Basophils (Percent)
Other names: % Basophils, Basophils %
What Are Basophils?
Basophils are a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) that plays an essential role in your immune system. They protect your body from allergens, pathogens, and parasites. Despite making up less than 1% of all white blood cells and having a short lifespan of just one to two days, basophils are critical in managing allergic reactions and supporting immune responses.
Characteristics of Basophils
- Granulocytes: Basophils belong to a category of white blood cells called granulocytes, which contain granules filled with enzymes such as histamine and heparin.
- Histamine Storage: They are the only circulating white blood cells that store histamine, a chemical responsible for allergy symptoms like sneezing and itching.
- Heparin Release: Heparin, a natural blood thinner, prevents excessive clotting and improves blood flow to affected areas.
- Mononuclear Cells: Basophils have a single, round nucleus, setting them apart from other types of white blood cells.
Basophils’ Role in Allergic Reactions
When your body encounters an allergen, basophils release histamine, which triggers inflammation and allergy symptoms such as:
- Runny nose
- Sneezing
- Itchy, watery eyes
Basophils also produce immunoglobulin E (IgE), an antibody that binds to both basophils and mast cells. This interaction enhances the release of histamine and serotonin, intensifying the body’s inflammatory response to allergens.
Functions of Basophils
Basophils support your immune system in multiple ways:
- Allergy Defense: Basophils respond rapidly to allergens by releasing histamine and initiating inflammation.
- Infection Control: They help fight infections, although this is not their primary function.
- Inflammation Regulation: Basophils manage blood flow and prevent excessive clotting during immune responses by releasing histamine and heparin.
- Phagocytosis: Basophils can engulf and neutralize harmful substances, supporting the immune system’s defense against allergens and infections.
Basophils Within the White Blood Cell Family
Basophils are one of five main types of white blood cells, all of which play unique roles in immune defense. While basophils are the least common, they are crucial in managing allergic reactions. The other types of white blood cells include:
- Neutrophils: The most abundant type, specializing in fighting bacterial and fungal infections.
- Eosinophils: Target parasitic infections and contribute to allergic reactions.
- Lymphocytes: Fight viruses and bacteria directly.
- Monocytes: Assist in clearing infections and removing damaged cells.
Where Are Basophils Found?
Basophils are produced in the bone marrow and circulate in the bloodstream. They travel to areas of tissue damage or infection to support healing and immune defense.
Testing Basophil Levels
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures basophil levels, offering valuable insights into your immune health.
- Normal Range: Basophils account for less than 1% of all white blood cells, with a typical range of 0.0–0.2 thousand cells per microliter (K/cumm or x10x3/µL).
- Elevated Levels: May indicate allergic reactions, chronic inflammation, or certain blood disorders.
- Low Levels: Typically not concerning unless accompanied by other abnormalities.
Conclusion
Basophils are an essential part of your immune system, contributing to allergic reactions, regulating inflammation, and defending against pathogens. While they represent a small fraction of your total white blood cells, their impact is significant. Monitoring basophil levels through blood tests can help detect potential health issues and guide treatment for allergies and other immune-related conditions.
What does it mean if your Basophils (Percent) result is too high?
What Is Basophilia?
Basophilia refers to elevated levels of basophils, a type of white blood cell, in the bloodstream. It is typically defined as a basophil count greater than 300 cells per microliter of blood or more than 2% of all white blood cells in peripheral blood. Basophils play a role in immune responses, especially in allergic reactions and inflammation.
Common Causes of Basophilia
Basophilia may result from a variety of medical conditions, including:
- Allergic reactions: Triggers may include pollen, food allergens, or venom.
- Parasitic infections: Particularly those involving tissue invasion.
- Inflammatory bowel disease: Conditions such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
- Autoimmune disorders: Examples include lupus or other collagen vascular diseases.
- Blood disorders:
- Polycythemia vera (a condition causing increased blood cell production).
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), a type of blood cancer.
Less Common Associations
- Iron deficiency anemia: Moderate increases in basophils have been reported.
