Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
Other names: Carbon Dioxide, Total, Bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻), Total CO₂, CO₂ (Serum), CO₂, Carbon Dioxide (Blood), TCO₂, Serum Bicarbonate, Plasma CO₂
What Is CO₂ on a Blood Test?
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) on a standard blood test does not measure carbon dioxide gas directly. Instead, it primarily reflects the amount of bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) in your blood.
Bicarbonate is a key electrolyte that helps regulate your body’s acid–base balance and maintain a stable blood pH. Because most carbon dioxide in the bloodstream exists in this bicarbonate form, the CO₂ value reported on a Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP) or Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP) is essentially a bicarbonate measurement.
You may see it listed as:
-
Carbon Dioxide, Total
-
CO₂
-
Total CO₂ (TCO₂)
-
Bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻)
What Does a CO₂ Blood Test Measure?
A CO₂ blood test measures total bicarbonate concentration in serum or plasma.
This helps determine whether your body is trending toward:
-
Acidosis (too acidic)
-
Alkalosis (too alkaline)
It also provides clues about whether an imbalance is coming from:
-
The kidneys (metabolic causes)
-
The lungs (respiratory causes)
Because of this, CO₂ is one of the most important markers for interpreting electrolyte patterns, dehydration status, kidney function, and acid–base disorders.
Why CO₂ Levels Matter
Bicarbonate acts as one of the body’s main buffering systems. Even small shifts can reflect underlying physiological stress.
Abnormal CO₂ levels may be associated with:
-
Dehydration or fluid loss
-
Vomiting or prolonged diarrhea
-
Kidney dysfunction
-
Lung disease affecting CO₂ elimination
-
Uncontrolled diabetes (ketoacidosis)
-
Severe infection (sepsis)
-
Certain medications (especially diuretics or acid–base altering drugs)
CO₂ should always be interpreted alongside:
-
Sodium
-
Potassium
-
Chloride
-
Anion gap
-
Creatinine
-
Glucose
-
Clinical symptoms
Normal CO₂ (Bicarbonate) Range
A typical adult reference range is:
20–29 mEq/L
Ranges vary slightly by laboratory.
A result slightly outside the range does not automatically mean something is dangerous. The degree of deviation and overall clinical context matter more than a single isolated value.
What Do Common CO₂ Values Mean?
Many people search for interpretation of specific numbers. While exact meaning depends on context, general patterns include:
-
CO₂ 30–32 mEq/L: Often mildly elevated. Commonly seen with dehydration, vomiting, or diuretic use.
-
CO₂ 33–34 mEq/L: More clearly elevated in many labs; warrants evaluation of chloride, potassium, and symptoms.
-
CO₂ 19–20 mEq/L: Mildly low; can occur with diarrhea, mild metabolic acidosis, or hyperventilation.
-
CO₂ below ~18 mEq/L: More concerning for metabolic acidosis and may require urgent evaluation depending on symptoms.
A value alone is rarely diagnostic — interpretation depends on accompanying labs and clinical presentation.
Is a High or Low CO₂ Level Dangerous?
It depends on:
-
How abnormal the number is
-
Whether blood pH is significantly disturbed
-
Whether symptoms are present
-
The underlying cause
Mild abnormalities are common and often reversible. Severe acid–base disturbances, however, can become serious and require medical attention.
Seek urgent evaluation if abnormal CO₂ is accompanied by:
-
Rapid or deep breathing
-
Confusion or altered mental status
-
Severe weakness
-
Chest pain
-
Signs of severe dehydration or shock
CO₂ vs. PaCO₂: Blood Test vs. Blood Gas
It’s important to distinguish between:
CMP/BMP CO₂:
-
Reflects bicarbonate (metabolic component)
Arterial or Venous Blood Gas (ABG/VBG):
-
Measures pH
-
Measures PaCO₂ (actual dissolved carbon dioxide gas)
-
Measures bicarbonate
-
Assesses oxygen levels
If there is uncertainty about whether a problem is metabolic or respiratory, a blood gas test provides more precise acid–base evaluation.
Key Takeaway
The CO₂ value on a metabolic panel is primarily a measure of bicarbonate — a critical regulator of acid–base balance. While abnormal results can reflect dehydration, kidney issues, respiratory disorders, or metabolic disturbances, they must be interpreted in context.
