Alpha Linoleic Acid is an “essential” fatty acid, meaning that your body cannot make it and you must obtain it from your diet. Alpha Linoleic Acid is by far the most abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid in most human tissues.
Dietary sources of alpha-linolenic acid include:
- Flaxseeds and flaxseed oil
- Canola (rapeseed) oil
- Soybeans and soybean oil
- Pumpkin seeds and pumpkin seed oil
- Perilla seed oil
- Tofu
- Walnuts and walnut oil
Note: Alpha-linolenic acid is not the same as alpha-lipoic acid, an antioxidant that helps the body turn glucose into energy. This can be confusing because both alpha-linolenic acid and alpha-lipoic acid are sometimes abbreviated as ALA.
Further notes:
- A modest dietary consumption of ALA (1.2-2g) is recommended
- Do not take alpha-linolenic acid supplements if you have prostate cancer or are at high risk for getting prostate cancer (e.g., you have a father or brother with prostate cancer). There is some evidence that alpha-linolenic acid might increase the chance of getting prostate cancer.
Names and Abbreviations of the Omega-6 and Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
| Omega-6 Fatty Acids | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Linoleic acid |
LA |
18:2n-6 |
α-Linolenic acid |
ALA |
18:3n-3 |
|
γ-Linolenic acid |
GLA |
18:3n-6 |
Stearadonic acid |
SDA |
18:4n-3 |
|
Dihomo-γ-linolenic acid |
DGLA |
20:3n-6 |
Eicosatetraienoic acid |
ETA |
20:4n-3 |
|
Arachidonic acid |
AA |
20:4n-6 |
Eicosapentaenoic acid |
EPA |
20:5n-3 |
|
Adrenic acid |
22:4n-6 |
Docosapentaenoic acid |
DPA (n-3) |
22:5n-3 |
|
|
Tetracosatetraenoic acid |
24:4n-6 |
Tetracosapentaenoic acid |
24:5n-3 |
||
|
Tetracosapentaienoic acid |
24:5n-6 |
Tetracosahexaenoic acid |
24:6n-3 |
||
|
Docosapentaenoic acid |
DPA (n-6) |
22:5n-6 |
Docosahexaenoic acid |
DHA |
22:6n-3 |
References:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4350958/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4224228/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3185114/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5768068/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2943064/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2943064/
- https://epi.grants.cancer.gov/diet/foodsources/fatty_acids/table6.html
What does it mean if your alpha Linolenic Acid result is too high?
- Elevated serum alpha-linolenic acid levels are associated with decreased chance of pregnancy after in vitro fertilization
- While omega-3 fatty acids have numerous benefits and clinical indications, as with any nutraceutical, caution should be exercised to avoid adverse reactions, and careful patient selection should be employed.