- Diabetes: Basophilia may occur in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
- Hypothyroidism: An underactive thyroid gland can lead to elevated basophil counts.
Understanding Basophilia
While an elevated basophil count can signal underlying health issues, it's important to remember:
- Temporary increases: Basophilia is often transient and resolves without treatment.
- Mild elevation: In many cases, the increase in basophil count is not significant.
- Accompanied by other changes: Basophilia is rarely an isolated finding and often occurs alongside abnormalities in other blood cells.
Diagnosis and Treatment
To diagnose basophilia and identify its cause, healthcare providers typically perform:
- Complete blood count (CBC): Measures overall white blood cell levels and differentiates basophils.
- Peripheral blood smear: Examines blood cell shapes and sizes.
- Additional diagnostic tests: Depending on symptoms, tests may include imaging, biopsies, or hormone evaluations.
Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying cause and may include:
- For allergies: Antihistamines or avoiding known allergens.
- For infections: Antibiotics for bacterial infections.
- For hypothyroidism: Thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
- For blood cancers: Chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapies.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If basophilia is identified in a blood test, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation. Basophilia can result from both benign conditions and serious health issues, so proper diagnosis and treatment are critical to addressing the underlying cause effectively.
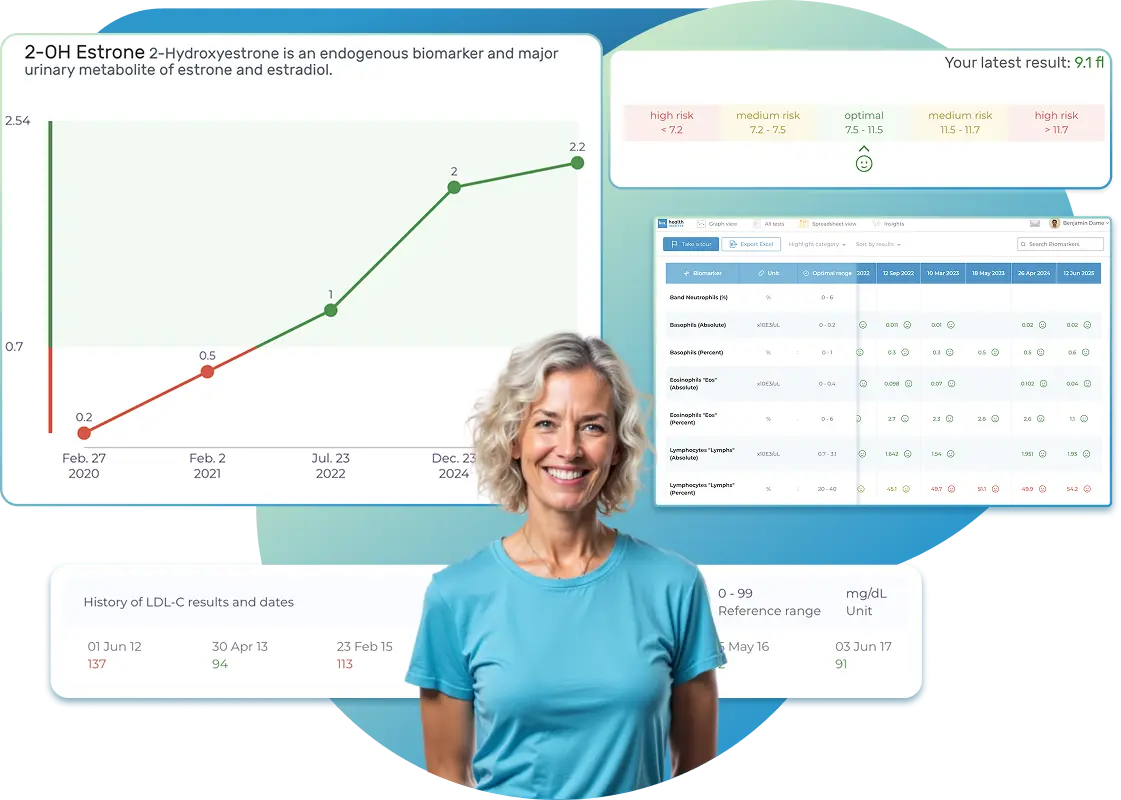
All Your Lab Results.