A single number rarely tells the full story. Trends over time, accompanying electrolyte changes, symptoms, and clinical background determine whether a CO₂ level is benign or requires further evaluation.
What does it mean if your Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) result is too high?
A high CO₂ level on a blood test usually reflects elevated bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) — not excess carbon dioxide gas.
In most cases, high CO₂ indicates metabolic alkalosis (your body is too alkaline) or compensation for chronic respiratory CO₂ retention, commonly seen in long-standing lung disease.
High CO₂ is not a diagnosis. It is a signal that your acid–base balance may be shifted.
What Is Considered High CO₂?
Most adult reference ranges fall between:
20–29 mEq/L
General interpretation:
-
30–32 mEq/L: Mildly elevated
-
33–34 mEq/L: Moderately elevated
-
35+ mEq/L: Clearly abnormal and requires evaluation
Severity depends on symptoms and accompanying lab findings.
What Does High CO₂ Mean?
High CO₂ typically reflects one of two patterns:
1. Metabolic Alkalosis (Most Common)
This occurs when the body loses acid or retains bicarbonate.
Common causes include:
-
Dehydration or volume depletion
-
Prolonged vomiting
-
Diuretic use (especially loop or thiazide diuretics)
-
Chloride depletion
-
Excess alkali intake (less common)
-
Certain endocrine disorders that increase mineralocorticoid activity
Dehydration is one of the most common reversible causes of mild CO₂ elevation.
2. Compensation for Chronic Respiratory Acidosis
In conditions like:
-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
-
Obesity hypoventilation syndrome
-
Long-standing respiratory disorders
The lungs retain CO₂ gas over time. The kidneys compensate by increasing bicarbonate levels, which raises CO₂ on a CMP.
This pattern is typically stable and chronic rather than acute.
Can Dehydration Cause High CO₂?
Yes.
Dehydration and fluid loss can lead to:
-
Relative bicarbonate concentration increase
-
Chloride depletion
-
Metabolic alkalosis
If high CO₂ is accompanied by low chloride and recent fluid loss, dehydration is a likely contributor.
Rehydration often normalizes mild elevations.
Symptoms of High CO₂
Mild elevations often cause no symptoms.
When metabolic alkalosis becomes more significant, symptoms may include:
-
Muscle cramps
-
Weakness
-
Fatigue
-
Lightheadedness
-
Nausea
-
Irregular heart rhythms (if potassium is low)
Symptoms are usually related to associated electrolyte imbalances rather than the CO₂ level itself.
Is a CO₂ Level of 30–32 Dangerous?
In most otherwise healthy individuals:
-
30–32 mEq/L is usually mildly elevated
-
Often related to dehydration or medication effects
-
Not automatically dangerous
However, persistent elevation should be evaluated in context of:
-
Chloride
-
Potassium
-
Kidney function
-
Respiratory history
When Is High CO₂ Concerning?
High CO₂ warrants closer evaluation when:
-
It exceeds 34–35 mEq/L
-
It is persistent across multiple tests
-
It is associated with low potassium
-
There are symptoms of electrolyte imbalance
-
There is known lung disease with worsening breathing
-
There is unexplained metabolic alkalosis
Severe metabolic alkalosis can interfere with heart rhythm and oxygen delivery.
What Should You Do If Your CO₂ Is High?
1. Review Accompanying Labs
Look at:
-
Chloride (often low in metabolic alkalosis)
-
Potassium (may be low with diuretics or vomiting)
-
Sodium
-
Creatinine
-
Anion gap
2. Review Medications
Diuretics are a very common cause.
3. Evaluate Hydration
Recent vomiting, diarrhea, or low fluid intake may explain mild elevation.
4. Consider Respiratory History
Chronic lung disease may cause compensatory elevation.
5. Repeat Testing if Needed
Mild isolated elevations often normalize with correction of fluid or electrolyte imbalance.
Bottom Line
High CO₂ on a blood test most commonly reflects metabolic alkalosis or chronic respiratory compensation — not excess carbon dioxide poisoning.
Mild elevations (30–32 mEq/L) are often related to dehydration or medication effects and are frequently reversible.
More significant elevations, persistent abnormalities, or associated symptoms require medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause.
