competing for resources can contribute to their decline.
Implications of Low Coprococcus:
- Digestive issues: Constipation, diarrhea, bloating, and gas are common symptoms associated with gut imbalances, which Coprococcus depletion can contribute to.
- Weakened immune system: Coprococcus plays a role in immune function by regulating inflammation and producing beneficial metabolites. Their low levels might leave you more susceptible to infections.
- Metabolic health: Some studies suggest a potential link between low Coprococcus and metabolic issues like insulin resistance and obesity, though the exact mechanisms are still being investigated.
- Neurological concerns: Emerging research suggests potential connections between Coprococcus and the gut-brain axis, with implications for conditions like anxiety, depression, and cognitive function.
Potential Treatment Options:
- Dietary adjustments: Increasing fiber intake from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide fuel for Coprococcus growth. Consider prebiotic-rich foods like onions, garlic, and Jerusalem artichokes.
- Targeted probiotics: Specific probiotic strains containing Coprococcus bacteria might be beneficial, though consult a healthcare professional for a personalized recommendation.
- Stress management: Techniques like yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can help regulate the gut-brain axis and create a more favorable environment for Coprococcus.
- Addressing underlying conditions: Treating any digestive diseases or managing stress and mental health issues can indirectly support Coprococcus growth.
- Prebiotic supplementation: Certain prebiotics, like inulin and fructooligosaccharides, can selectively promote the growth of Coprococcus and other beneficial bacteria.
Remember: Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. While the science on Coprococcus is evolving, taking proactive steps to support your gut health can pave the way for a more balanced microbiome and potentially improve your overall well-being.
Additional Resources:
- The American Gastroenterological Association: https://journals.lww.com/ajg/pages/default.aspx
- The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/
- The International Probiotics Association: https://internationalprobiotics.org/home/
By understanding the potential causes and implications of low Coprococcus levels, you can take informed steps towards restoring balance in your gut microbiome and supporting your overall health. Remember, a healthy gut is a cornerstone of well-being, and proactive initiatives can empower you to nurture your unique ecosystem of microbes.
Laboratories
Bring All Your Lab Results Together — In One Place