One Simple Dashboard.
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results Easily
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
What does it mean if your Basophils (Percent) result is too low?
Basopenia: A Decrease in Basophils
Basopenia is a condition characterized by a lower-than-normal number of basophils, a type of white blood cell, in the bloodstream. Basophils play an important role in immune responses, particularly in combating allergens and pathogens, so a decrease may point to specific medical conditions or treatments.
Possible Causes of Basopenia
Basopenia can result from various factors, including:
- Acute (pyogenic) infections
- Hyperthyroidism
- Stress reactions, such as:
- Pregnancy
- Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
- Medical treatments, such as:
- Prolonged steroid or corticosteroid use
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Other potential causes:
- Hereditary absence of basophils
- Drug-induced reactions
- Cancer
Important Considerations
Low basophil levels are commonly observed in healthy individuals and are typically not a cause for concern. However, extremely low basophil counts may indicate more serious issues, such as:
- Severe systemic responses: Conditions like overwhelming infections or severe allergic reactions may rapidly deplete white blood cells, including basophils.
- Drug-related effects: Chemotherapy and corticosteroids are known to suppress basophil production.
- Underlying cancer: Certain cancers, such as those affecting bone marrow, may reduce basophil levels.
In women, pregnancy can naturally result in lower basophil counts due to hormonal and physiological changes.
Potential Treatment Approaches
Treatment for basopenia depends on addressing the underlying cause. Possible approaches include:
- Avoiding allergens: Reducing exposure to allergens and using antihistamines if allergic reactions are contributing to basopenia.
- Medication adjustments: Changing the dosage or timing of medications under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
- Treating underlying conditions: Managing hyperthyroidism, infections, or cancer with appropriate therapies.
- Addressing infections and injuries: Supporting recovery through targeted treatments, such as antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications.
Conclusion
Basopenia is often not a standalone medical condition but rather a sign of an underlying issue or a response to certain treatments or stressors. While low basophil levels are common and may not always require intervention, extremely low counts warrant further investigation. If basopenia is detected, consult with a healthcare provider to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment or monitoring.