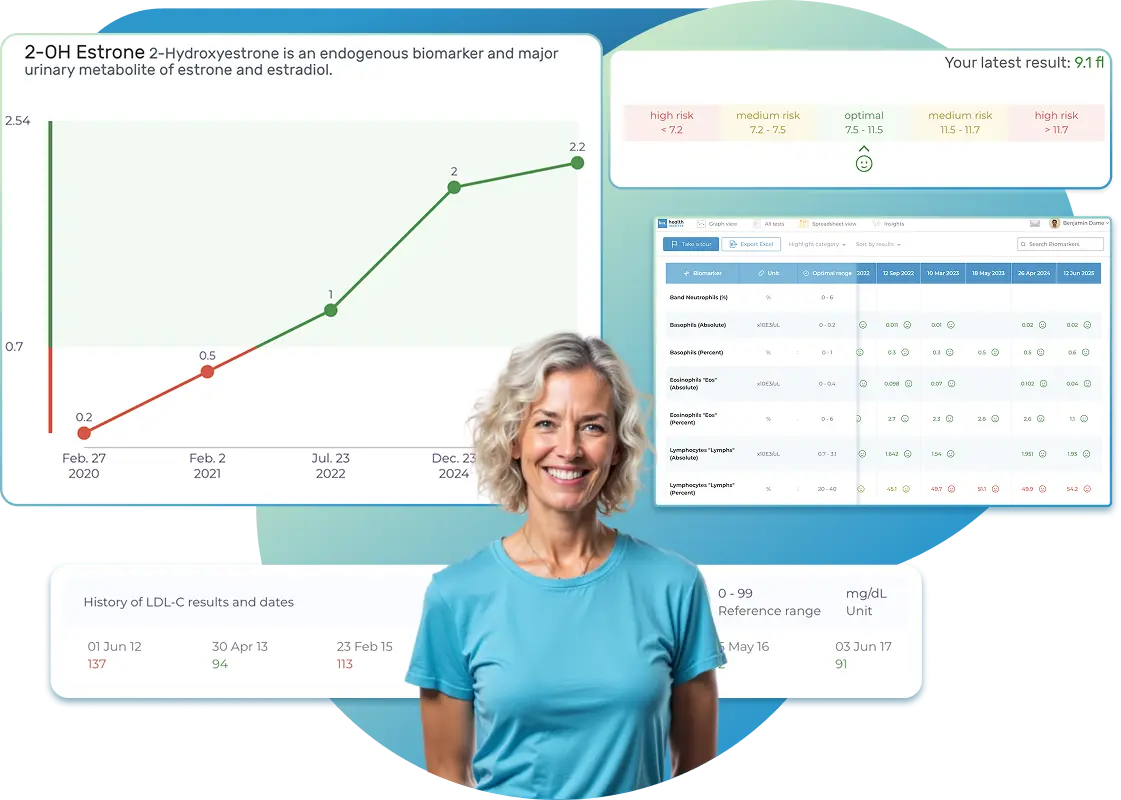
All Your Lab Results.
One Simple Dashboard.