- The cardioprotective effects of higher ALA intakes do not appear to be related to changes in serum lipid profiles. A meta-analysis of 14 randomized controlled trials concluded that ALA supplementation had no effect on total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, or triglyceride levels.
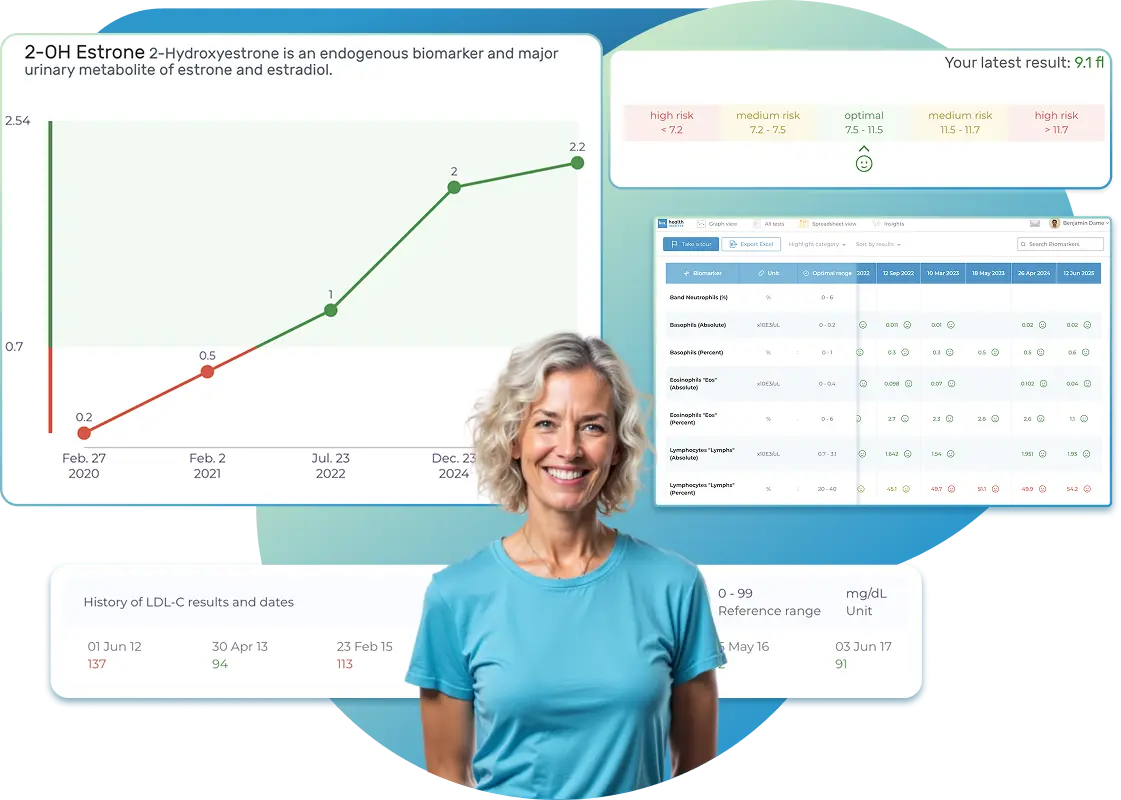
All Your Lab Results.
One Simple Dashboard.
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results Easily
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
What does it mean if your alpha Linolenic Acid result is too low?
One of the most common essential fatty acid deficiencies is that of alpha linolenic acid.
Alpha Linolenic Acid may be converted into eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), a longer fatty acid that is involved in regulation of inflammatory processes and prevention of platelet “stickiness.” Diminished platelet stickiness reduces the blood clotting that can lead to heart attack or stroke. Your body can make the other polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acids from ALA. However, many things can interfere with this process including zinc deficiency, alcohol, obesity, and aging.
Severe deficiency in omega-3 intake pointed by numerous epidemiologic studies may increase the brain’s vulnerability representing an important risk factor in the development and/or deterioration of certain cardio- and neuropathologies.
Some signs of alpha-linolenic acid deficiency include:
- Loss of motor coordination
- Tingling in the extremities
- Vision impairment
- Behavioral changes.
----------------------
Dietary sources of alpha-linolenic acid include:
- Flaxseeds and flaxseed oil
- Canola (rapeseed) oil
- Soybeans and soybean oil
- Pumpkin seeds and pumpkin seed oil
- Perilla seed oil
- Tofu
- Walnuts and walnut oil
Sometimes the active ingredients in products with alpha-linolenic acid can be destroyed by exposing them to air, heat, or light. Generally, look for oil bottled in light-resistant containers, refrigerated, and marked with an expiration date. These oils are not healthful when used for cooking. Instead, use them in salad dressings and dips.
How to Take It:
The recommended adequate intake of alpha-linolenic acid in the diet is listed below:
Pediatric
- Infants who are breastfed should get enough alpha-linolenic acid if the mother eats a healthy diet.
- Infant formula should contain alpha-linolenic acid.
- Children should not need supplements.
Adult
- 1 to 2 g per day
Amounts of alpha-linolenic acid in oils and foods vary. For instance:
- Flaxseed has about 2.2 g per tbsp
- Canola oil, 1.3 g per tbsp
- Flaxseed oil, 8.5 g per tbsp
- English walnuts, .7 g per tbsp