Laboratories
Bring All Your Lab Results Together — In One Place
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.
Pricing Table
Gather Your Lab History — and Finally Make Sense of It
Finally, Your Lab Results Organized and Clear
Personal plans
$79/ year
Advanced Plan
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 5 reports entered for you
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
$250/ once
Unlimited Account
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 10 reports entered for you
- No subscriptions. No extra fees.
$45/ month
Pro Monthly
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track lab results for multiple clients
- Customize reference ranges per client
- Export lab histories and reports
- Begin with first report entered by us
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
About membership
What's included in a Healthmatters membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
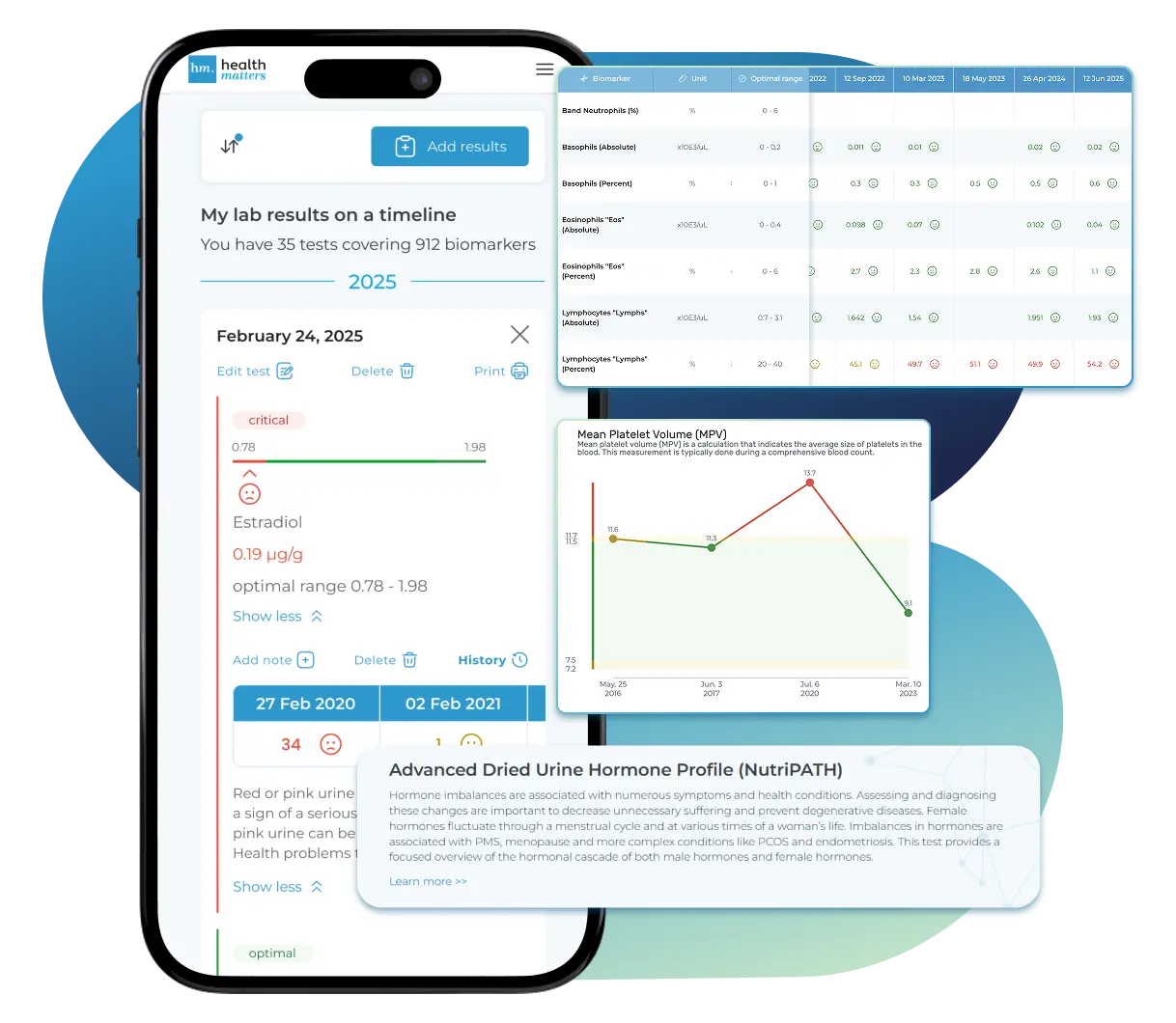
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
 Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Let Your Lab Results Tell the Full Story
Once your results are in one place, see the bigger picture — track trends over time, compare data side by side, export your full history, and share securely with anyone you trust.





Bring all your results together to compare, track progress, export your history, and share securely.
What Healthmatters Members Are Saying
Frequently asked questions
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
- Individuals who want to track and understand their health over time.
- Health professionals, such as doctors, nutritionists, and wellness coaches, need to manage and interpret lab data for their clients.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
- Upload lab reports from any lab
- View your data in interactive graphs, tables, and timelines
- Track trends and monitor changes over time
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export and share your full lab history
- Access your results anytime, from any device
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 10000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
- The GI Effects® Comprehensive Stool Profile,
- GI-MAP,
- The NutrEval FMV®,
- The ION Profile,
- Amino Acids Profile,
- Dried Urine Test for Comprehensive Hormones (DUTCH),
- Organic Acids Test,
- Organix Comprehensive Profile,
- Toxic Metals,
- Complete Blood Count (CBC),
- Metabolic panel,
- Thyroid panel,
- Lipid Panel,
- Urinalysis,
- And many, many more.
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
We implement proven measures to keep your data safe.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
