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results Easily
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
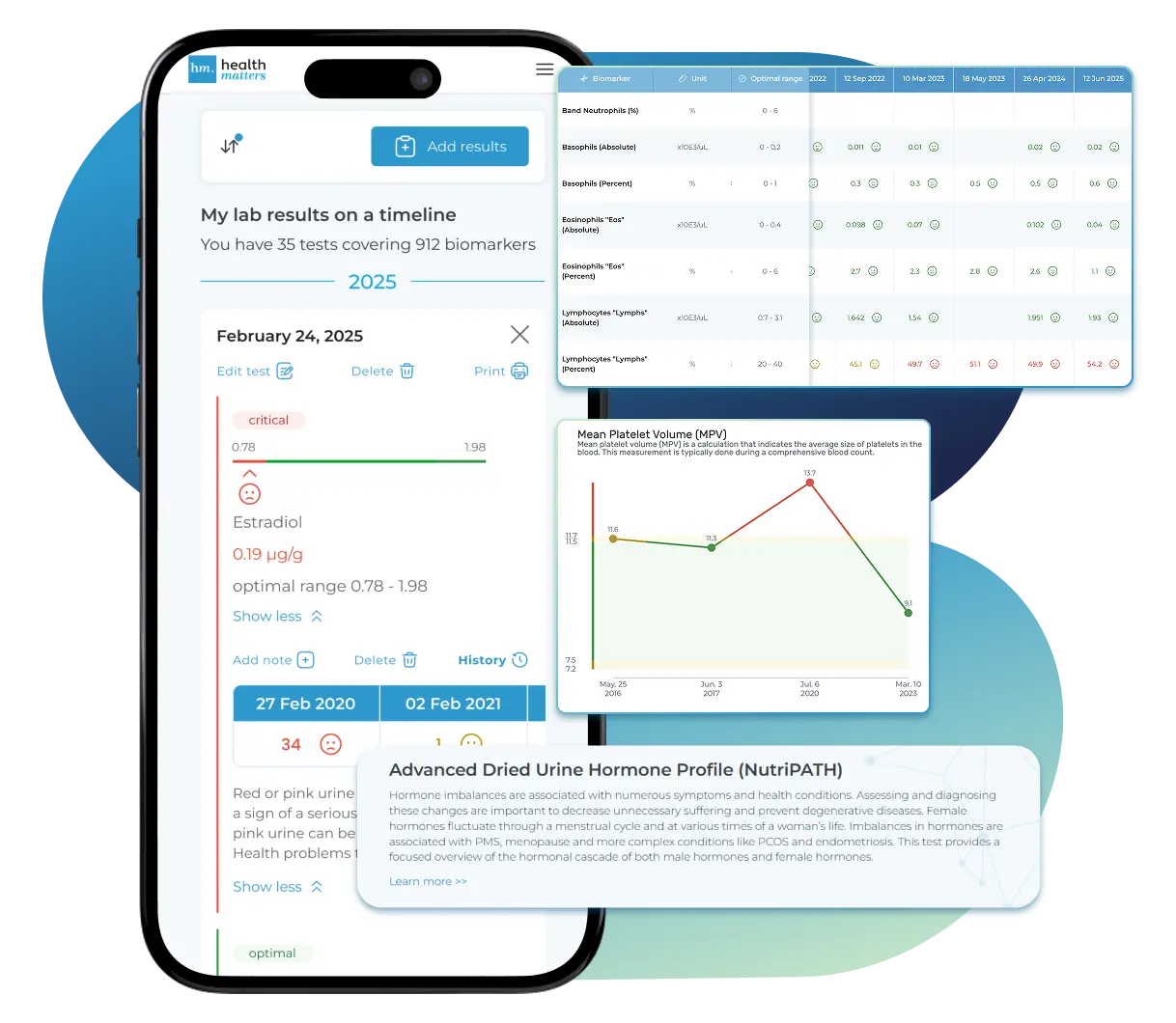
What does it mean if your Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) result is too low?
A low CO₂ level on a blood test almost always reflects low bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) — a key regulator of your body’s acid–base balance.
In most cases, low CO₂ signals metabolic acidosis, a condition where the body is too acidic. Less commonly, it may reflect respiratory alkalosis from excessive breathing (hyperventilation).
Low CO₂ is not a diagnosis by itself. It is a warning signal that something is disrupting normal acid regulation.
What Is Considered Low CO₂?
Most adult reference ranges fall between:
20–29 mEq/L
General interpretation:
-
19–20 mEq/L: Mildly low
-
17–18 mEq/L: Moderately low
-
Below 16 mEq/L: Concerning and often clinically significant
The lower the number, the more likely there is a true acid–base disorder requiring evaluation.
What Does Low CO₂ Mean?
Low CO₂ usually means one of two things:
1. Metabolic Acidosis (Most Common)
This occurs when:
-
The body produces too much acid
-
The kidneys cannot remove acid properly
-
Bicarbonate is lost from the body
Common causes include:
-
Chronic kidney disease
-
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
-
Lactic acidosis (shock, severe illness, low oxygen)
-
Sepsis
-
Severe or prolonged diarrhea
-
Toxin exposure (e.g., salicylates)
-
Advanced liver failure
This is the most important category to rule out.
2. Respiratory Alkalosis (Less Common Cause of Low CO₂ on CMP)
Excessive breathing lowers carbon dioxide levels, which can indirectly reduce bicarbonate.