Laboratories
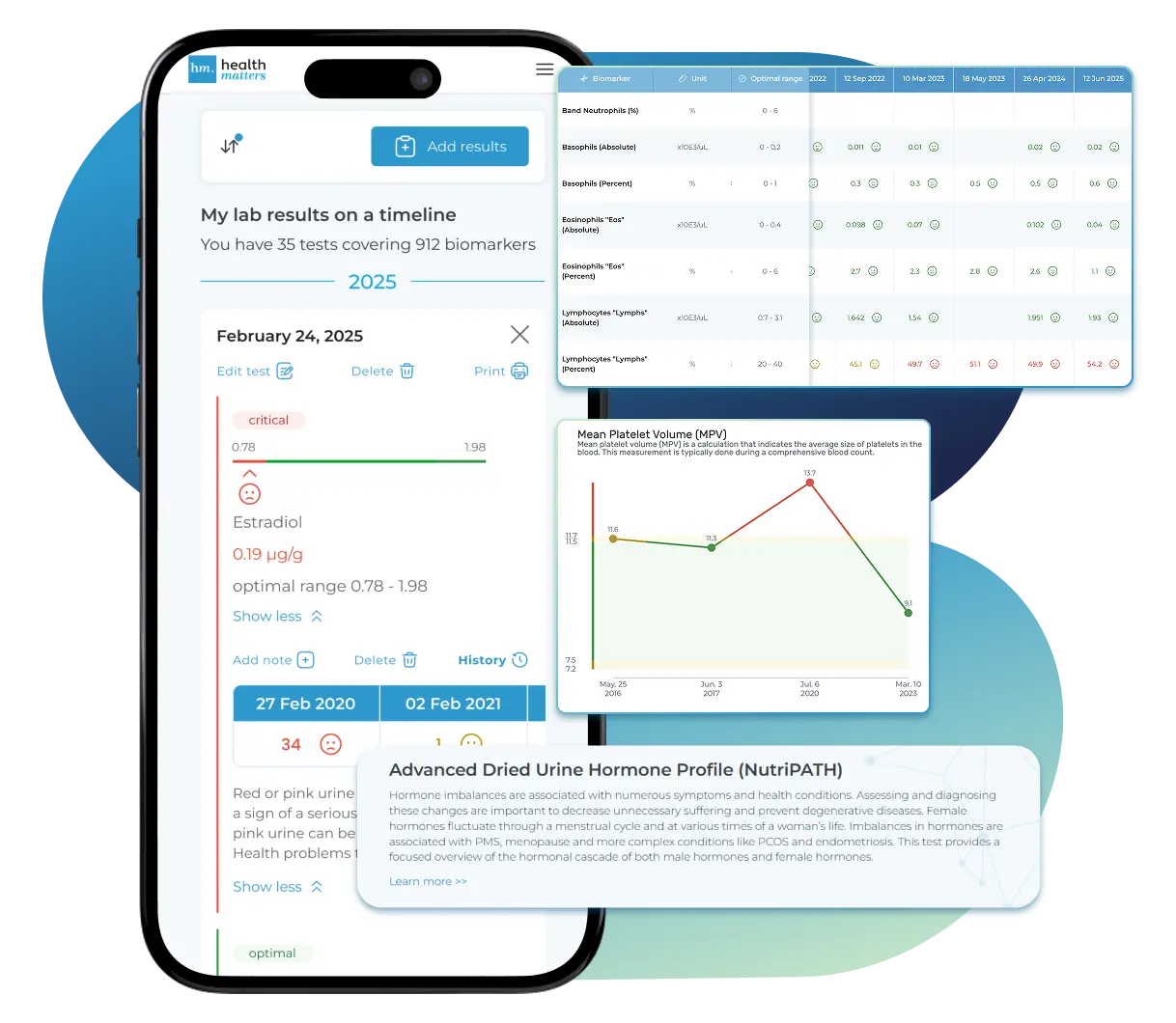
Bring All Your Lab Results Together — In One Place
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.
Pricing Table
Gather Your Lab History — and Finally Make Sense of It
Finally, Your Lab Results Organized and Clear
Personal plans
$79/ year
Advanced Plan
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 5 reports entered for you
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
$250/ once
Unlimited Account
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 10 reports entered for you
- No subscriptions. No extra fees.
$45/ month
Pro Monthly
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track lab results for multiple clients
- Customize reference ranges per client
- Export lab histories and reports
- Begin with first report entered by us
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
About membership
What's included in a Healthmatters membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
 Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Let Your Lab Results Tell the Full Story
Once your results are in one place, see the bigger picture — track trends over time, compare data side by side, export your full history, and share securely with anyone you trust.





Bring all your results together to compare, track progress, export your history, and share securely.
What Healthmatters Members Are Saying
Frequently asked questions
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
- Individuals who want to track and understand their health over time.
- Health professionals, such as doctors, nutritionists, and wellness coaches, need to manage and interpret lab data for their clients.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
- Upload lab reports from any lab
- View your data in interactive graphs, tables, and timelines
- Track trends and monitor changes over time
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export and share your full lab history
- Access your results anytime, from any device
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 10000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
- The GI Effects® Comprehensive Stool Profile,
- GI-MAP,
- The NutrEval FMV®,
- The ION Profile,
- Amino Acids Profile,
- Dried Urine Test for Comprehensive Hormones (DUTCH),
- Organic Acids Test,
- Organix Comprehensive Profile,
- Toxic Metals,
- Complete Blood Count (CBC),
- Metabolic panel,
- Thyroid panel,
- Lipid Panel,
- Urinalysis,
- And many, many more.
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
We implement proven measures to keep your data safe.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
