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.
Pricing Table
Gather Your Lab History — and Finally Make Sense of It
Finally, Your Lab Results Organized and Clear
Personal plans
$79/ year
Advanced Plan
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 5 reports entered for you
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
$250/ once
Unlimited Account
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 10 reports entered for you
- No subscriptions. No extra fees.
$45/ month
Pro Monthly
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track lab results for multiple clients
- Customize reference ranges per client
- Export lab histories and reports
- Begin with first report entered by us
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
About membership
What's included in a Healthmatters membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
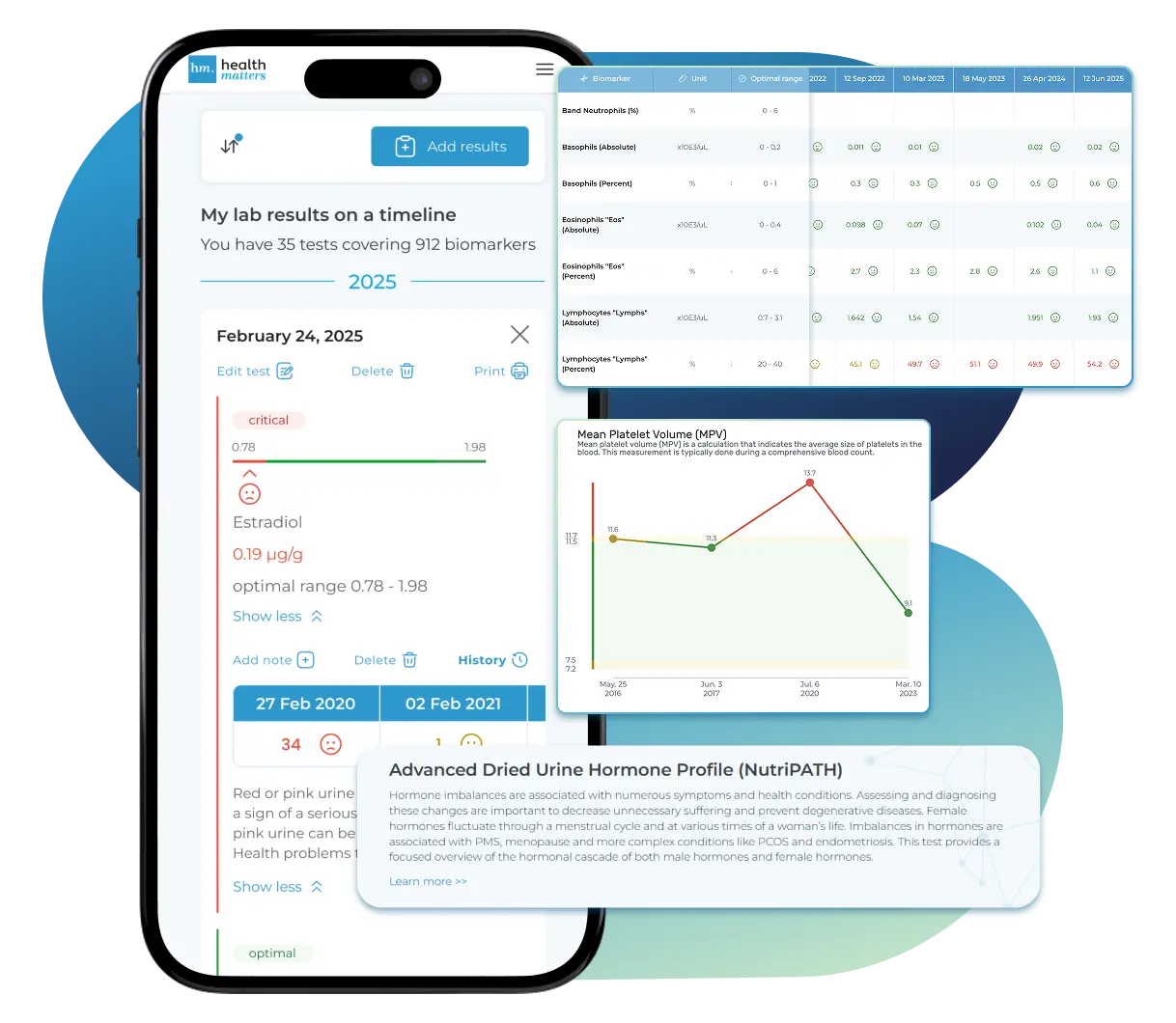
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
 Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Let Your Lab Results Tell the Full Story
Once your results are in one place, see the bigger picture — track trends over time, compare data side by side, export your full history, and share securely with anyone you trust.





Bring all your results together to compare, track progress, export your history, and share securely.
What Healthmatters Members Are Saying
Frequently asked questions
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
- Individuals who want to track and understand their health over time.
- Health professionals, such as doctors, nutritionists, and wellness coaches, need to manage and interpret lab data for their clients.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
- Upload lab reports from any lab
- View your data in interactive graphs, tables, and timelines
- Track trends and monitor changes over time
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export and share your full lab history
- Access your results anytime, from any device
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 10000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
- The GI Effects® Comprehensive Stool Profile,
- GI-MAP,
- The NutrEval FMV®,
- The ION Profile,
- Amino Acids Profile,
- Dried Urine Test for Comprehensive Hormones (DUTCH),
- Organic Acids Test,
- Organix Comprehensive Profile,
- Toxic Metals,
- Complete Blood Count (CBC),
- Metabolic panel,
- Thyroid panel,
- Lipid Panel,
- Urinalysis,
- And many, many more.
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
We implement proven measures to keep your data safe.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
