Common triggers:
-
Anxiety or panic attacks
-
Severe pain
-
Fever
-
Acute illness
-
High altitude
This pattern is usually clarified with a blood gas test.
Can Dehydration Cause Low CO₂?
Yes — especially if dehydration is due to diarrhea, which causes direct bicarbonate loss.
However, simple mild dehydration alone is more often associated with slight elevations, not severe reductions.
If low CO₂ is present, evaluate for fluid loss, electrolyte imbalance, and kidney function.
Symptoms of Low CO₂
Symptoms depend on the severity and underlying cause. They may include:
-
Rapid or deep breathing
-
Fatigue or weakness
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Confusion
-
Headache
-
Shortness of breath
Severe metabolic acidosis can become life-threatening if untreated.
When Is Low CO₂ Dangerous?
Low CO₂ becomes concerning when:
-
It falls below ~17–18 mEq/L
-
It is associated with an elevated anion gap
-
Kidney function is impaired
-
Blood glucose and ketones are abnormal
-
The patient has confusion, rapid breathing, or systemic illness
If CO₂ is 15 or lower, urgent medical evaluation is typically warranted.
What Should You Do If Your CO₂ Is Low?
1. Review Accompanying Labs
Look at:
-
Anion gap
-
Chloride
-
Potassium
-
Creatinine
-
Glucose and ketones
These often clarify the cause immediately.
2. Evaluate Symptoms
Mild low CO₂ without symptoms may be monitored.
Severe symptoms require urgent care.
3. Identify the Trigger
Common reversible causes:
-
Diarrhea
-
Dehydration
-
Medication effects
-
Poorly controlled diabetes
4. Consider Further Testing
An arterial or venous blood gas (ABG/VBG) may be needed to confirm metabolic acidosis and determine severity.
Common Questions
Is CO₂ of 19 Dangerous?
Usually mildly abnormal. It requires context but is not automatically dangerous if other labs are stable.
What About CO₂ of 16 or Lower?
This is more concerning and should prompt evaluation for metabolic acidosis.
Can Low CO₂ Be Temporary?
Yes. Mild reductions may occur during acute illness, short-term diarrhea, or transient hyperventilation.
Bottom Line
Low CO₂ on a blood test most often reflects metabolic acidosis — a disruption in acid–base balance that can range from mild and reversible to medically urgent.
The number alone does not determine severity. The combination of symptoms, kidney function, anion gap, and clinical context determines risk.
If the value is significantly low or accompanied by symptoms, seek medical evaluation promptly.
Laboratories
Bring All Your Lab Results Together — In One Place
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.
Pricing Table
Gather Your Lab History — and Finally Make Sense of It
Finally, Your Lab Results Organized and Clear
Personal plans
$79/ year
Advanced Plan
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 5 reports entered for you
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
$250/ once
Unlimited Account
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 10 reports entered for you
- No subscriptions. No extra fees.
$45/ month
Pro Monthly
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track lab results for multiple clients
- Customize reference ranges per client
- Export lab histories and reports
- Begin with first report entered by us
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
About membership
What's included in a Healthmatters membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
 Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Let Your Lab Results Tell the Full Story
Once your results are in one place, see the bigger picture — track trends over time, compare data side by side, export your full history, and share securely with anyone you trust.





Bring all your results together to compare, track progress, export your history, and share securely.
What Healthmatters Members Are Saying
Frequently asked questions
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
- Individuals who want to track and understand their health over time.
- Health professionals, such as doctors, nutritionists, and wellness coaches, need to manage and interpret lab data for their clients.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
- Upload lab reports from any lab
- View your data in interactive graphs, tables, and timelines
- Track trends and monitor changes over time
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export and share your full lab history
- Access your results anytime, from any device
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 10000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
- The GI Effects® Comprehensive Stool Profile,
- GI-MAP,
- The NutrEval FMV®,
- The ION Profile,
- Amino Acids Profile,
- Dried Urine Test for Comprehensive Hormones (DUTCH),
- Organic Acids Test,
- Organix Comprehensive Profile,
- Toxic Metals,
- Complete Blood Count (CBC),
- Metabolic panel,
- Thyroid panel,
- Lipid Panel,
- Urinalysis,
- And many, many more.
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
We implement proven measures to keep your data safe.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
















